|
Visual Guidance Docking System
A stand guidance system is a system which gives information to a pilot attempting to park an aircraft at an airport stand, usually via visual methods, leading to the term ''Visual Docking Guidance System'' (VDGS) and also ''A-VDGS'' (the A standing for advanced) This allows them to remain clear of obstructions and ensures that jetways can reach the aircraft. AGNIS VDGS Azimuth Guidance for Nose-In Stand is one of the most popular forms of stand guidance. It consists of two coloured lights mounted side by side. If the pilot is on the stand centreline they will see two green lights. If they are off centreline, one of the lights will appear red and the pilot then steers towards the green one. AGNIS alone provides only azimuth guidance, it does not inform pilots when they should stop. It is relatively imprecise but cheap to implement and reliable. PAPA The Parallax Aircraft Parking Aid is frequently combined with an AGNIS system, informing flight crews when to stop. The device featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetways
A jet bridge (also termed jetway, jetwalk, airgate, gangway, aerobridge/airbridge, skybridge, finger, airtube, expedited suspended passenger entry system (E-SPES), or its official industry name passenger boarding bridge (PBB)) is an enclosed, movable connector which most commonly extends from an airport terminal gate to an airplane, and in some instances from a port to a boat or ship, allowing passengers to board and disembark without going outside and being exposed to harsh weather. Depending on building design, sill heights, fueling positions, and operational requirements, a jet bridge may be fixed or movable, swinging radially, and/or extending in length. The jetway was invented by Frank Der Yuen. Similar devices are used for astronauts to enter spacecraft, which are installed in the appropriate height of the launch tower. History Before the introduction of jet bridges, passengers normally boarded an aircraft by walking along the ground-level ramp and climbing a set o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
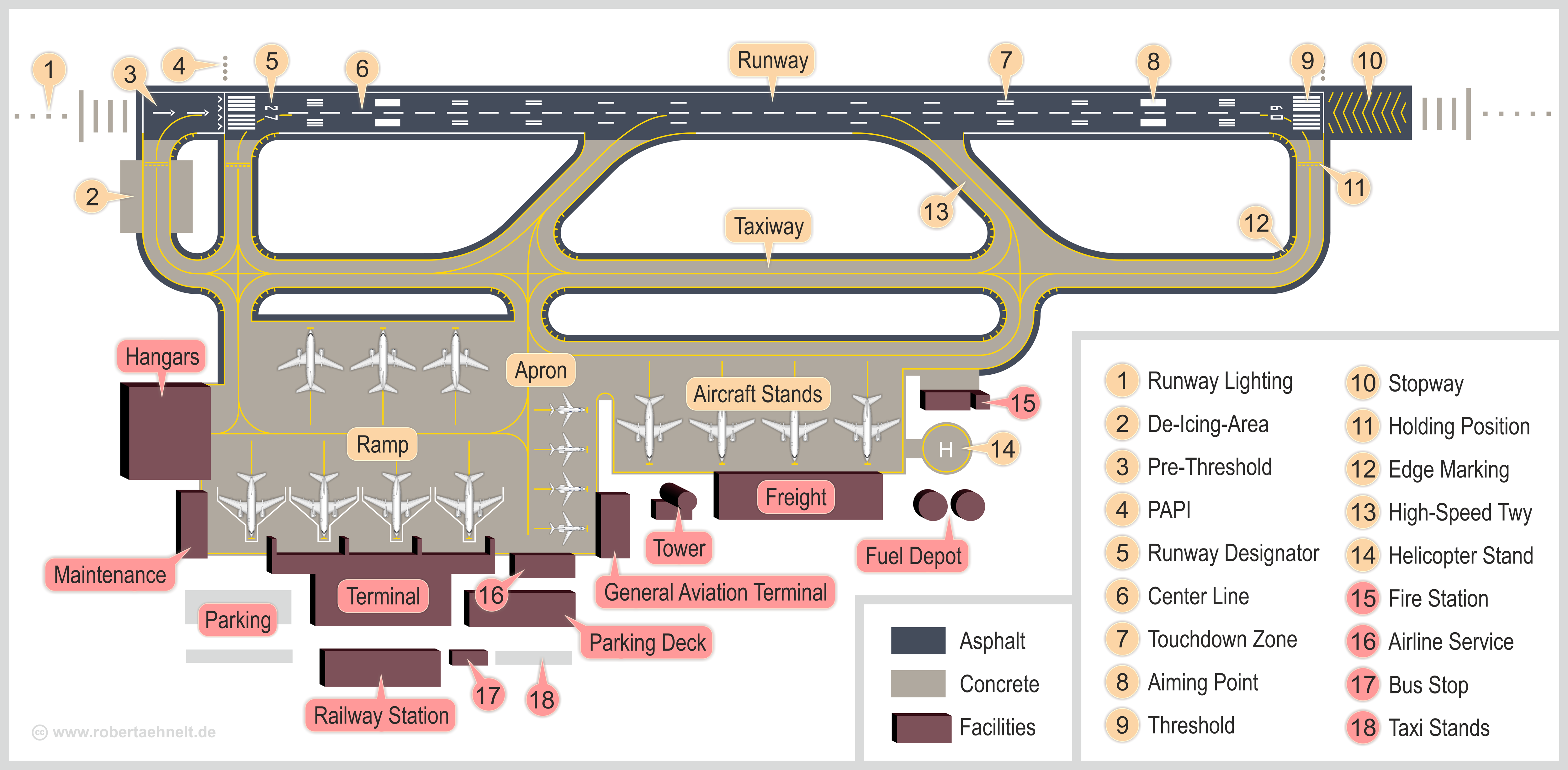
Airport Infrastructure
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |