|
Villers Abbey
Villers Abbey (''abbaye de Villers'') is an ancient Cistercian abbey located in the town of Villers-la-Ville, in the Walloon Brabant province of Wallonia (Belgium), one piece of the ''Wallonia's Major Heritage''. Founded in 1146, the abbey was abandoned in 1796. Most of the site has since fallen into ruins. History In 1146, 12 Cistercian monks and three lay brothers from Clairvaux came to Villers in order to establish the abbey on land granted them by Gauthier de Marbais. After establishing several preliminary sites (Villers I and Villers II), work was finally undertaken in the 13th century to build the current site. The choir was constructed by 1217, the crypt by 1240, and the refectory by 1267. The church itself took 70 years to build and was completed by the end of the century. During this period, the abbey reached the height of its fame and importance. Contemporary accounts suggest that roughly 100 monks and 300 lay brothers resided within its walls, although this is possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villers-la-Ville JPG00V (1)
Villers-la-Ville (; wa, L' Abeye) is a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality of Wallonia located in the Belgium, Belgian province of Walloon Brabant. On January 1, 2006, Villers-la-Ville had a total population of 9,572. The total area is 47.45 km2 which gives a population density of 202 inhabitants per km2. The municipality includes also the villages of Marbais, Mellery, Sart-Dames-Avelines and Tilly, Villers-la-Ville, Tilly. History ''To be expanded'' Sites To the north of the village lie the ruins of the Villers Abbey, which was one of the most important Cistercian abbeys of Europe. It was founded in 1147 and destroyed by the French republicans in 1795. In the ruined church attached to the abbey the tombstones of several Duke of Brabant, dukes of Brabant of the 13th and 14th centuries are still to be found. The ruins also appear in the final episode of season 2 of sense8. Postal history The MARBAIS post office opened on 1 June 1838. It used postal distribution code 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crisóstomo Henríquez
Crisóstomo Henríquez (1594 – 23 December 1632) was a Spanish Cistercian monk and ecclesiastical historian, who belonged to the Spanish congregation of that order, and who worked in the Spanish Netherlands. Biography Early life, education, and career Henríquez was born in Madrid, Spain, in 1594. At the age of 13, after having finished his humanities, he entered the Cistercian Abbey of Huerta, Spain, where he received the religious habit, and in 1612 was admitted to monastic profession. He was then sent by his superiors to various monasteries of the Order, where he studied successively philosophy and theology under the most eminent professors. During his studies he manifested a marked aptitude and taste for historical research. While still a student, he published his first work, the ''History of the Monastery of Meyra''. Having completed his studies, he returned to Huerta. During this time his parents had left Spain to take up their residence at the court of the Archduke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruined Christian Monasteries In Belgium
Ruins () are the remains of a civilization's architecture. The term refers to formerly intact structures that have fallen into a state of partial or total disrepair over time due to a variety of factors, such as lack of maintenance, deliberate destruction by humans, or uncontrollable destruction by natural phenomena. The most common root causes that yield ruins in their wake are natural disasters, armed conflict, and population decline, with many structures becoming progressively derelict over time due to long-term weathering and scavenging. There are famous ruins all over the world, with notable sites originating from ancient China, the Indus Valley and other regions of ancient India, ancient Iran, ancient Israel and Judea, ancient Iraq, ancient Greece, ancient Egypt, Roman sites throughout the Mediterranean Basin, and Incan and Mayan sites in the Americas. Ruins are of great importance to historians, archaeologists and anthropologists, whether they were once individual fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose Windows
A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can be erect shrubs, climbing, or trailing, with stems that are often armed with sharp prickles. Their flowers vary in size and shape and are usually large and showy, in colours ranging from white through yellows and reds. Most species are native to Asia, with smaller numbers native to Europe, North America, and northwestern Africa. Species, cultivars and hybrids are all widely grown for their beauty and often are fragrant. Roses have acquired cultural significance in many societies. Rose plants range in size from compact, miniature roses, to climbers that can reach seven meters in height. Different species hybridize easily, and this has been used in the development of the wide range of garden roses. Etymology The name ''rose'' comes from Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent collapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vault (architecture)
In architecture, a vault (French ''voûte'', from Italian ''volta'') is a self-supporting arched form, usually of stone or brick, serving to cover a space with a ceiling or roof. As in building an arch, a temporary support is needed while rings of voussoirs are constructed and the rings placed in position. Until the topmost voussoir, the keystone, is positioned, the vault is not self-supporting. Where timber is easily obtained, this temporary support is provided by centering consisting of a framed truss with a semicircular or segmental head, which supports the voussoirs until the ring of the whole arch is completed. Vault types Corbelled vaults, also called false vaults, with horizontally joined layers of stone have been documented since prehistoric times; in the 14th century BC from Mycenae. They were built regionally until modern times. The real vault construction with radially joined stones was already known to the Egyptians and Assyrians and was introduced into the buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charleroi
Charleroi ( , , ; wa, Tchålerwè ) is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By 1 January 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593.Statistics Belgium; ''Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008'' (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 19 October 2008. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of with a total population of 522,522 by 1 January 2008, ranking it as the 5th most populous in |
Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve
Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve (; wa, Ocgniye-Li Noû Lovén) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the Belgian province of Walloon Brabant. On January 1, 2006, Ottignies-Louvain-la-Neuve had a total population of 29,521. The total area is 32.96 km² which gives a population density of 896 inhabitants per km². The municipality consists of the following sub-municipalities: Ottignies, Louvain-la-Neuve, Céroux-Mousty, and Limelette. Louvain-la-Neuve (sometimes abbreviated as "LLN") is a new town developed from 1968 in order to provide a home for the University of Louvain (UCLouvain), the French-speaking part of the former Catholic University of Louvain on its separation from the Dutch-speaking part, which remained in the ancient city of Louvain (''Leuven''). Louvain-la-Neuve Science Park Created in 1971, Louvain-la-Neuve Science Park is the first of its kind in Belgium and is the biggest one in Wallonia (the French-speaking part of Belgium). It covers spread over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne Of Kiev
Anne of Kiev or Anna Yaroslavna, Russian: Анна Ярославна (c. 1030 – 1075) was a Rus' princess who became Queen of France in 1051 upon marrying King Henry I. She ruled the kingdom as regent during the minority of their son Philip I from Henry's death in 1060 until her controversial marriage to Count Ralph IV of Valois. Anne founded the Abbey of St. Vincent at Senlis. Childhood Anne was a daughter of Yaroslav the Wise, Grand Prince of Kiev and Prince of Novgorod, and his second wife Ingegerd Olofsdotter of Sweden. Her exact birthdate is unknown; Philippe Delorme has suggested 1027, while Andrew Gregorovich has proposed 1032, citing a mention in a Kievan chronicle of the birth of a daughter to Yaroslav in that year. Anne's exact place in the birth order of her siblings is unknown, although she was almost certainly the youngest daughter. Little is known about Anne's childhood or education. It is assumed that she was literate, at least enough to write her name, beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juliana Of Liège
Juliana of Liège (also called Juliana of Mount-Cornillon), ( 1192 or 1193 – 5 April 1258) was a medieval Norbertine canoness regular and mystic in what is now Belgium. Traditional scholarly sources have long recognized her as the promoter of the Feast of Corpus Christi, first celebrated in Liège in 1246, and later adopted for the Catholic Church in 1264. More recent scholarship includes manuscript analysis of the initial version of the Office, as found in ''The Hague, National Library of the Netherlands'' (KB 70.E.4) and a close reading of her Latin ''vita'', a critical edition of which was published in French by the Belgian scholar, Jean-Pierre Delville. Newer scholarly work notes the many references to her musical and liturgical performances. Modern women scholars recognize Juliana as the "author" of the initial version of the Latin Office''Animarum cibus'' which takes its title from the beginning of its first antiphon. Biography Juliana and her twin sister Agnes were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
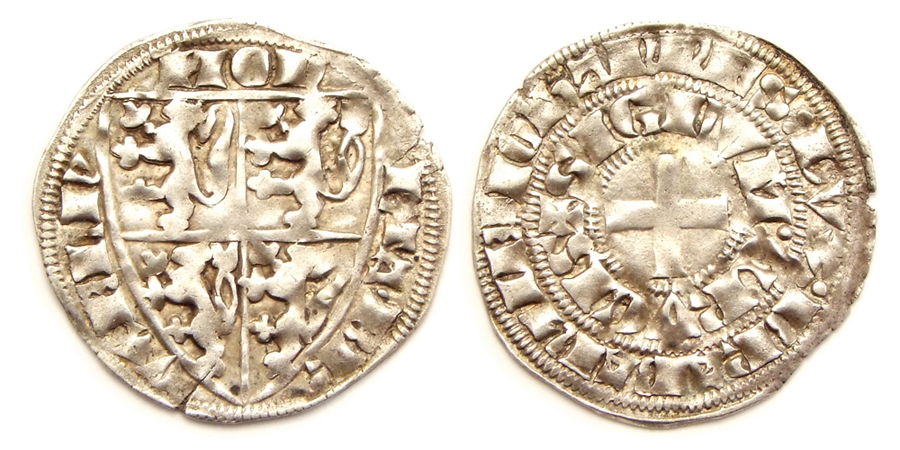
John III, Duke Of Brabant
John III ( nl, Jan; 1300 – 5 December 1355) was Duke of Brabant, Duke of Lothier, Lothier (1312–1355) and List of rulers of Limburg, Limburg (1312–1347 then 1349–1355). He was the son of John II, Duke of Brabant, and Margaret of England, Duchess of Brabant, Margaret of England. John and the towns of Brabant The early fourteenth century, an economic boom time for Brabant, marks the rise of the duchy's towns, which depended on English wool for their essential cloth industry. During John's minority, the major towns of Brabant had the authority to appoint councillors to direct a regency, under terms of the Charter of Kortenberg granted by his father in the year of his death (1312). By 1356 his daughter and son-in-law were forced to accept the Joyous Entry of 1356, famous Joyous Entry as a condition for their recognition, so powerful had the states of Brabant become. The marital alignment with France was tested and failed as early as 1316, when Louis X of France, Louis X reque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |