|
Visnagin
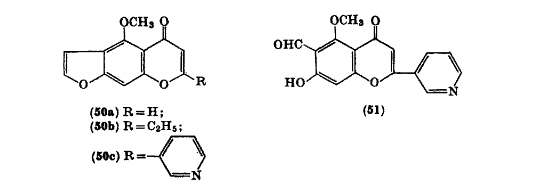
Visnagin is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C13 H10 O4 It is a furanochromone, a compound derivative of chromone (1,4-benzopyrone) and furan. History ''Ammi visnaga'', the main source for visnagin, has been used in traditional medicine in the Middle East to ease urinary tract pain associated with kidney stones and to promote stone passage. Occurrences Visnagin naturally occurs in ''Ammi visnaga'', a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by many common names, including bisnaga, toothpickweed, and khella. Visnagin-containing khella seeds are usually found mainly in Middle East countries such as Egypt and Turkey and also in Northern African countries such as Morocco. Visnagin can be extracted directly from khella seeds. Synthesis Modified synthesis of the naturally occurring visnagin is reported. Starting from phloroghrcin aldehyde, and building on the 2-methyl-y-pyrone, 2-methyl-5,7-dihydroxy-dfo-yl-chromone was obtained. Construction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visnagin Olygomer
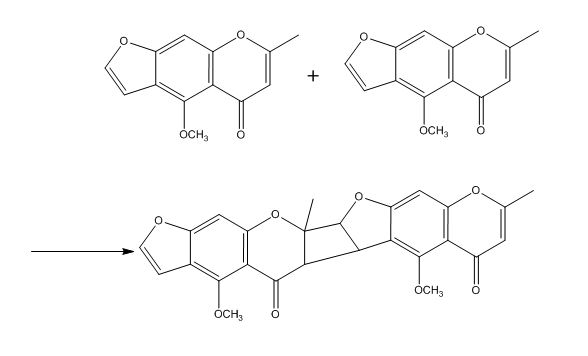
Visnagin is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C13 H10 O4 It is a furanochromone, a compound derivative of chromone (1,4-benzopyrone) and furan. History ''Ammi visnaga'', the main source for visnagin, has been used in traditional medicine in the Middle East to ease urinary tract pain associated with kidney stones and to promote stone passage. Occurrences Visnagin naturally occurs in ''Ammi visnaga'', a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by many common names, including bisnaga, toothpickweed, and khella. Visnagin-containing khella seeds are usually found mainly in Middle East countries such as Egypt and Turkey and also in Northern African countries such as Morocco. Visnagin can be extracted directly from khella seeds. Synthesis Modified synthesis of the naturally occurring visnagin is reported. Starting from phloroghrcin aldehyde, and building on the 2-methyl-y-pyrone, 2-methyl-5,7-dihydroxy-dfo-yl-chromone was obtained. Construction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visnagin Reaction
Visnagin is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C13 H10 O4 It is a furanochromone, a compound derivative of chromone (1,4-benzopyrone) and furan. History ''Ammi visnaga'', the main source for visnagin, has been used in traditional medicine in the Middle East to ease urinary tract pain associated with kidney stones and to promote stone passage. Occurrences Visnagin naturally occurs in ''Ammi visnaga'', a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by many common names, including bisnaga, toothpickweed, and khella. Visnagin-containing khella seeds are usually found mainly in Middle East countries such as Egypt and Turkey and also in Northern African countries such as Morocco. Visnagin can be extracted directly from khella seeds. Synthesis Modified synthesis of the naturally occurring visnagin is reported. Starting from phloroghrcin aldehyde, and building on the 2-methyl-y-pyrone, 2-methyl-5,7-dihydroxy-dfo-yl-chromone was obtained. Construction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammi Visnaga
''Visnaga daucoides'' is a species of flowering plant in the carrot family known by many common names, including toothpick-plant, toothpickweed, bisnaga, khella, or sometimes bishop's weed. It is native to Europe, Asia, and North Africa, but it can be found throughout the world as an introduced species. Description This is an erect annual plant growing from a taproot to a maximum height near . The leaves are up to long and generally oval to triangular in shape but dissected into many small linear to lance-shaped segments. The inflorescence is a compound umbel of white flowers similar to those of other Apiaceae species. The fruit is a compressed oval-shaped body less than 3 millimeters long. This species is a source of khellin, a diuretic extract. Like its close relative ''Ammi majus'', ''Visnaga daucoides'' is commonly seen in gardens where it is grown from seed annually. Some authorities regard ''Visnaga daucoides'' as a synonym of ''Ammi visnaga''; and it is still widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChemSpider
ChemSpider is a database of chemicals. ChemSpider is owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry. Database The database contains information on more than 100 million molecules from over 270 data sources including: * EPA DSSTox * U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) * Human Metabolome Database * Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry * KEGG * KUMGM * LeadScope * LipidMAPS * Marinlit * MDPI * MICAD * MLSMR * MMDB * MOLI * MTDP * Nanogen * Nature Chemical Biology * NCGC * NIAID * National Institutes of Health (NIH) * NINDS Approved Drug Screening Program * NIST * NIST Chemistry WebBook * NMMLSC * NMRShiftDB * PANACHE * PCMD * PDSP * Peptides * Prous Science Drugs of the Future * QSAR * R&D Chemicals * San Diego Center for Chemical Genomics * SGCOxCompounds, SGCStoCompounds * SMID * Specs * Structural Genomics Consortium * SureChem * Synthon-Lab * Thomson Pharma * Total TOSLab Building-Blocks * UM-BBD * UPCMLD * UsefulChem * Web of Science * xPharm Each chemical is given a unique i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malate Dehydrogenase
Malate dehydrogenase () (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP+). Isozymes Several isozymes of malate dehydrogenase exist. There are two main isoforms in eukaryotic cells. One is found in the mitochondrial matrix, participating as a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle that catalyzes the oxidation of malate. The other is found in the cytoplasm, assisting the malate-aspartate shuttle with exchanging reducing equivalents so that malate can pass through the mitochondrial membrane to be transformed into oxaloacetate for further cellular processes. Humans and most other mammals express the following two malate dehydrogenases: Protein families The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. An irregular heart beat and fainting may occur. Those affected are at an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Types of cardiomyopathy include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (broken heart syndrome). In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the heart muscle enlarges and thickens. In dilated cardiomyopathy the ventricles enlarge and weaken. In restrictive cardiomyopathy the ventricle stiffens. In many cases, the cause cannot be determined. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually inherited, whereas dilated cardiomyopathy is inherited in about one third of cases. Dilated cardiomyopathy may also result from alcohol, heavy m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin, sold under the brand name Adriamycin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. This includes breast cancer, bladder cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is often used together with other chemotherapy agents. Doxorubicin is given by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, vomiting, rash, and inflammation of the mouth. Other serious side effects may include allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, heart damage, tissue damage at the site of injection, radiation recall, and treatment-related leukemia. People often experience red discoloration of the urine for a few days. Doxorubicin is in the anthracycline and antitumor antibiotic family of medications. It works in part by interfering with the function of DNA. Doxorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Versions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) below 0°C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0°C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay. Nucleation is a common mechanism which generates first-order phase transitions, and it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phases at continuous phase transitions start to form immedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Stones
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |