|
Video Shader
Video Shader is a graphics card feature that ATI advertises on their R300 and R400 cards. The R500 card is advertised as having Video Shader HD. Video shader is a feature that describes ATI's process of using Pixel Shaders In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene - a process known as '' shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of ... to improve quality of video playback. It can also be used to perform post-processing, like adding a film grain, or adding other special effects. One feature of Video Shader is ATI Full Stream. Full Stream detects the edges of video compression blocks and uses a pixel shader based filter to smooth the picture hiding the blocks. Another is Video Soap, which reduces video noise. Other features are DXVA support for Hardware Motion Compensation, iDCT, DCT and color space conversion. Support for Hardware Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to integrated graphics. A graphics processing unit that performs the necessary computations is the main component of a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the central processing unit. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and CUDA allow using graphics cards for general-purpose computing. Applications of general-purpose computing on graphics cards include AI training, cryptocurrency mining, and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATI (brand)
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as going fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and FPGAs for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. History First twelve years Advanced Micro Devices was formally incorporated by Jerry Sanders, along with seven of his colleagues from Fairchild Semiconductor, on May 1, 1969. Sanders, an electrical engineer who was the director of marketing at Fairchild, had, like many Fairchild executives, grown frustrated with the increasing lack of support, opportunity, and flexibility within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radeon R300
The R300 GPU, introduced in August 2002 and developed by ATI Technologies, is its third generation of GPU used in ''Radeon'' graphics cards. This GPU features 3D acceleration based upon Direct3D 9.0 and OpenGL 2.0, a major improvement in features and performance compared to the preceding R200 design. R300 was the first fully Direct3D 9-capable consumer graphics chip. The processors also include 2D GUI acceleration, video acceleration, and multiple display outputs. The first graphics cards using the R300 to be released were the Radeon 9700. It was the first time that ATI marketed its GPU as a Visual Processing Unit (VPU). R300 and its derivatives would form the basis for ATI's consumer and professional product lines for over 3 years. The integrated graphics processor based upon R300 is the ''Xpress 200''. Development ATI had held the lead for a while with the Radeon 8500 but Nvidia retook the performance crown with the launch of the GeForce 4 Ti line. A new high-end refresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radeon R400
The R420 GPU, developed by ATI Technologies, was the company's basis for its 3rd-generation DirectX 9.0/OpenGL 2.0-capable graphics cards. Used first on the Radeon X800, the R420 was produced on a 0.13 micrometer (130 nm) low-''K'' photolithography process and used GDDR-3 memory. The chip was designed for AGP graphics cards. Driver support of this core was discontinued as of Catalyst 9.4, and as a result there is no official Windows 7 support for any of the X700 - X850 products. Development In terms of supported DirectX features, R420 (codenamed Loki) was very similar to the R300. R420 basically takes a "wider is better" approach to the previous architecture, with some small tweaks thrown in to enhance it in various ways. The chip came equipped with over double the pixel and vertex pushing resources compared to the Radeon 9800 XT's R360 (a minor evolution of the R350), with 16 DirectX 9.0b pixel pipelines and 16 ROPs. One would not be far off seeing the X800 XT basically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radeon R500
