|
Virginius Clark
Virginius Evans Clark (February 27, 1886 – January 30, 1948) was an officer in the United States Army, a military aviation pioneer, and a World War I engineer. Clark designed the 1922 Clark Y airfoil used by many early aircraft. Biography He was born on February 27, 1886, to Harry Scott Clark in Uniontown, Pennsylvania. Clark graduated the United States Naval Academy in 1907. He participated in the 1908-1909 round-the-world battleship voyage with the Great White Fleet. Later he was part of the Coast Artillery until 1912. In 1913 Clark joined the Aeronautical Division, U.S. Signal Corps. In 1914, Clark attended Massachusetts Institute of Technology for an aviation engineering course. In 1917, Clark became a NACA member, and a member on the Joint Army and Navy Board on Rigid Airships. In 1917 Clark became the Commanding officer of McCook Field founding the current Aeronautical Systems Center. While at McCook, Clark and Verville designed the VCP-1, and Engineering Divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Systems Center
The Aeronautical Systems Center (ASC) is an inactivated Air Force product center that designed, developed and delivered weapon systems and capabilities for U.S. Air Force, other U.S. military, allied and coalition-partner warfighters. ASC managed 420 Air Force, joint and international aircraft acquisition programs and related projects; executed an annual budget of $19 billion and employed a workforce of more than 11,000 people located at Wright-Patterson Air Force base and 38 other locations worldwide. ASC's portfolio included capabilities in fighter/attack, long-range strike, reconnaissance, mobility, agile combat support, special operations forces, training, unmanned aircraft systems, human systems integration and installation support. ASC was deactivated during a July 20, 2012 ceremony held at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio. History Early Aviation The Airplane Engineering Department, precursor of ASC, was first established under the U.S. Army's Aviation Section, U.S. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spruce Goose
The Hughes H-4 Hercules (commonly known as the ''Spruce Goose''; registration NX37602) is a prototype strategic airlift flying boat designed and built by the Hughes Aircraft Company. Intended as a transatlantic flight transport for use during World War II, it was not completed in time to be used in the war. The aircraft made only one brief flight, on November 2, 1947, and the project never advanced beyond the single example produced. Built from wood (Duramold process) because of wartime restrictions on the use of aluminum and concerns about weight, the aircraft was nicknamed the ''Spruce Goose'' by critics, although it was made almost entirely of birch.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 49–58, Cypress, CA, 2013. . The Hercules is the largest flying boat ever built, and it had the largest wingspan of any aircraft that had ever flown until the Scaled Composites Stratolaunch first flew on April 13, 2019. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duramold
Duramold is a composite material process developed by Virginius E. Clark. Birch or Populus, poplar plies are impregnated with phenolic resin and laminated together in a mold under heat (280 °F, 138 °C) and pressure for use as a lightweight structural material. Similar to plywood, Duramold and other lightweight composite materials like the similar Haskelite were considered critical during periods of material shortage in World War II, replacing scarce materials like aluminum alloys and steel.Dana T. Parker, ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II'', Cypress, CA, 2013, , pp. 51-52, 56. . The material has some advantages over metal in strength, construction technique, and weight. A cylinder made of Duramold is 80% stronger than a cylinder made of aluminum. Over 17 varieties of Duramold were developed, using various combinations of types of wood in thin plies. The Duramold process has also been used to make radomes for aircraft as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Aircraft Company
