|
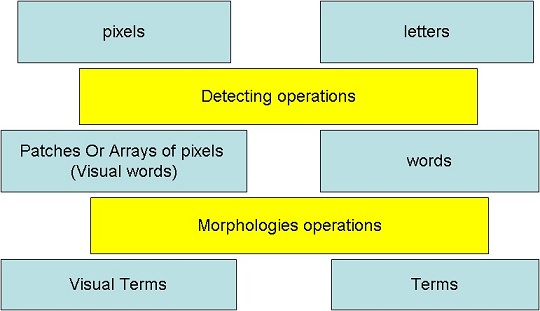
Visual Word
Visual words, as used in image retrieval systems, refer to small parts of an image that carry some kind of information related to the features (such as the color, shape, or texture) or changes occurring in the pixels such as the filtering, low-level feature descriptors (SIFT or SURF). History The approaches of text retrieval system (or information retrieval IR system) which were developed over 40 years, are based on keywords or Term. The advantage of these approaches is that they are effective and fast. Text-search engines are able to quickly find documents from hundreds or millions (by using a vector space model). At the same time, text retrieval systems have huge successes, whereas the standard image retrieval systems (like simple search by colors or shapes) have a large number of limitations. Consequently, researchers try to take advantage of text retrieval techniques to apply them to image retrieval. That can be accomplished by a new kind of vision to understand images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text File
A text file (sometimes spelled textfile; an old alternative name is flatfile) is a kind of computer file that is structured as a sequence of lines of electronic text. A text file exists stored as data within a computer file system. In operating systems such as CP/M and MS-DOS, where the operating system does not keep track of the file size in bytes, the end of a text file is denoted by placing one or more special characters, known as an end-of-file marker, as padding after the last line in a text file. On modern operating systems such as Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems, text files do not contain any special EOF character, because file systems on those operating systems keep track of the file size in bytes. Most text files need to have end-of-line delimiters, which are done in a few different ways depending on operating system. Some operating systems with record-orientated file systems may not use new line delimiters and will primarily store text files with lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bag-of-words Model In Computer Vision
In computer vision, the bag-of-words model (BoW model) sometimes called bag-of-visual-words model can be applied to image classification or retrieval, by treating image features as words. In document classification, a bag of words is a sparse vector of occurrence counts of words; that is, a sparse histogram over the vocabulary. In computer vision, a ''bag of visual words'' is a vector of occurrence counts of a vocabulary of local image features. Image representation based on the BoW model To represent an image using the BoW model, an image can be treated as a document. Similarly, "words" in images need to be defined too. To achieve this, it usually includes following three steps: feature detection, feature description, and codebook generation. A definition of the BoW model can be the "histogram representation based on independent features". Content based image indexing and retrieval (CBIR) appears to be the early adopter of this image representation technique. Feature r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user or searcher enters a query into the system. Queries are formal statements of information needs, for example search strings in web search engines. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Recognition System
A facial recognition system is a technology capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image. Development began on similar systems in the 1960s, beginning as a form of computer application. Since their inception, facial recognition systems have seen wider uses in recent times on smartphones and in other forms of technology, such as robotics. Because computerized facial recognition involves the measurement of a human's physiological characteristics, facial recognition systems are categorized as biometrics. Although the accuracy of facial recognition systems as a biometric technology is lower than iris recognition and fingerprint recognition, it is widely adopted due to its contactless process. Facial recognition systems have been deployed in advanced human–comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content-based Image Retrieval
Content-based image retrieval, also known as query by image content ( QBIC) and content-based visual information retrieval (CBVIR), is the application of computer vision techniques to the image retrieval problem, that is, the problem of searching for digital images in large databases (see this surveyContent-based Multimedia Information Retrieval: State of the Art and Challenges' (Original source, 404'''Content-based Multimedia Information Retrieval: State of the Art and Challenges'', Michael Lew, et al., ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, pp. 1–19, 2006. for a scientific overview of the CBIR field). Content-based image retrieval is opposed to traditional concept-based approaches (see Concept-based image indexing). "Content-based" means that the search analyzes the contents of the image rather than the metadata such as keywords, tags, or descriptions associated with the image. The term "content" in this context might refer to colors, sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Language
