|
Vitifer Mine
Birch Tor and Vitifer mine was a tin mine on Dartmoor, Devon, England. Located in the valley of the Redwater Brook, to the east of the B3212 Moretonhampstead to Princetown road, below the Warren House Inn, the mine was worked between the mid–18th century and 1925. History In medieval times, or even before, the area later occupied by this mine was at the centre of the most extensive surface mining operations on Dartmoor, and today it is still scarred by the waste heaps left by stream working and numerous gullies of open cast mining.Greeves 2001, pp.21–24 Strictly speaking, Birch Tor mine on the eastern side of the Redwater Brook valley and Vitifer mine on the west were separate mines, but for most of their working lives they were operated under the same management, so they are usually considered together. The first documentary reference to "Vitifer Mine" was in 1750, and to "Burch Tor Bounds" in 1757. By the 1780s Vitifer was being operated by the Dartmoor Mining and Smeltin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers . The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous Period of geological history. The landscape consists of moorland capped with many exposed granite hilltops known as tors, providing habitats for Dartmoor wildlife. The highest point is High Willhays, above sea level. The entire area is rich in antiquities and archaeology. Dartmoor National Park is managed by the Dartmoor National Park Authority, whose 22 members are drawn from Devon County Council, local district councils and Government. Parts of Dartmoor have been used as military firing ranges for over 200 years. The public is granted extensive land access rights on Dartmoor (including restricted access to the firing ranges) and it is a popular tourist destination. Physical geography Geology Dartmoor includes the largest area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining In The United Kingdom
Mining in the United Kingdom produces a wide variety of fossil fuels, metals, and industrial minerals due to its complex geology. In 2013, there were over 2,000 active mines, quarries, and offshore drilling sites on the continental land mass of the United Kingdom producing £34bn of minerals and employing 36,000 people. Brief history The United Kingdom has a rich history of mining. Mining of non-ferrous minerals, particularly of copper and tin, has been ongoing since the Bronze Age. For example, copper was mined in Wales during approximately 2200–850 BC. Metalworking debris found beneath the ramparts at Beeston Castle in Cheshire is evidence of bronze production during the Bronze Age. Later, lead and copper attracted the Romans to Britain. The Romans introduced iron tools and used local slaves to mine galena, an important lead ore mineral, from which they refined lead, tin and silver. These metals were used locally and also transported by ship throughout the Roman Empire. Gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moretonhampstead
Moretonhampstead (anciently ''Moreton Hampstead'') is a market town, parish and ancient manor in Devon, situated on the north-eastern edge of Dartmoor, within the Dartmoor National Park. The parish now includes the hamlet of Doccombe (), and it is surrounded clockwise from the north by the parishes of Drewsteignton, Dunsford, Bridford, Bovey Tracey, Lustleigh, North Bovey and Chagford. At the 2011 census the population of the parish was 1,703, and Moorland electoral ward, in which Moretonhampstead lies, had a population of 2,806. The parish church is dedicated to St. Andrew. Along with a few other places in Devon, it is one of the longest place names in England with 16 letters. Moretonhampstead is twinned with Betton in France. Etymology The Domesday Book of 1086 records the manor as ''MORTONE''. This part of the name derives from the Old English for a farmstead in moorland, referring to the town's situation on the edge of Dartmoor. By 1493 "Hampstead" had been added to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princetown
Princetown is a villageDespite its name, Princetown is not classed as a town today – it is not included in the County Council's list of the 29 towns in Devon: located within Dartmoor national park in the English county of Devon. It is the principal settlement of the civil parish of Dartmoor Forest. The village has its origins in 1785, when Sir Thomas Tyrwhitt, then secretary to the Prince of Wales, leased a large area of moorland from the Duchy of Cornwall estate, hoping to convert it into good farmland. He encouraged people to live in the area and suggested that a prison be built there. He called the settlement Princetown after the Prince of Wales. Princetown is the site of Dartmoor Prison. At around 1,430 feet (435 m) above sea level, it is the highest settlement on the moor, and one of the highest in the United Kingdom. It is also the largest settlement located on the high moor. The Princetown Railway, closed in 1956, was also the highest railway line in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren House Inn
The Warren House Inn is a remote and isolated public house in the heart of Dartmoor, Devon, England. It is the highest pub in southern England at 1,425 feet (434 m) above sea level. It is located on an ancient road across the moor, about 2 miles (3 km) north east of the village of Postbridge and has been a stopping point for travellers since the middle of the 18th century. History In 1905 Robert Burnard wrote: "When packhorses were used on the Moreton track, New House, or as it is now called, Warren House Inn, was on the right side of the road proceeding from Postbridge towards Moreton, and it is so shown on Donne's map. This old building was burnt down some years ago and was rebuilt in 1845 by J. Wills on the other side of the present road, here it occupies the site of the ancient packhorse way." As Burnard said, the current building dates from 1845, but the original inn on the southern side of the packhorse track was probably built in the middle of the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmoor Tin-mining
The tin mining industry on Dartmoor, Devon, England, is thought to have originated in pre-Roman times, and continued right through to the 20th century, when the last commercially worked mine (Golden Dagger Mine) closed in November 1930 (though it saw work during the Second World War). From the 12th century onwards tin mining was regulated by a stannary parliament which had its own laws. Tin is smelted from cassiterite, a mineral found in hydrothermal veins in granite, and the uplands of Dartmoor were a particularly productive area. The techniques used for the extraction of tin from Dartmoor followed a progression from streaming through open cast mining to underground mining. Today, there are extensive archaeological remains of these three phases of the industry, as well as of the several stages of processing that were necessary to convert the ore to tin metal. Stannary law Mining became such an important part of life in the region that as early as the 12th century, tin miners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adit
An adit (from Latin ''aditus'', entrance) is an entrance to an underground mine which is horizontal or nearly horizontal, by which the mine can be entered, drained of water, ventilated, and minerals extracted at the lowest convenient level. Adits are also used to explore for mineral veins. Construction Adits are driven into the side of a hill or mountain, and are often used when an ore body is located inside the mountain but above the adjacent valley floor or coastal plain. In cases where the mineral vein outcrops at the surface, the adit may follow the lode or vein until it is worked out, in which case the adit is rarely straight. The use of adits for the extraction of ore is generally called drift mining. Adits can only be driven into a mine where the local topography permits. There will be no opportunity to drive an adit to a mine situated on a large flat plain, for instance. Also if the ground is weak, the cost of shoring up a long adit may outweigh its possible advantage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
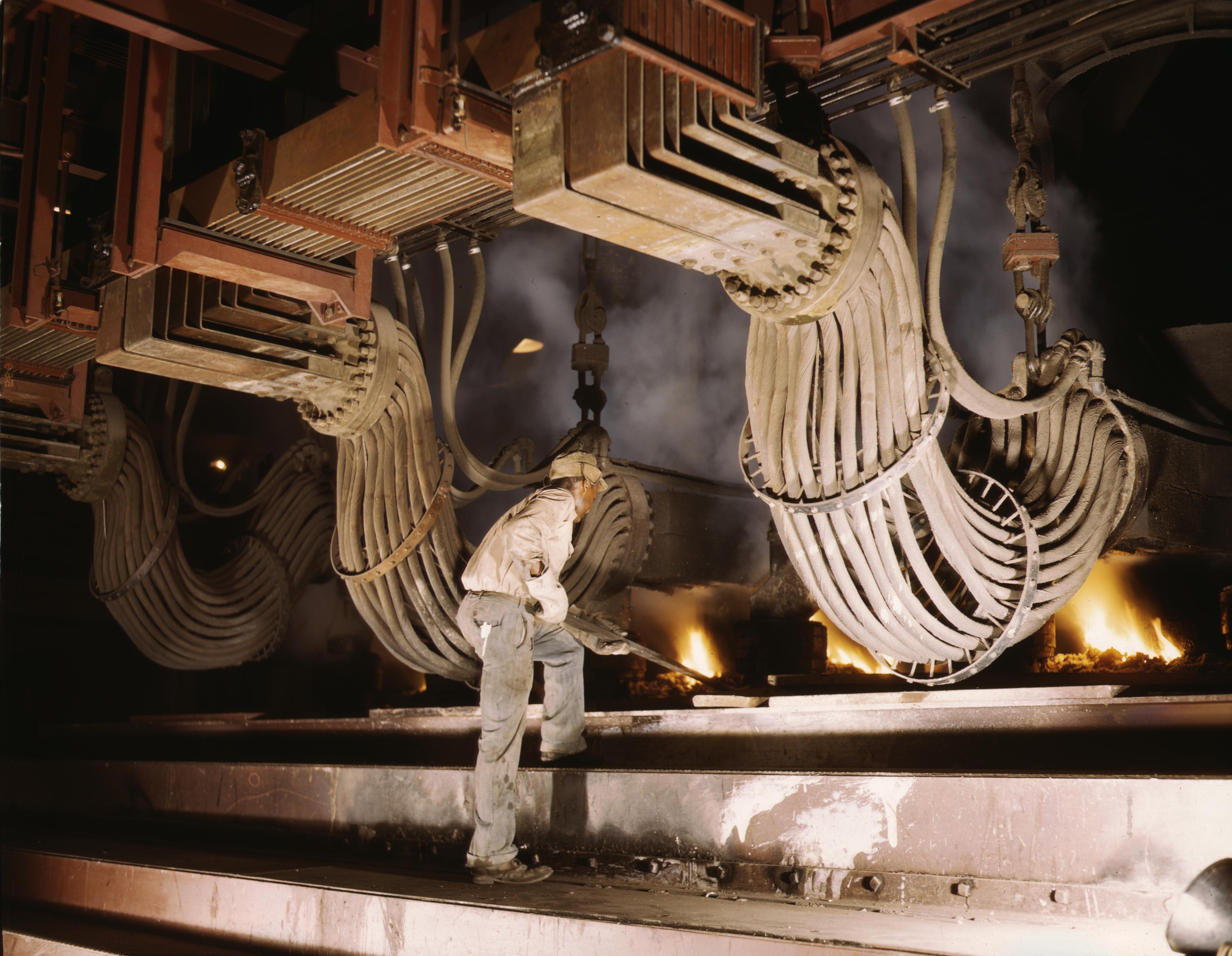
Smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore, to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures due to the lower potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide (). Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is converted into steel. The carbon source acts as a chemical reactant to remove oxygen from the ore, yielding the purified metal element as a product. The carbon source is oxidized in two stages. First, the carbon (C) combusts with oxygen (O2) in the air to produce carbon monoxide (CO). Second, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eylesbarrow Mine
Eylesbarrow mine was a tin mine on Dartmoor, Devon, England that was active during the first half of the 19th century. In its early years it was one of the largest and most prosperous of the Dartmoor tin mines, along with Whiteworks and the Birch Tor and Vitifer mines. Its name has several variant spellings, such as Eylesburrow, Ailsborough, Ellisborough, Hillsborough etc. It was also known as Wheal Ruth for a short period around 1850. The extensive remains lie to the north of the River Plym, less than north-east of Drizzlecombe, on the southern shoulder of the hill called Eylesbarrow on top of which are two prominent Bronze Age barrows. Geology The country rock of the mine is granite. The large mining sett (about ) is crossed by many tin-bearing lodes which are substantially vertical and trend east-north-east. Most of the mine's excavations were made into just three of these lodes and were relatively shallow.Cook et al. 1974, Appendix A, pp.200-201 The formation of the lodes wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Tin
Black tin is the raw ore of tin, usually cassiterite, as sold by a tin mine to a smelting company. After mining, the ore must be concentrated by several processes to reduce the amount of gangue it contains before it can be sold. It contrasts with white tin, which is the refined, metallic tin produced after smelting. The term "black tin" was historically associated with tin mining in Devon and Cornwall Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic .... References * * * * Tin mining Mining in Cornwall {{Mining-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
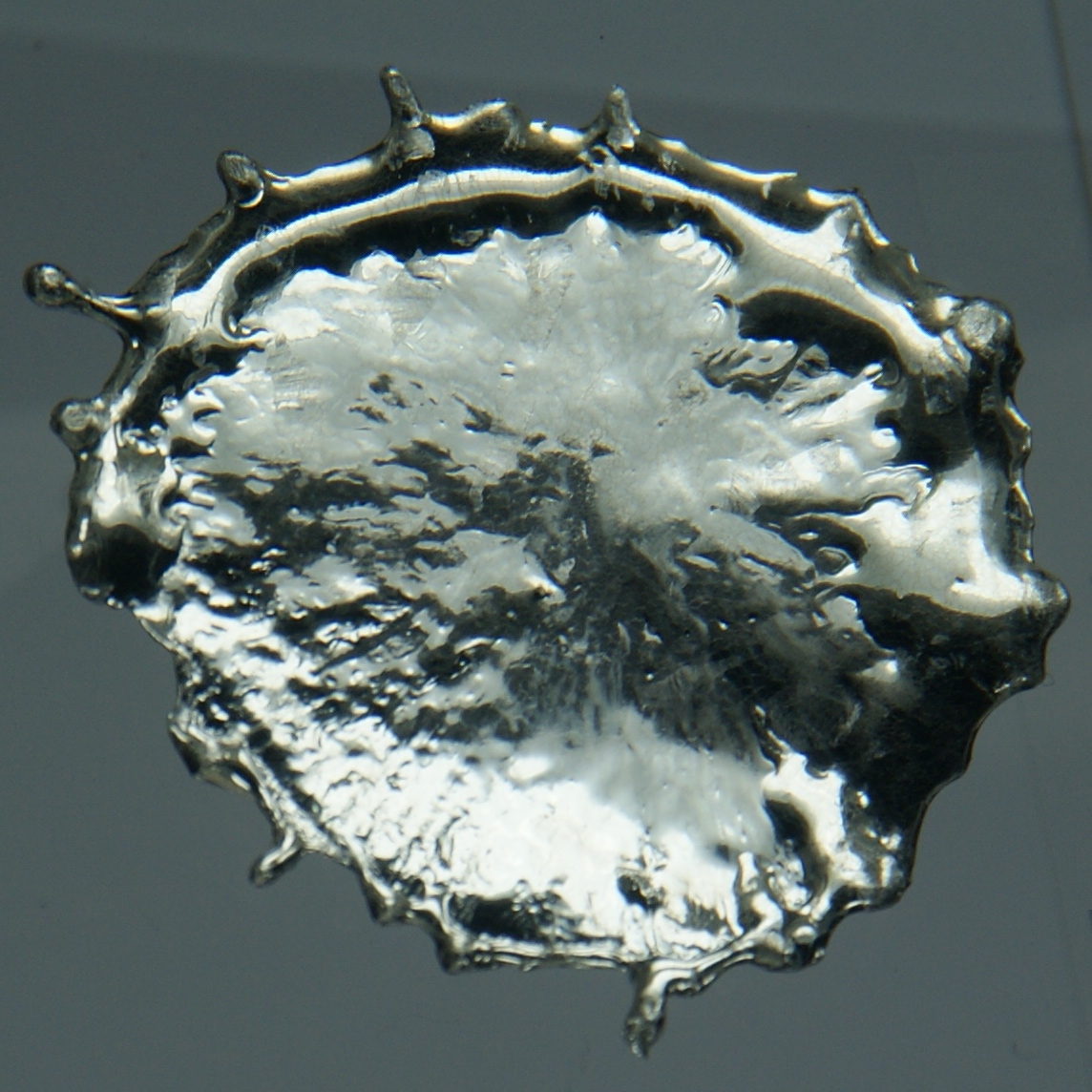
Tin Mines In Devon
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal. Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in the solid state. Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)