The R520 (codenamed Fudo) is a graphics processing unit (GPU) developed by ATI Technologies and produced by TSMC. It was the first GPU produced using a 90 nm photolithography process. The R520 is the foundation for a line of DirectX 9.0c and OpenGL 2.0 3D accelerator X1000 video cards. It is ATI's first major architectural overhaul since the R300 and is highly optimized for Shader Model 3.0. The Radeon X1000 series using the core was introduced on October 5, 2005, and competed primarily against Nvidia's GeForce 7000 series. ATI released the successor to the R500 series with the R600 series on May 14, 2007. ATI does not provide official support for any X1000 series cards for Windows 8 or Windows 10; the last AMD Catalyst for this generation is the 10.2 from 2010 up to Windows 7. AMD stopped providing drivers for Windows 7 for this series in 2015. A series of open source Radeon drivers are available when using a Linux distribution. The same GPUs are also found in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel Shaders
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene - a process known as '' shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of specialized functions in computer graphics special effects and video post-processing, as well as general-purpose computing on graphics processing units. Traditional shaders calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility. Most shaders are coded for (and run on) a graphics processing unit (GPU), though this is not a strict requirement. ''Shading languages'' are used to program the GPU's rendering pipeline, which has mostly superseded the fixed-function pipeline of the past that only allowed for common geometry transforming and pixel-shading functions; with shaders, customized effects can be used. The position and color ( hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast) of all pixels, vertices, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Post-processing
The term post-processing (or postproc for short) is used in the video/film business for quality-improvement image processing (specifically digital image processing) methods used in video playback devices, such as stand-alone DVD-Video players; video playing software; and transcoding software. It is also commonly used in real-time 3D rendering (such as in video games) to add additional effects. Uses in video production Video post-processing is the process of changing the perceived quality of a video on playback (done after the decoding process). Image scaling routines such as linear interpolation, bilinear interpolation, or cubic interpolation can for example be performed when increasing the size of images; this involves either subsampling (reducing or shrinking an image) or zooming (enlarging an image). This helps reduce or hide image artifacts and flaws in the original film material. It is important to understand that post-processing always involves a trade-off between speed, sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
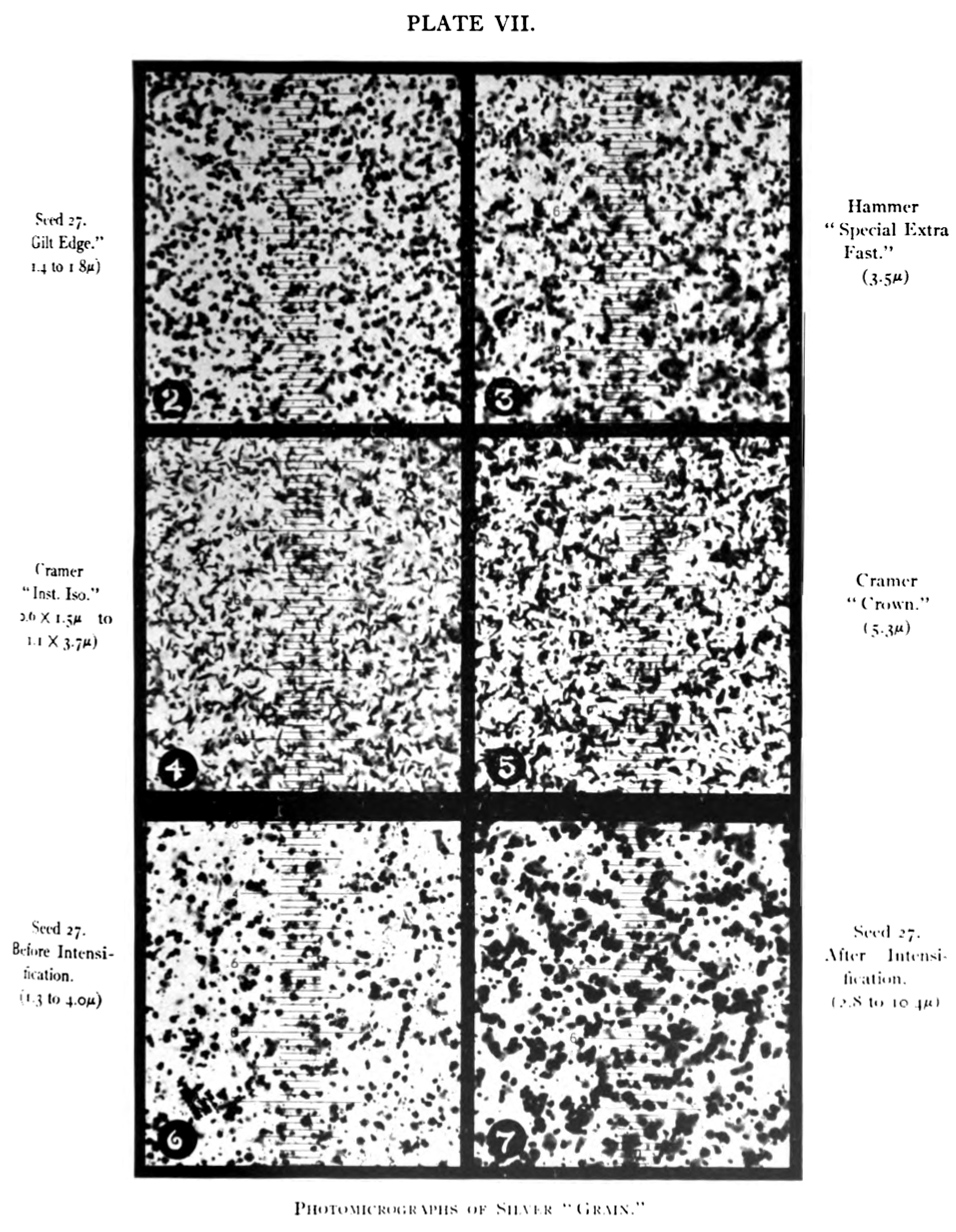
Film Grain
Film grain or granularity is the random optical texture of processed photographic film due to the presence of small particles of a metallic silver, or dye clouds, developed from silver halide that have received enough photons. While film grain is a function of such particles (or dye clouds) it is not the same thing as such. It is an optical effect, the magnitude of which (amount of grain) depends on both the film stock and the definition at which it is observed. It can be objectionably noticeable in an over-enlarged film photograph. RMS granularity Granularity, or RMS granularity, is a numerical quantification of density non-uniformity, equal to the root-mean-square (rms) fluctuations in optical density, measured with a microdensitometer with a 0.048 mm (48-micrometre) diameter circular aperture, on a film area that has been exposed and normally developed to a mean density of 1.0 D (that is, it transmits 10% of light incident on it). Granularity is sometimes quoted as "di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Effects
Special effects (often abbreviated as SFX, F/X or simply FX) are illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, video game, amusement park and simulator industries to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual world. Special effects are traditionally divided into the categories of mechanical effects and optical effects. With the emergence of digital film-making a distinction between special effects and visual effects has grown, with the latter referring to digital post-production and optical effects, while "special effects" refers to mechanical effects. Mechanical effects (also called practical or physical effects) are usually accomplished during the live-action shooting. This includes the use of mechanized props, scenery, scale models, animatronics, pyrotechnics and atmospheric effects: creating physical wind, rain, fog, snow, clouds, making a car appear to drive by itself and blowing up a building, etc. Mechanical effects are also often inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DXVA
DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) is a Microsoft API specification for the Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360 platforms that allows video decoding to be hardware-accelerated. The pipeline allows certain CPU-intensive operations such as iDCT, motion compensation and deinterlacing to be offloaded to the GPU. DXVA 2.0 allows more operations, including video capturing and processing operations, to be hardware-accelerated as well. DXVA works in conjunction with the video rendering model used by the video card. DXVA 1.0, which was introduced as a standardized API with Windows 2000 and is currently available on Windows 98 or later, can use either the overlay rendering mode or VMR 7/9. DXVA 2.0, available only on Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 and later OSs, integrates with Media Foundation (MF) and uses the Enhanced Video Renderer (EVR) present in MF. Overview The DXVA is used by software video decoders to define a codec-specific pipeline for hardware-accelerated decoding and ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unified Video Decoder
Unified Video Decoder (UVD, previously called Universal Video Decoder) is the name given to AMD's dedicated video decoding ASIC. There are multiple versions implementing a multitude of video codecs, such as H.264 and VC-1. UVD was introduced with the Radeon HD 2000 Series and is integrated into some of AMD's GPUs and APUs. UVD occupies a considerable amount of the die surface at the time of its introduction and is not to be confused with AMD's Video Coding Engine (VCE). As of AMD Raven Ridge (released January 2018), UVD and VCE were succeeded by Video Core Next (VCN). Overview The UVD is based on an ATI Xilleon video processor, which is incorporated onto the same die as the GPU and is part of the ATI Avivo HD for hardware video decoding, along with the Advanced Video Processor (AVP). UVD, as stated by AMD, handles decoding of H.264/AVC, and VC-1 video codecs entirely in hardware. The UVD technology is based on the Cadence Tensilica Xtensa processor, which was origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Coding Engine
Video Code Engine (VCE, was earlier referred to as Video Coding Engine, Video Compression Engine or Video Codec Engine in official AMD documentation) is AMD's video encoding application-specific integrated circuit implementing the video codec H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Since 2012 it was integrated into all of their GPUs and APUs except Oland. VCE was introduced with the Radeon HD 7000 Series on 22 December 2011. VCE occupies a considerable amount of the die surface at the time of its introduction and is not to be confused with AMD's Unified Video Decoder (UVD). As of AMD Raven Ridge (released January 2018), UVD and VCE were succeeded by Video Core Next (VCN). Overview The handling of video data involves computation of data compression algorithms and possibly of video processing algorithms. As the template compression methods shows, lossy video compression algorithms involve the steps: motion estimation (ME), discrete cosine transform (DCT), and entropy encoding (EC). AMD V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)