A visual language is a system of communication using visual elements. Speech as a means of communication cannot strictly be separated from the whole of human communicative activity which includes the visual and the term 'language' in relation to vision is an extension of its use to describe the perception, comprehension and production of visible signs. Overview An image which dramatizes and communicates an idea presupposes the use of a visual language. Just as people can 'verbalize' their thinking, they can 'visualize' it. A diagram, a map, and a painting are all examples of uses of visual language. Its structural units include line, shape, colour, form, motion, texture, pattern, direction, orientation, scale, angle, space and proportion. The elements in an image represent concepts in a spatial context, rather than the linear form used for words. Speech and visual communication are parallel and often interdependent means by which humans exchange information. Visual language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Word
Visual words, as used in image retrieval systems, refer to small parts of an image that carry some kind of information related to the features (such as the color, shape, or texture) or changes occurring in the pixels such as the filtering, low-level feature descriptors (SIFT or SURF). History The approaches of text retrieval system (or information retrieval IR system) which were developed over 40 years, are based on keywords or Term. The advantage of these approaches is that they are effective and fast. Text-search engines are able to quickly find documents from hundreds or millions (by using a vector space model). At the same time, text retrieval systems have huge successes, whereas the standard image retrieval systems (like simple search by colors or shapes) have a large number of limitations. Consequently, researchers try to take advantage of text retrieval techniques to apply them to image retrieval. That can be accomplished by a new kind of vision to understand images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Images
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as ''pixels'', each with ''finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions fed as input by its spatial coordinates denoted with ''x'', ''y'' on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. Raster Raster images have a finite set of digital values, called ''picture elements'' or pixels. The digital image contains a fixed number of rows and columns of pixels. Pixels are the smallest individual element in an image, holding antiquated values that represent the brightness of a given color at any specific point. Typically, the pixels are stored in computer memory as a raster image or raster map, a two-dimensional array of small integers. These values are often transmitted or stored in a compressed form. Raster images can be created b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
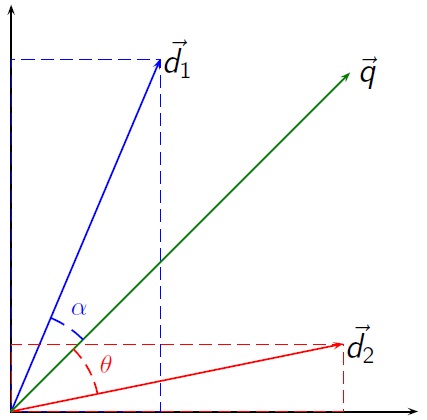
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (and any objects, in general) as vectors of identifiers (such as index terms). It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ''term'' depends on the application. Typically terms are single words, keywords, or longer phrases. If words are chosen to be the terms, the dimensionality of the vector is the number of words in the vocabulary (the number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Retrieval
An image retrieval system is a computer system used for browsing, searching and retrieving images from a large database of digital images. Most traditional and common methods of image retrieval utilize some method of adding metadata such as captioning, keywords, title or descriptions to the images so that retrieval can be performed over the annotation words. Manual image annotation is time-consuming, laborious and expensive; to address this, there has been a large amount of research done on automatic image annotation. Additionally, the increase in social web applications and the semantic web have inspired the development of several web-based image annotation tools. The first microcomputer-based image database retrieval system was developed at MIT, in the 1990s, by Banireddy Prasaad, Amar Gupta, Hoo-min Toong, and Stuart Madnick. A 2008 survey article documented progresses after 2007. All image retrieval systems as of 2021 were designed for 2D images, not 3D ones. Search m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Text Search
In text retrieval, full-text search refers to techniques for searching a single computer-stored document or a collection in a full-text database. Full-text search is distinguished from searches based on metadata or on parts of the original texts represented in databases (such as titles, abstracts, selected sections, or bibliographical references). In a full-text search, a search engine examines all of the words in every stored document as it tries to match search criteria (for example, text specified by a user). Full-text-searching techniques became common in online bibliographic databases in the 1990s. Many websites and application programs (such as word processing software) provide full-text-search capabilities. Some web search engines, such as AltaVista, employ full-text-search techniques, while others index only a portion of the web pages examined by their indexing systems. Indexing When dealing with a small number of documents, it is possible for the full-text-search en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |