|
Village Earth
Village Earth: The Consortium for Sustainable Village-Based Development (CSVBD) DBA: Village Earth is a publicly supported 501(c)(3) non-profit, non-governmental organization (NGO) based in Fort Collins, Colorado, US. The organization works for the empowerment of rural and indigenous communities around the world with active projects with the Oglala Lakota on the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, the Shipibo-Konibo of the Amazon region of Peru, India, Cambodia, and Guatemala. Village Earth is associated with the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) at Colorado State University. Village Earth is also the publisher for The Appropriate Technology Library and The Appropriate Technology Sourceboo a low-cost rural-development resource initiated by Volunteers in Asia in 1975 but transferred to Village Earth in 1995. Objectives The roots of Village Earth's approach to community development grew from the reformist tradition of development which emerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice L
Maurice may refer to: People *Saint Maurice (died 287), Roman legionary and Christian martyr *Maurice (emperor) or Flavius Mauricius Tiberius Augustus (539–602), Byzantine emperor * Maurice (bishop of London) (died 1107), Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of England * Maurice of Carnoet (1117–1191), Breton abbot and saint * Maurice, Count of Oldenburg (fl. 1169–1211) * Maurice of Inchaffray (14th century), Scottish cleric who became a bishop *Maurice, Elector of Saxony (1521–1553), German Saxon nobleman * Maurice, Duke of Saxe-Lauenburg (1551–1612) * Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange (1567–1625), stadtholder of the Netherlands *Maurice, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel or Maurice the Learned (1572–1632) *Maurice of Savoy (1593–1657), prince of Savoy and a cardinal *Maurice, Duke of Saxe-Zeitz (1619–1681) * Maurice of the Palatinate (1620–1652), Count Palatine of the Rhine *Maurice of the Netherlands (1843–1850), prince of Orange-Nassau * Maurice Chevalier (1888–19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Livelihoods Approach
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable living). Sustainability is commonly described as having three dimensions (also called pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many publications state that the environmental dimension (also called "planetary integrity" or "ecological integrity") is the most important, and, in everyday usage, "sustainability" is often focused on countering major environmental problems, such as climate change, loss of biodiversity, loss of ecosystem services, land degradation, and air and water pollution. Humanity is now exceeding several "planetary boundaries". A closely related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used synonymously. However, UNESCO distinguishes the two thus: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swadeshi Movement
The Swadeshi movement was a self-sufficiency movement that was part of the Indian independence movement and contributed to the development of Indian nationalism. Before the BML Government's decision for the partition of Bengal was made public in December 1903, there was a lot of growing discontentment among the Indians. In response the Swadeshi movement was formally started from Town Hall Calcutta on 7 August 1905 to curb foreign goods by relying on domestic production. Mahatma Gandhi described it as the soul of swaraj (self-rule). The movement took its vast size and shape after rich Indians donated money and land dedicated to Khadi and Gramodyog societies which started cloth production in every household. It also included other village industries so as to make village self-sufficient and self-reliant. The Indian National Congress used this movement as arsenal for its freedom struggle and ultimately on 15 August 1947, a hand-spun Khadi 'tricolor ashok chakra' Indian flag was unfur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Is Beautiful
''Small Is Beautiful: A Study of Economics As If People Mattered'' is a collection of essays published in 1973 by German-born British economist E. F. Schumacher. The title "Small Is Beautiful" came from a principle espoused by Schumacher's teacher Leopold KohrDr. Leopold Kohr, 84; Backed Smaller States obituary, 28 February 1994. (1909–1994) advancing small, appropriate technologies, policies, and polities as a superior alternative to the mainstream ethos of "bigger is better". Overlapping environmental, soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Resource
A renewable resource, also known as a flow resource, is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of time in a human time scale. When the recovery rate of resources is unlikely to ever exceed a human time scale, these are called perpetual resources. Renewable resources are a part of Earth's natural environment and the largest components of its ecosphere. A positive life-cycle assessment is a key indicator of a resource's sustainability. Definitions of renewable resources may also include agricultural production, as in agricultural products and to an extent water resources.What are “Renewable Resources”? by A. John Armstrong, Esq. & Dr. Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Sociology
Rural sociology is a field of sociology traditionally associated with the study of social structure and conflict in rural areas. It is an active academic field in much of the world, originating in the United States in the 1910s with close ties to the national Department of Agriculture and land-grant university colleges of agriculture. While the issue of natural resource access transcends traditional rural spatial boundaries, the sociology of food and agriculture is one focus of rural sociology, and much of the field is dedicated to the economics of farm production. Other areas of study include rural migration and other demographic patterns, environmental sociology, amenity-led development, public-lands policies, so-called " boomtown" development, social disruption, the sociology of natural resources (including forests, mining, fishing and other areas), rural cultures and identities, rural health-care, and educational policies. Many rural sociologists work in the areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Community Development
Rural community development encompasses a range of approaches and activities that aim to improve the welfare and livelihoods of people living in rural areas. As a branch of community development, these approaches pay attention to social issues particularly community organizing. This is in contrast to other forms of rural development that focus on public works (e.g. rural roads and electrification) and technology (e.g. tools and techniques for improving agricultural production). Rural community development is important in developing countries where a large part of the population is engaged in farming. Consequently, a range of community development methods have been created and used by organisations involved in international development. Most of these efforts to promote rural community development are led by 'experts' from outside the community such as government officials, staff of non-governmental organizations and foreign advisers. This has led to a long debate about the issue o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is farming in sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem services. There are many methods to increase the sustainability of agriculture. When developing agriculture within sustainable food systems, it is important to develop flexible business process and farming practices. Agriculture has an enormous environmental footprint, playing a significant role in causing climate change (food systems are responsible for one third of the anthropogenic GHG emissions), water scarcity, water pollution, land degradation, deforestation and other processes; it is simultaneously causing environmental changes and being impacted by these changes. Sustainable agriculture consists of environment friendly methods of farming that allow the production of crops or livestock without damage to human or natural systems. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community-based Economics
Community-based economics or community economics is an economic system that encourages local substitution. It is similar to the lifeways of those practicing voluntary simplicity, including traditional Mennonite, Amish, and modern eco-village communities. It is also a subject in urban economics, related to moral purchasing and local purchasing. The community-based economy can refer to the various initiatives coordinated through multiple forms of interactions. These interactions may involve some form of work performance; project participation; and/or relationship exchange. The forms of interaction can exclude the need to contract; can do away with the need to include some form of monetisation; as well as be free from the need to establish a structure of hierarchy. Community-based economies have been seen to involve aspects of social bonding; value promotion; and establishing community-orientated social goals. It has been suggested that communities that meet their own needs need the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
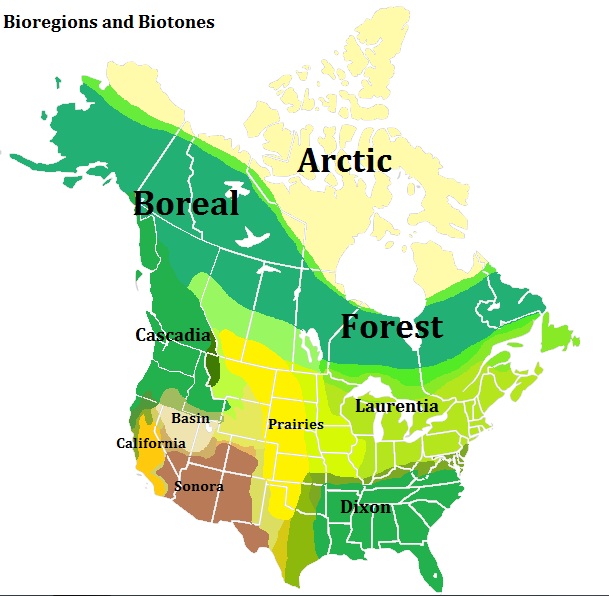
Bioregionalism
Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called bioregions, similar to ecoregions. Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions. Bioregionalism asserts "that a bioregion's environmental components (geography, climate, plant life, animal life, etc.) directly influence ways for human communities to act and interact with each other which are, in turn, optimal for those communities to thrive in their environment. As such, those ways to thrive in their totality—be they economic, cultural, spiritual, or political—will be distinctive in some capacity as being a product of their bioregional environment." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grassroots Support Organization
Grassroots Support Organizations (GSOs) are a specialized subset of Intermediate Non-Governmental Organizations (INGOs) that provides services and support to local groups of disadvantaged rural or urban households and individuals. In its capacity as an intermediary institution, a GSO forges links between beneficiaries and the often remote levels of government, donor, and financial institutions. It may also provide services indirectly to other organizations that support the poor or perform coordinating or networking functions.Carrol, Thomas F., Intermediary NGOs: The Supporting Link in Grassroots Development. Kumarian Press, Inc., 1992 Martinez (2008) defines GSOs as development NGOs providing services and resources that enhance the capacity of impoverished communities and their organizations to build sustainable alternatives to their challenging life conditions.Rafael A. Boglio Martínez, Grassroots Support Organizations and Transformative Practices, Journal of Community Practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |