|
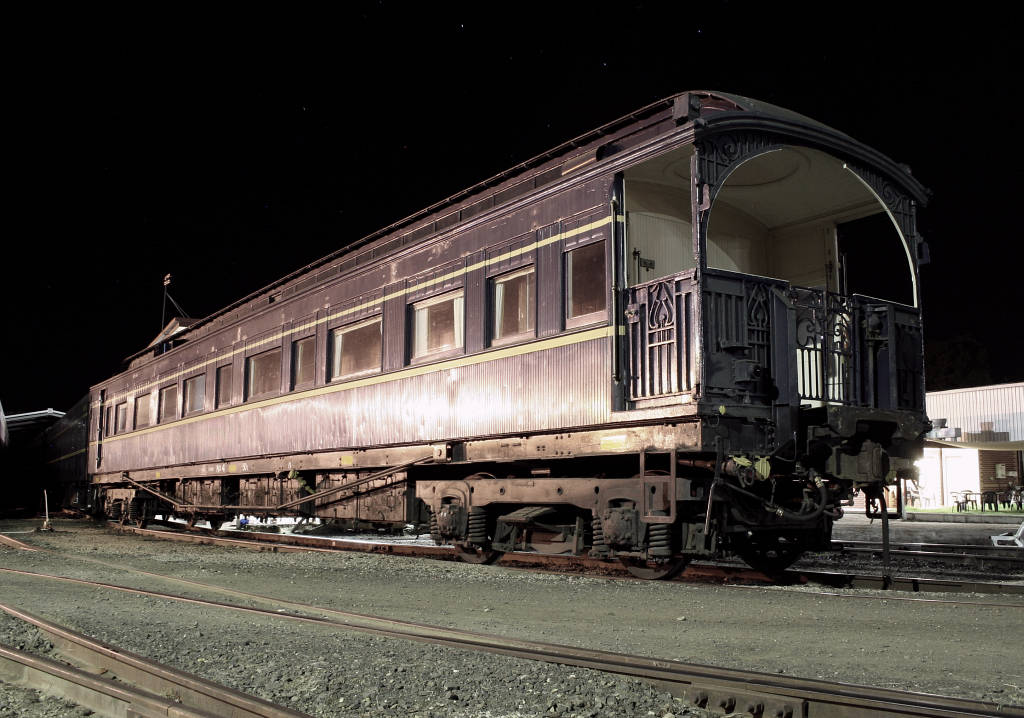
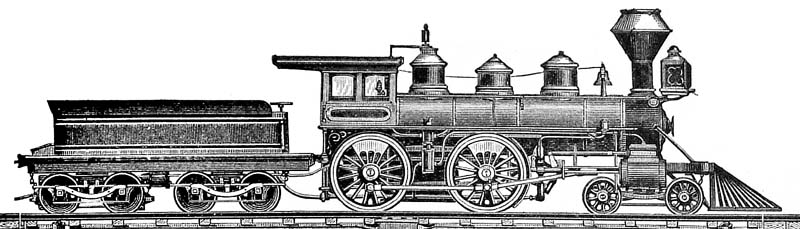
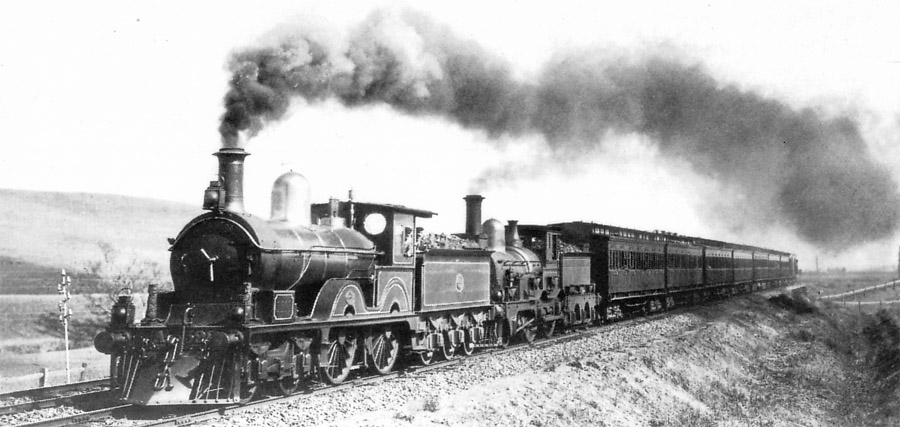
Victorian Railways B Class
The mainline passenger locomotives, later classified as B class, ran on the Victorian Railways (VR) between 1862 and 1917. They used a wheel arrangement, which provided greater traction on the new, more heavily graded Geelong–Ballarat railway line, Geelong–Ballarat railway and the Deniliquin railway line, Melbourne-Bendigo-Echuca railway, as opposed to the 2-2-2 arrangement previously selected for the relatively level Warrnambool railway line, Geelong line. The B class locomotives are regarded as the first mainline VR motive power, and were highly successful in passenger operations. History The Victorian Railways was formed after the government had taken over the struggling Melbourne, Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company in 1856 and the Geelong and Melbourne Railway Company line in 1860. The new organisation began the construction of two main lines to serve the booming gold-mining towns of Ballarat, Castlemaine, Victoria, Castlemaine and Bendigo, Sandhurst (Bendig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
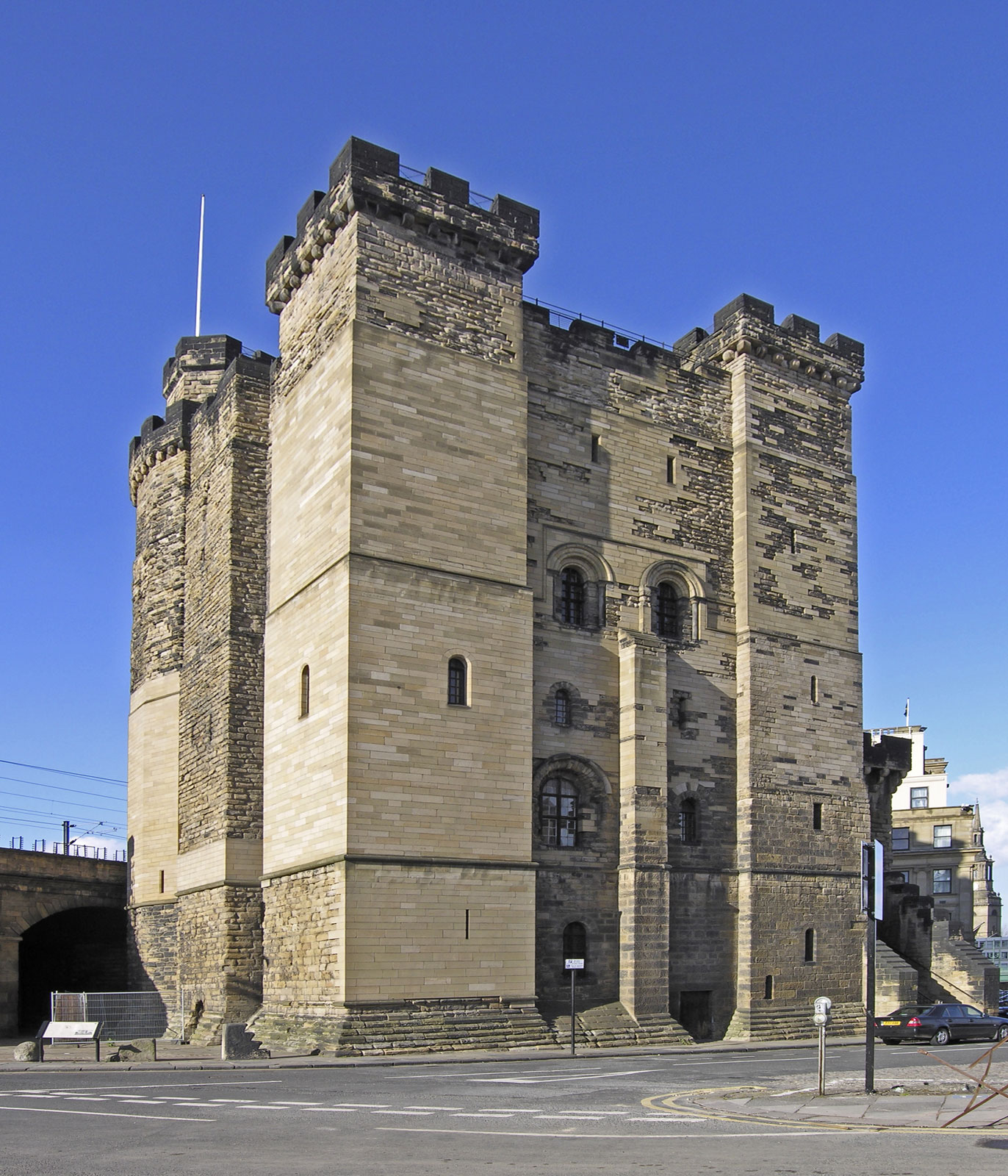
R And W Hawthorn
R and W Hawthorn Ltd was a locomotive manufacturer in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, from 1817 until 1885. Locomotive building Robert Hawthorn first began business at Forth Bank Works in 1817, building marine and stationary steam engines. In 1820, his brother William joined him and the firm became R and W Hawthorn. Possibly after having attended the Rainhill Trials in 1829, they became interested in locomotives, and sold their first engine in 1831. Printed and online sources claim this to be ''Mödling'' for the Vienna Gloggnitz railway. That is wrong, that locomotive was delivered in 1841. The 1831 order was placed by the Stockton and Darlington Railway. There followed a number of orders for the Stockton and Darlington Railway. They were great innovators - not always successfully - and their locos had many original features. In 1838 two were built for the Isambard Kingdom Brunel#Great Western Railway, broad gauge Great Western Railway to the patent of Thomas Elliot Harrison, T.&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is also the most populous city of North East England. Newcastle developed around a Roman settlement called Pons Aelius and the settlement later took the name of a castle built in 1080 by William the Conqueror's eldest son, Robert Curthose. Historically, the city’s economy was dependent on its port and in particular, its status as one of the world's largest ship building and repair centres. Today, the city's economy is diverse with major economic output in science, finance, retail, education, tourism, and nightlife. Newcastle is one of the UK Core Cities, as well as part of the Eurocities network. Famous landmarks in Newcastle include the Tyne Bridge; the Swing Bridge; Newcastle Castle; St Thomas’ Church; Grainger Town including G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benalla, Victoria
Benalla is a small city located on the Broken River gateway to the High Country north-eastern region of Victoria, Australia, about north east of the state capital Melbourne. At the the population was 10,822. It is the administrative centre for the Rural City of Benalla local government area. History Prior to the European settlement of Australia, the Benalla region was populated by the Taungurung people, an Indigenous Australian people. A 1906 history recounts that prior to white settlement "as many as 400 blacks would meet together in the vicinity of Benalla to hold a corrobboree". The area was first sighted by Europeans during an expedition of Hamilton Hume and William Hovell in 1824 and was noted as an agricultural settlement called "Swampy". The expedition was followed by that of Major Thomas Mitchell in 1834. Rev. Joseph Docker settled in 1838 creating a pastoral run called ''Benalta Run'', said to be from an Aboriginal word for musk duck. Docker's property was inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stawell, Victoria
Stawell (pronounced /stɔːl/, "Stawl"), is an Australian town in the Wimmera region of Victoria (Australia), Victoria west-north-west of the state capital, Melbourne. Located within the Shire of Northern Grampians Local government in Australia, local government area, it is a seat of local government for the shire and its main administrative centre. At the , Stawell had a population of . It was founded in 1853 as Pleasant Creek (nice) during the Victorian gold rush. It is one of few towns in Victoria retaining an active gold mining industry. Stawell is famed for the Stawell Gift, a professional foot race that began in 1878. It is also known as the gateway to the Grampians National Park. One of the most significant Aboriginal sacred site, Aboriginal cultural sites in south-eastern Australia is Bunjil's Shelter, within the Black Range Scenic Reserve, south of Stawell. It is named after William Stawell, Sir William Foster Stawell (1815–89), the Chief Justice of Victoria. Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred, Duke Of Saxe-Coburg And Gotha
Alfred (Alfred Ernest Albert; 6 August 184430 July 1900) was the sovereign duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha from 1893 to 1900. He was the second son and fourth child of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert. He was known as the Duke of Edinburgh from 1866 until he succeeded his paternal uncle Ernest II as the reigning Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha in the German Empire. Early life Prince Alfred was born on 6 August 1844 at Windsor Castle to the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria, and her husband, Prince Albert, the second son of Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. Nicknamed Affie, he was second in the line of succession to the British throne behind his elder brother, the Prince of Wales. Alfred was baptised by the Archbishop of Canterbury, William Howley, at the Private Chapel in Windsor Castle on 6 September 1844. His godparents were his mother's first cousin, Prince George of Cambridge (represented by his father, the Duke of Cambridge); his paternal aunt, the Duchess of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Railways Royal Train
The Victorian Railways' (VR) Royal Trains operated to transport members of the Royal Family on their numerous tours of Australia on the Victorian rail network. The same carriages were also used for a number of vice-regal trains for the Governor-General of Australia and the Governor of Victoria. The last Royal Train ran in 1988. Operation Royal trains usually operated with special carriage stock set aside for the purpose. Most trains operated with double headed locomotives to reduce the chance of the train being stranded due to locomotive failure, with a third locomotive running in front of the train to ensure the track was clear. A special headboard with the royal coat of arms was usually affixed to the front of the leading locomotive. Carriages In the history of the Victorian Railways there were five special carriages designated for royal train and other special services, designated State Car 1 through to State Car 5. From 1954, the carriages were painted in the standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A And B Class VR Locomotives
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermic Syphon
Thermic siphons (alt. thermic syphons) are Heat-exchanger, heat-exchanging elements in the Firebox (steam engine), firebox or Combustion chamber#Steam engine, combustion chamber of some steam boiler and steam locomotive designs. As they are directly exposed to the radiant heat of combustion, they have a high evaporative capacity relative to their size. By arranging them near-vertically, they also have good water circulation by means of the thermosyphon effect. History The concept of a self-circulating thermic syphon began with stationary boilers and relatively simple Galloway tubes. They reached their peak in steam locomotive boilers, where the complexity of a syphon was justified by the need for a compact and lightweight means of increasing boiler capacity. One of the best-known forms for locomotives was invented by the English locomotive engineer who received a US patent. The Nicholson form combined a complex shape that provided more heating area in a given space than did the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firedoor
Boilers for generating steam or hot water have been designed in countless shapes, sizes and configurations. An extensive terminology has evolved to describe their common features. This glossary provides definitions for these terms. Terms which relate solely to boilers used for space heating or generating hot water are identified by (HVAC). A-B ; : A container beneath the furnace, catching ash and clinker that falls through the firebars. This may be made of brickwork for a stationary boiler, or steel sheet for a locomotive. Ashpans are often the location of the damper. They may also be shaped into hoppers, for easy cleaning during disposal. ; Blastpipe: Part of the exhaust system that discharges exhaust steam from the cylinders into the smokebox beneath the chimney in order to increase the draught through the fire. ; Blow-down: Periodic venting of water from the boiler. This water contains the most concentrated precursors for sludge build-up, so by venting it whilst still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firebox (locomotive)
In a steam engine, the firebox is the area where the fuel is burned, producing heat to boil the water in the boiler. Most are somewhat box-shaped, hence the name. The hot gases generated in the firebox are pulled through a rack of tubes running through the boiler. Steam locomotive fire tube firebox In the standard steam locomotive fire-tube boiler, the firebox is surrounded by water space on five sides. The bottom of the firebox is open to atmospheric pressure, but covered by fire grates (solid fuel) or a firing pan (liquid fuel). If the engine burns solid fuel, like wood or coal, there is a grate covering most of the bottom of the firebox to hold the fire. An ashpan, mounted underneath the firebox and below the grates, catches and collects hot embers, ashes, and other solid combustion waste as it falls through the grates. In a coal-burning locomotive, the grates may be shaken to clean dead ash from the bottom of the fire. They are shaken either manually or (in larger locomotiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tank Locomotive
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of a more traditional tender. Most tank engines also have bunkers (or fuel tanks) to hold fuel; in a tender-tank locomotive a tender holds some or all of the fuel, and may hold some water also. There are several different types of tank locomotive, distinguished by the position and style of the water tanks and fuel bunkers. The most common type has tanks mounted either side of the boiler. This type originated about 1840 and quickly became popular for industrial tasks, and later for shunting and shorter-distance main line duties. Tank locomotives have advantages and disadvantages compared to traditional locomotives that required a separate tender to carry needed water and fuel. History Origins The first tank locomotive was the ''Novelty'' that ran at the Rainhill Trials in 1829. It was an example of a ''Well Tank''. However, the more common fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)