|
Virtual World
A virtual world (also called a virtual space or spaces) is a Computer simulation, computer-simulated environment which may be populated by many simultaneous users who can create a personal Avatar (computing), avatar and independently explore the virtual world, participate in its activities, and communicate with others. These avatars can be textual, graphical representations, or live video avatars with auditory and touch sensations. Virtual worlds are closely related to mirror worlds. In a virtual world, the User (computing), user accesses a computer-simulated world which presents Perception, perceptual stimuli to the user, who in turn can manipulate elements of the modeled world and thus experience a degree of Immersion (virtual reality)#Presence, presence. Such modeled worlds and their rules may draw from reality or fantasy worlds. Example rules are gravity, topography, animal locomotion, locomotion, real-time computer graphics, real-time actions, and communication. Communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immersion (virtual Reality)
In virtual reality (VR), immersion is the perception of being physically Presence (telepresence), present in a non-physical world. The perception is created by surrounding the user of the VR system in images, sound or other Stimulation, stimuli that provide an engrossing total environment. Etymology The name is a metaphoric use of the experience of wikt:submerge, submersion applied to representation, fiction or simulation. Immersion can also be defined as the state of consciousness where a "visitor" (Maurice Benayoun) or "immersant" (Char Davies) has their awareness of their physical self transformed by being surrounded in an artificial environment. The term is used to describe partial or complete suspension of disbelief, enabling action or reaction to stimulations encountered in a virtual or artistic environment. The greater the suspension of disbelief, the greater the degree of presence achieved. Types According to Ernest W. Adams, immersion can be separated into three main c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SL Motorbike
SL may refer to: Arts and entertainment * SL (rapper), a rapper from London * ''Second Life'', a multi-user 3D virtual world * Sensei's Library, an Internet site dedicated to the game of Go * Subdominant leittonwechselklänge * Leica SL, a mirrorless system camera by Leica Camera AG Business and organizations * Sociedad Limitada, the Spanish version of a private limited company Politics * Serbian Left (2022), Serbian Left (''Srpska levica''), a political party in Serbia * Stronnictwo Ludowe, a defunct Polish political party * Soyons Libres, a French political party Transportation and vehicles * SL Corporation, a Korean auto parts company * Rio Sul Serviços Aéreos Regionais (IATA code SL), a Brazilian airline * Salt Lake City Southern Railroad (reporting mark SL) * Stor-Oslo Lokaltrafikk, a public transport operator in Akershus, Norway * Storstockholms Lokaltrafik, the public transport operator in Stockholm, Sweden * Thai Lion Air (IATA airline code SL) * Mercedes-Benz SL-Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports
Sport is a physical activity or game, often competitive and organized, that maintains or improves physical ability and skills. Sport may provide enjoyment to participants and entertainment to spectators. The number of participants in a particular sport can vary from hundreds of people to a single individual. Sport competitions may use a team or single person format, and may be open, allowing a broad range of participants, or closed, restricting participation to specific groups or those invited. Competitions may allow a "tie" or "draw", in which there is no single winner; others provide tie-breaking methods to ensure there is only one winner. They also may be arranged in a tournament format, producing a champion. Many sports leagues make an annual champion by arranging games in a regular sports season, followed in some cases by playoffs. Sport is generally recognised as system of activities based in physical athleticism or physical dexterity, with major competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
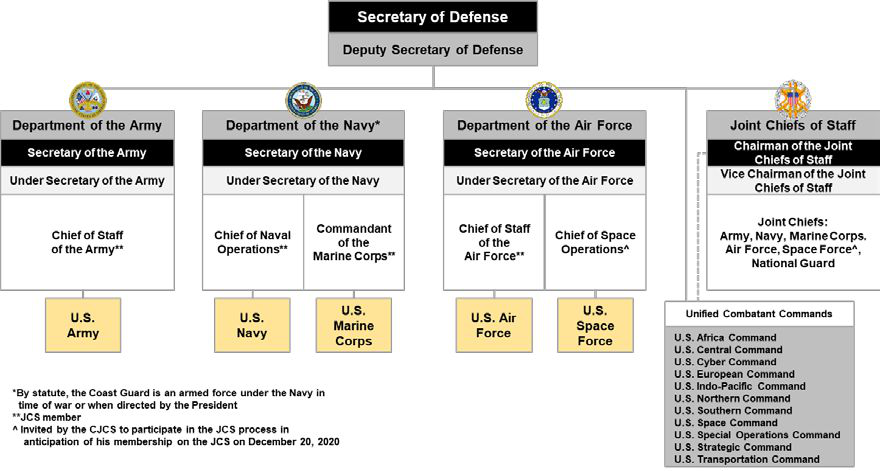
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (now DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense. Building on the ideas of J. C. R. Licklider, Robert Taylor (computer scientist), Bob Taylor initiated the ARPANET project in 1966 to enable resource sharing between remote computers. Taylor appointed Lawrence Roberts (scientist), Larry Roberts as program manager. Roberts made the key decisions about the request for proposal to build the network. He incorporated Donald Davies' concepts and designs for packet switching, and sought input from Paul Baran on dynamic routing. In 1969, ARPA awarded the contract to build the Interface Message Processors (IMPs) for the network to Bolt Berane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maze War
''Maze'', also known as ''Maze War'', is a 3D multiplayer first-person shooter maze game originally developed in 1973 and expanded in 1974. The first version was developed by high school students Steve Colley, Greg Thompson, and Howard Palmer for the Imlac PDS-1 minicomputer during a school work/study program at the NASA Ames Research Center. By the end of 1973 the game featured shooting elements and could be played on two computers connected together. After Thompson began school at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), he brought the game to the school's computer science laboratory in February 1974, where he and Dave Lebling expanded it into an eight-player game using the school's Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-10 mainframe computer and PDS-1 terminals along with adding scoring, top-down map views, and a level editor. Other programmers at MIT improved this version of the game, which was also playable between people at different universities over the nascent ARPAN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Sutherland
Ivan Edward Sutherland (born May 16, 1938) is an American computer scientist and Internet pioneer, widely regarded as a pioneer of computer graphics. His early work in computer graphics as well as his teaching with David C. Evans in that subject at the University of Utah in the 1970s was pioneering in the field. Sutherland, Evans, and their students from that era developed several foundations of modern computer graphics. He received the Turing Award from the Association for Computing Machinery in 1988 for the invention of the Sketchpad, an early predecessor to the sort of graphical user interface that has become ubiquitous in personal computers. He is a member of the National Academy of Engineering, as well as the National Academy of Sciences among many other major awards. In 2012, he was awarded the Kyoto Prize in Advanced Technology for "pioneering achievements in the development of computer graphics and interactive interfaces". Early life and education Sutherland's father w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video games), education (such as medical, safety, or military training) and business (such as virtual meetings). VR is one of the key technologies in the Reality–virtuality continuum, reality-virtuality continuum. As such, it is different from other digital visualization solutions, such as augmented virtuality and augmented reality. Currently, standard virtual reality systems use either virtual reality headsets or multi-projected environments to generate some realistic images, sounds, and other sensations that simulate a user's physical presence in a virtual environment. A person using virtual reality equipment is able to look around the artificial world, move around in it, and interact with virtual features or items. The effect is commonly creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