The Hughes Aircraft Company was a major American aerospace and defense contractor founded on February 14, 1934 by Howard Hughes in Glendale, California, as a division of Hughes Tool Company. The company was known for producing, among other products, the Hughes H-4 Hercules ''Spruce Goose'' aircraft, the atmospheric entry probe carried by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft, and the AIM-4 Falcon guided missile. Hughes Aircraft was founded to construct Hughes' H-1 Racer world speed record aircraft, and it later modified aircraft for his transcontinental and global circumnavigation speed record flights. The company relocated to Culver City, California, in 1940 and began manufacturing aircraft parts as a subcontractor. Hughes attempted to mold it into a major military aircraft manufacturer during World War II; however, its initial military projects ended in failure, with millions of dollars in U.S. government funds expended but only three aircraft actually built, resulting in a highly publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild 46-A
The Fairchild F-46, also known as the Duramold Aircraft Corporation F-46 A, is a light aircraft that was built using the Duramold process, later used on the Spruce Goose. Development The process was developed jointly by the Haskelite Manufacturing Corporation as Plymold and the Fairchild Engine and Aircraft Corporation as Duramold. The plywood employed heat, pressure, plastics and wood to make complex structures in less time than could be done with aluminum construction. The Haskelite Corporation used this plywood for railway cars, buses, automobiles, and boats. Fairchild created its own use of the technology for making airplane structures. Design The Model 46 is a low-wing, cabin aircraft, with conventional landing gear and structures made using Duramold processes. The fuselage is constructed of two halves bonded together. The wings use wooden spars with plywood covering. The control surfaces use aluminum frames with aircraft fabric covering. A fuel tank was mounted in each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild 150
The General Aviation GA-43 was a single engine low-wing monoplane airliner produced in small numbers in the United States in the mid-1930s, also known as the Pilgrim 150, Fairchild 150, and sometimes but erroneously as the Clark GA-43 for the designer, Virginius E. Clark who was also responsible for the Clark Y airfoil section used. The prototype was developed and built by Fairchild's American Pilgrim division, but the program was taken over by General Aviation when the firm purchased American Pilgrim shortly before the prototype had flown. Although this first flight took place in 1932, manufacture did not commence until 1934, by which time General Motors had, in turn, gained a controlling interest in North American Aviation and merged it with General Aviation General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild 100
The Fairchild 100 Pilgrim is an American single-engined high-wing monoplane transport, and was one of a series of single-engine utility transports built by Fairchild Aircraft. Design and development The 100 was similar in design to the Fairchild C-8 and was an enlarged version of it. The first flight of the aircraft (NC754Y) was October 22, 1930. Although only one aircraft was completed, a modified version also known as the Pilgrim 100-A was in production for American Airways, the first operator of the type in 1931. After a total of 16 aircraft, an additional batch of ten aircraft with a larger fin were manufactured by the restructured American Aircraft & Engine Corporation that emerged in 1931 from the Fairchild Aircraft Co. The continuing series was built under the designations, Pilgrim 100-B and American/Fairchild Y1C-24. The first six in the new series went to American Airways. The parent company later reinstated the Fairchild name. Operational history The sturdy Fairchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Aircraft
Fairchild was an American aircraft and aerospace manufacturing company based at various times in Farmingdale, New York; Hagerstown, Maryland; and San Antonio, Texas. History Early aircraft The company was founded by Sherman Fairchild in 1924 as Fairchild Aviation Corporation, based in Farmingdale, and East Farmingdale, New York. It was established as the parent company for Fairchild's many aviation interests. The company produced the first US aircraft to include a fully enclosed cockpit and hydraulic landing gear, the Fairchild FC-1. At some point, it was also known as the Fairchild Aircraft Manufacturing Company. The Fairchild Aircraft Ltd. of Longueuil, Quebec, Canada was an aircraft manufacturer during the period of 1920 to 1950, which served as a subsidiary of the Fairchild company of the United States. The Fairchild Engine Company was formed with the purchase of the Caminez Engine Company in 1925. In 1929, Sherman Fairchild purchased a majority stock interest in Kre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Aircraft
The Consolidated Aircraft Corporation was founded in 1923 in aviation, 1923 by Reuben H. Fleet in Buffalo, New York, the result of the Gallaudet Aircraft Company's liquidation and Fleet's purchase of designs from the Dayton-Wright Company as the subsidiary was being closed by its parent corporation, General Motors.Yenne 2009, p. 15. Consolidated became famous, during the 1920s and 1930s, for its line of flying boats. The most successful of the Consolidated patrol boats was the PBY Catalina, which was produced throughout World War II and used extensively by the Allies. Equally famous was the B-24 Liberator, a heavy bomber which, like the Catalina, saw action in both the Asiatic-Pacific Theater, Pacific and European Theater of Operations, European theaters. In 1943 in aviation, 1943, Consolidated merged with Vultee Aircraft to form Consolidated-Vultee Aircraft, later known as Convair. History Consolidated Aircraft (and later Convair) had their headquarters in San Diego, California, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dayton-Wright Company
The Dayton-Wright Company was formed in 1917, on the declaration of war between the United States and Germany, by a group of Ohio investors that included Charles F. Kettering and Edward A. Deeds of Dayton Engineering Laboratories Company ( DELCO). Orville Wright lent his name and served as a consultant, but other than that, the location of one of its three factories in the original Wright Company factory buildings in Dayton, Ohio was the only connection to the Wright brothers. In addition to plant 3 (the former Wright Company buildings), Dayton-Wright operated factories in Moraine (plant 1, the main factory) and Miamisburg (plant 2), Ohio. During the course of the war, Dayton-Wright produced about 3,000 DH-4s, as well as 400 Standard SJ-1 trainers. The company was hurt by the reputation of the DH-4s it produced as "flaming coffins" or "flying coffins", although they were not in reality more subject to catching fire than other aircraft, and by scandals it faced. History Deed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
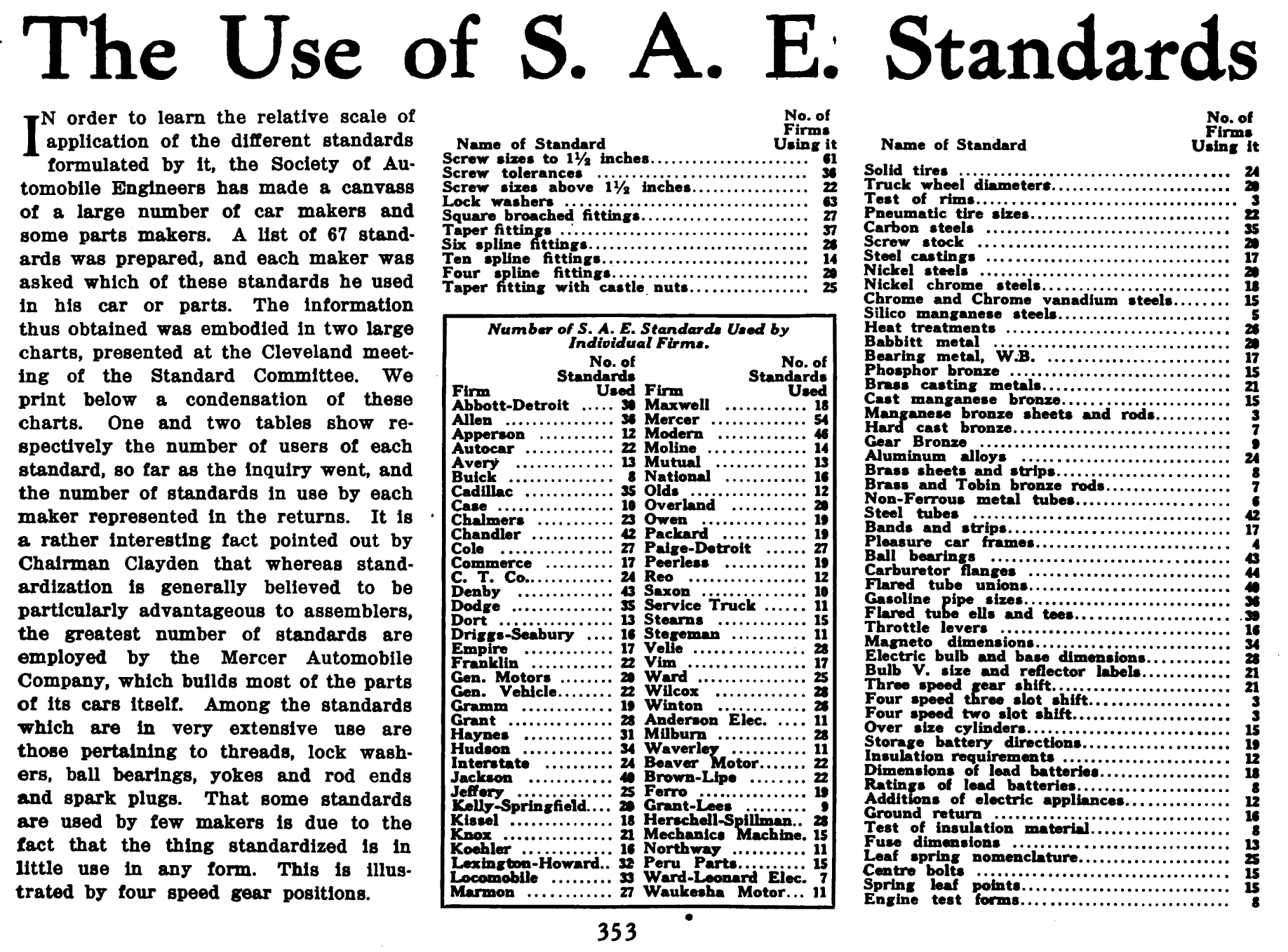
Society Of Automotive Engineers
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.jpg)