|
Vlierbeek Abbey
Vlierbeek Abbey ( nl, Abdij van Vlierbeek) is a former Benedictine abbey to the north-east of Leuven in Belgium, in the sub-district Kessel-Lo. History On the abbey site in 1127 a priory was founded by Affligem Abbey, to whom Godfrey I of Louvain had given the land on the Vlierbeek two years previously. In 1163 or 1165 the priory was elevated to the status of an abbey. The Benedictines cultivated the surrounding land, and played a great role in the spiritual and intellectual development of the area. Over the next few centuries they worked almost constantly on the abbey complex, having often to repair or rebuild what had been destroyed by fire or conflict. In 1170 a stone church in Romanesque style replaced the first church, which was made of clay. In 1572 the abbey was burnt down by the troops of William of Orange. The reconstruction of the abbey was spread over two periods. The first lasted from 1642 to c. 1730. The second, under the direction of Laurent-Benoît Dewez, la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diest
Diest () is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. Situated in the northeast of the Hageland region, Diest neighbours the provinces of Antwerp to its North, and Limburg to the East and is situated around 60 km from Brussels. The municipality comprises the city of Diest proper and the towns of Deurne, Kaggevinne, Molenstede, Schaffen and Webbekom. As of January 1, 2006, Diest had a total population of 22,845. The total area is 58.20 km² which gives a population density of 393 inhabitants per km². History Between 1499 and 1795 the town was controlled by the House of Nassau (as were Breda in the Netherlands, Dillenburg in Germany and Orange in France) which was also the family of the Princes of Orange who at the end of the Napoleonic Wars became in 1815 the kings and queens of the Netherlands after the termination of the Dutch republic at the hands of revolutionary forces in 1795. The most famous representative of the House of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jef Van Den Eynde
Jozef Maria August Antoon (Jef) Van den Eynde (21 December 1879 – 12 April 1929) was a prominent figure from Leuven's student life, an activist and member of the Council of Flanders during the First World War. After the war, he fled to the Netherlands, having received a 20-year sentence in absentia for collaboration. He made a valuable contribution as secretary of the linguistic society ''Met Tijd en Vlijt'' and of the Social Speakers Union ( Dutch: ''Sociale Sprekersbond''). He became president of the East Flemish student guild and founder-conductor of the student orchestra, in which he played the piano and violin himself. From 1901 to 1908 he was editor-in-chief of '' Ons Leven'' and president of the ''Vlaamsch Verbond''. During his many years as a perpetual student, he managed to leave a mark on student traditions and student life. His main goal was to bring the students to a higher cultural level. Many prominent Flemish leaders were invited by him to address the students, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emiel Vliebergh
Emiel is a Dutch cognate of the masculine given name ''Emil''. People with the name include: *Emiel Boersma ((born 1980), Dutch beach volleyball player *Emiel Christensen (1895–1988), American architect from Nebraska * (1909–1995), Belgian Bishop of Bruges *Emiel Faignaert (1919–1980), Belgian cyclist *Emiel van Lennep (1915–1996), Dutch diplomat and Minister of State *Emiel Mellaard (born 1966), Dutch long jumper *Emiel Pauwels (1918–2014), Belgian track and field athlete *Emiel Pijnaker, Dutch film producer, composer and singer *Emiel Puttemans (born 1947), Belgian middle- and long-distance runner *Emiel Rogiers (1923–1998), Belgian racing cyclist *Emiel Van Cauter (1931–1975), Belgian racing cyclist *Emiel van Heurck (1871–1931), Belgian folklorist *Emiel Wastyn Emiel Wastyn (born 1 January 1992) is a Belgian professional racing cyclist. He now rides for the Continental Team . His biggest victory was in 2015 where he managed to win Izegem Koerse, he won the spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Alberdingk Thijm
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) * Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity *Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer * Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church * Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire * Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general * Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist * Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary *Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer * Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals *Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia *Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people *Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk *Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir (architecture)
A choir, also sometimes called quire, is the area of a church or cathedral that provides seating for the clergy and church choir. It is in the western part of the chancel, between the nave and the sanctuary, which houses the altar and Church tabernacle. In larger medieval churches it contained choir-stalls, seating aligned with the side of the church, so at right-angles to the seating for the congregation in the nave. Smaller medieval churches may not have a choir in the architectural sense at all, and they are often lacking in churches built by all denominations after the Protestant Reformation, though the Gothic Revival revived them as a distinct feature. As an architectural term "choir" remains distinct from the actual location of any singing choir – these may be located in various places, and often sing from a choir-loft, often over the door at the liturgical western end. In modern churches, the choir may be located centrally behind the altar, or the pulpit. The back-choir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium (). A trapezoid is necessarily a Convex polygon, convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' (or the ''lateral sides'') if they are not parallel; otherwise, the trapezoid is a parallelogram, and there are two pairs of bases). A ''scalene trapezoid'' is a trapezoid with no sides of equal measure, in contrast with the #Special cases, special cases below. Etymology and ''trapezium'' versus ''trapezoid'' Ancient Greek mathematician Euclid defined five types of quadrilateral, of which four had two sets of parallel sides (known in English as square, rectangle, rhombus and rhomboid) and the last did not have two sets of parallel sides – a τραπέζια (''trapezia'' literally "a table", itself fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome. The word derives, via Italian, from lower Latin ''cupula'' (classical Latin ''cupella''), (Latin ''cupa''), indicating a vault resembling an upside-down cup. Background The cupola evolved during the Renaissance from the older oculus. Being weatherproof, the cupola was better suited to the wetter climates of northern Europe. The chhatri, seen in Indian architecture, fits the definition of a cupola when it is used atop a larger structure. Cupolas often serve as a belfry, belvedere, or roof lantern above a main roof. In other cases they may crown a spire, tower, or turret. Barns often have cupolas for ventilation. Cupolas can also appear as small buildings in their own right. The square, dome-like segment of a North American railroad train caboose that contains the seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
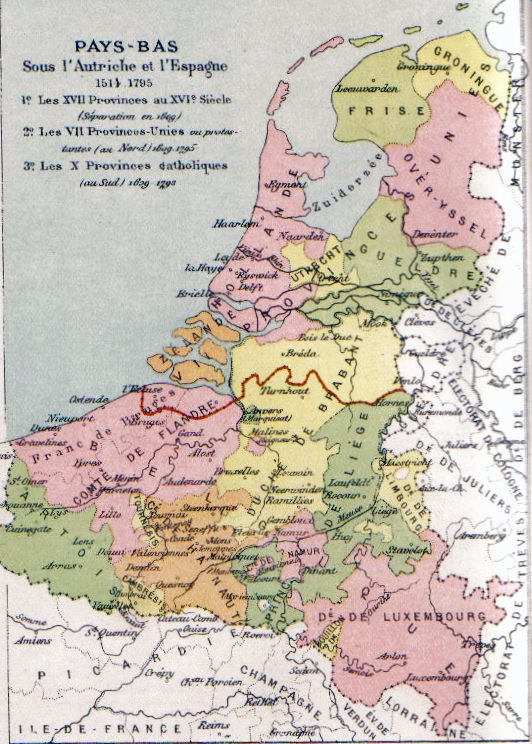
Province Of Brabant
The Province of Brabant (, , ) was a province in Belgium from 1830 to 1995. It was created in 1815 as South Brabant, part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 1995, it was split into the Dutch-speaking Flemish Brabant, the French-speaking Walloon Brabant and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region. History United Kingdom of the Netherlands After the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, the United Kingdom of the Netherlands was created at the Congress of Vienna, consisting of territories which had been added to France by Napoleon: the former Dutch Republic and the Southern Netherlands. In the newly created kingdom, the former French département of Dyle became the new province of South Brabant, distinguishing it from Central Brabant (later Antwerp province); and from North Brabant (now part of the Netherlands), all named after the former Duchy of Brabant. The provincial governors during this time were: * 1815–1818: François Joseph Charles Marie de Mercy-Argenteau * 1818–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)