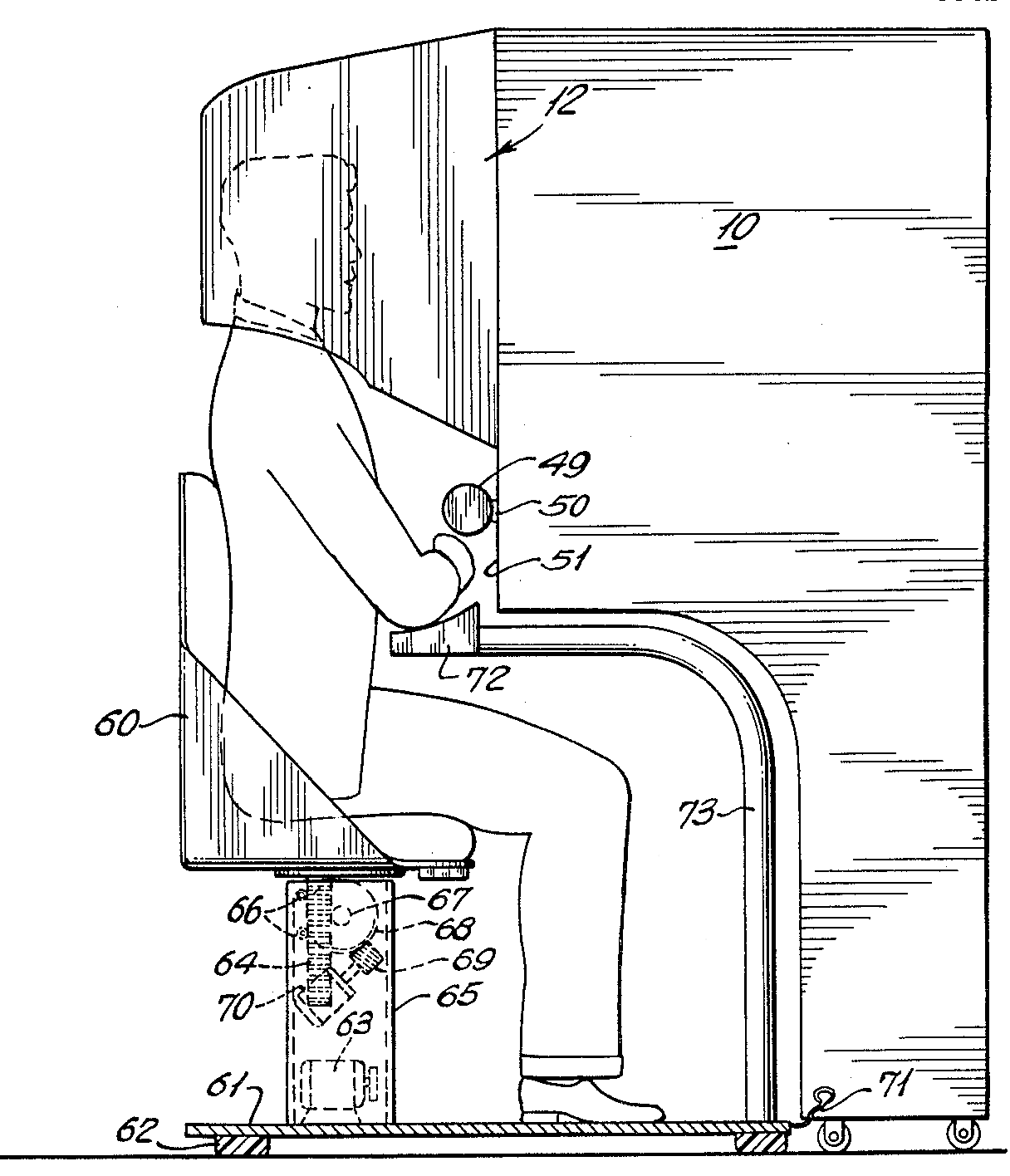
Sensorama
The Sensorama was a machine that is one of the earliest known examples of immersive, multi-sensory (now known as multimodal) technology. This technology, which was introduced in 1962 by Morton Heilig, is considered one of the earliest virtual reality (VR) systems. Development Heilig, who today would be thought of as a "multimedia" specialist, in the 1950s saw theater as an activity that could encompass all the senses in an effective manner, thus drawing the viewer into the onscreen activity. He dubbed it "Experience Theater", and detailed his vision of multi-sensory theater in a 1955 paper, "The Cinema of the Future" (Robinett 1994). In 1962 he built a prototype of his vision, dubbed the Sensorama, along with five short films for it to display. The Sensorama was a mechanical device, which includes a stereoscopic color display, fans, odor emitters, stereo‐sound system, and a motional chair. It simulated a motorcycle ride through New York and created the experience by having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morton Heilig
Morton Leonard Heilig (December 22, 1926 – May 14, 1997) was an American pioneer in virtual reality (VR) technology and a filmmaker. He applied his cinematographer experience and with the help of his partner developed the Sensorama over several years from 1957, patenting it in 1962. Sensorama The Sensorama is big, bulky, and shaped like a 1980s era video arcade game. It was impressive for 1960s technology. The viewing cabinet gave the viewer the experience of riding a motorcycle on the streets of Brooklyn. The viewer felt the wind on their face, the vibration of the motorcycle seat, a stereoscopic 3D view, and smells of the city. Heilig wanted to create “cinema of the future.” The Sensorama was doomed, however, from the high costs of the filmmaking. The problem was not that the apparatus addressed the wrong senses; the business community just couldn't figure out how to sell it. He was not able to find the amount of funds necessary to create new 3-D films “obtained with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Castronova
Edward "Ted" Castronova is a professor of media at Indiana University Bloomington. He is known in particular for his work on the economies of synthetic worlds. Biography Castronova obtained a BS in international affairs from Georgetown University in 1985 and a PhD in economics from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1991. In between, he spent 18 months studying German postwar reconstruction and social policy at universities and research institutes in Mannheim, Frankfurt, and Berlin. From 1991 to 2000, he worked as an assistant and then associate professor of public policy and political science at University of Rochester, after which he became an associate professor of economics in the College of Business and Economics at California State University, Fullerton. In the fall 2004, he joined the faculty of Indiana University Bloomington as an associate professor of telecommunication and cognitive science, later becoming a full professor and also the director of graduate studies i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |