|
Victorian Central Highlands
The Central Highlands subregion is part of the Grampians region in western Victoria. It includes the municipalities of Rural City of Ararat, City of Ballarat, Golden Plains Shire, Shire of Hepburn, Shire of Moorabool, Shire of Pyrenees The term is mainly used in a geological context to describe that part of the Great Dividing Range that is west of its alpine areas but does not extend to its western end in Victoria's west. The area is situated east of Ballarat, south of Bendigo, north and east of Melbourne, and west of the alpine areas. Major towns of the Central Highlands include Castlemaine, Creswick, Daylesford, Gisborne, Kyneton and Woodend. All these towns are located in what is usually referred to as the West Central Highlands. The more mountainous and more sparsely populated eastern part of the Central Highlands is referred to as the East Central Highlands and has extensive areas of temperate rainforest. Rainforests The East Victorian Central Highlands, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grampians (region)
The Grampians is an economic rural region located in the western part of Victoria, Australia. The region lies to the northwest of the western suburbs of Greater Melbourne, to the state's western border with South Australia and includes the Grampians National Park and significant gold mining heritage assets. The Grampians region has two sub-regions, Grampians Central Highlands and Wimmera Southern Mallee. As at the 2016 Australian census, the Grampians region had a population of , with almost half of the population located in the City of Ballarat. The principal centres of the region, in descending order of population, are Ballarat, Bacchus Marsh, , , and . Administration Political representation For the purposes of Australian federal elections for the House of Representatives, the Grampians region is contained within all or part of the electoral divisions of Ballarat, Corangamite, Mallee, and Wannon. For the purposes of Victorian elections for the Legislative Ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylesford, Victoria
Daylesford is a spa town located in the foothills of the Great Dividing Range, within the Shire of Hepburn, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia, approximately 108 kilometres north-west of Melbourne. First established in 1852 as a gold-mining town, today Daylesford has a population of 2,548 as of the 2016 Australian census, 2016 census. As one of Australia’s few spa towns, Daylesford is a notable tourist destination. The town’s numerous spas, restaurants and galleries are popular alongside the many gardens and country-house-conversion styled bed and breakfasts. The broader area around the town, including Hepburn Springs, Victoria, Hepburn Springs to the north, is known for its natural spring mineral spas and is the location of over 80 per cent of Australia's effervescent mineral water reserve. It is also the filming location for the third season of ''The Saddle Club'', and scenes from the 2004 film ''Love's Brother''. History Prior to European settlement the area was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars. Logging is the beginning of a supply chain that provides raw material for many products societies worldwide use for housing, construction, energy, and consumer paper products. Logging systems are also used to manage forests, reduce the risk of wildfires, and restore ecosystem functions, though their efficiency for these purposes has been challenged. In forestry, the term logging is sometimes used narrowly to describe the logistics of moving wood from the stump to somewhere outside the forest, usually a sawmill or a lumber yard. In common usage, however, the term may cover a range of forestry or silviculture activities. Illegal logging refers to the harvesting, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20124-01-04 Toolangi Tree House 600 2810 1 2 (Soft 4)
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
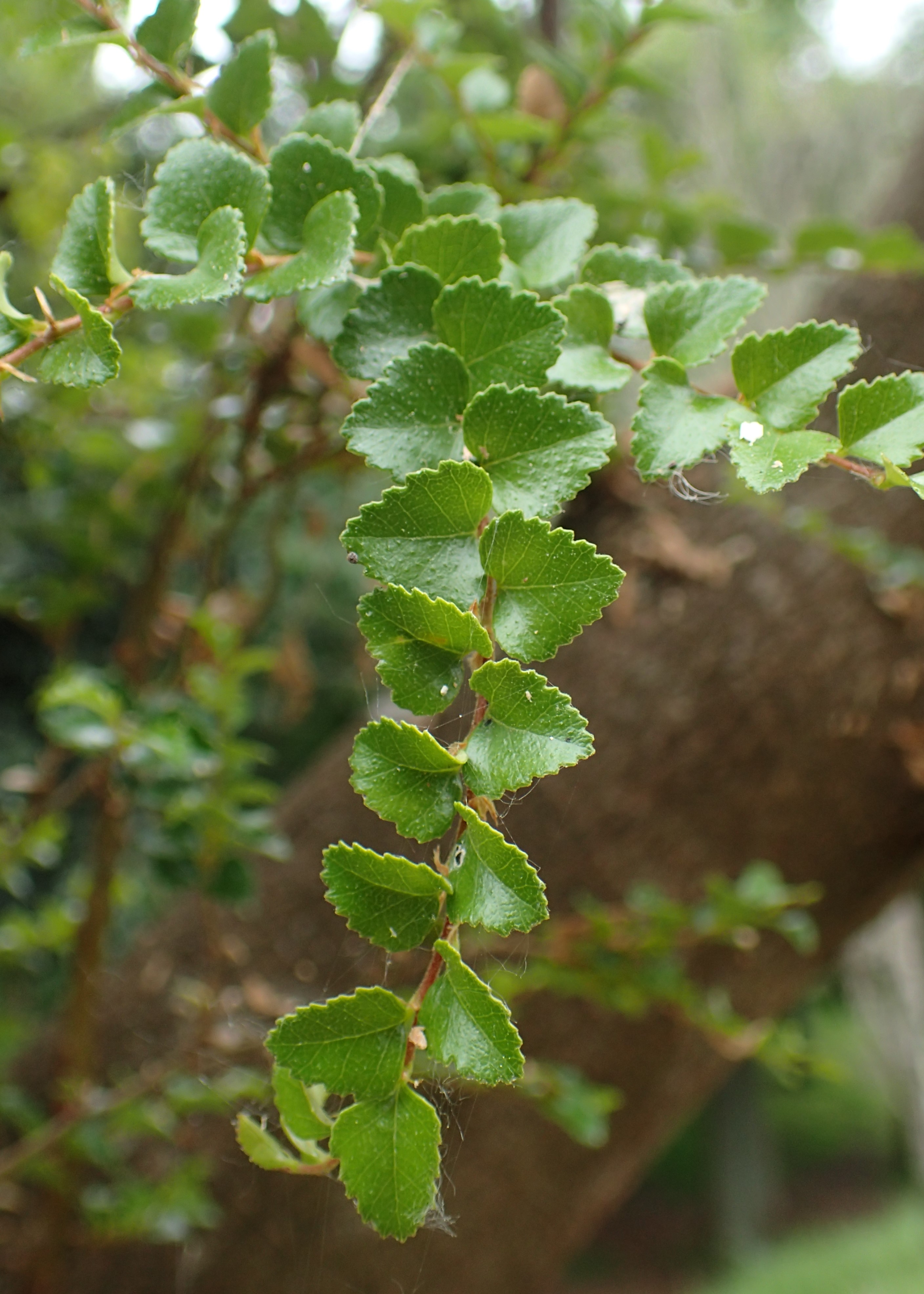
Acacia Melanoxylon
''Acacia melanoxylon'', commonly known as the Australian blackwood, is an ''Acacia'' species native in South eastern Australia. The species is also known as Blackwood, hickory, mudgerabah, Tasmanian blackwood, or blackwood acacia. The tree belongs to the ''Plurinerves'' section of ''Acacia'' and is one of the most wide-ranging tree species in eastern Australia and is quite variable mostly in the size and shape of the phyllodes. Description The tree is able to grow to a height of around and has a bole that is approximately in diameter. It has deeply fissured, dark-grey to black coloured bark that appears quite scaly on older trees. It has angular and ribbed branches The bark on older trunks is dark greyish-black in colour, deeply fissured and somewhat scaly. Younger branches are glabrous, ribbed and angular to flattened near the greenish coloured tips. The stems of younger plants are occasionally hairy. Like most species of ''Acacia'' it has phyllodes rather than true leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalypt
Eucalypt is a descriptive name for woody plants with capsule fruiting bodies belonging to seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australasia: ''Eucalyptus'', '' Corymbia'', '' Angophora'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum''. Taxonomy For an example of changing historical perspectives, in 1991, largely genetic evidence indicated that some prominent ''Eucalyptus'' species were actually more closely related to ''Angophora'' than to other eucalypts; they were accordingly split off into the new genus ''Corymbia''. Although separate, all of these genera and their species are allied and it remains the standard to refer to the members of all seven genera ''Angophora'', ''Corymbia'', ''Eucalyptus'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' as "eucalypts" or as the eucalypt group. The extant genera ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' comprise six k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. Ferns first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Sassafras
''Atherosperma moschatum'', the southern sassafras or blackheart sassafras, is an evergreen tree native to the cool temperate rainforests of Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria, and New South Wales in Australia. It is common in the rainforests of Tasmania and Victoria, but more scattered and rare in the higher altitudes of eastern New South Wales. The northernmost area is at Mount Grundy, west of Port Macquarie. Taxonomy The southern sassafras was first described by French naturalist Jacques Labillardière in 1806, and was the only member of the genus ''Atherosperma''. A subspecies, Atherosperma moschatum subsp. integrifolium, ''A. m.'' subsp.'' integrifolium'', has been considered a separate species. Its generic name is derived from the Ancient Greek ''ather'' "awn", and ''sperma'' "seed", from the hairs on the fruit, and the specific epithet ''moschatum'' is the Latin adjective meaning "musk-scented", from the smell of the bark. It is a member of the small family Atherosper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrtle Beech
''Nothofagus cunninghamii,'' commonly known as myrtle beech or Tasmanian myrtle, is the dominant species of cool temperate rainforests in Tasmania and Southern Victoria. It has low fire resistance and grows best in partial shade conditions. It has rough bark covered in mosses and epiphytic growth. Its leaves are triangular-shaped, small, and dark green with differentiated margins. It has white unisexual flowers. Description & Habit ''N. cunninghamii'' range from trees of up to 50 meters in protected rainforest valleys to low-growing alpine shrubs less than 1 m tall in exposed conditions. Maximum height is about 55 m. The leaves are simple and alternate, growing 0.5–1.5 cm long, and in Victoria up to 2 cm (0.8 in) long. The leaves are dark green, with new growth brilliant red, pink or orange in spring. They are triangular with irregular minute teeth with craspedodromous veins with all secondary veins terminate at leaf margins and spread from a central primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforests
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic species being indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the " world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforest are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, high humidity, the presence of moisture-dependent vegetation, a moist layer of leaf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate Rainforest
Temperate rainforests are coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rain. Temperate rain forests occur in oceanic moist regions around the world: the Pacific temperate rain forests of North American Pacific Northwest as well as the Appalachian temperate rainforest of the Eastern U.S. Sun Belt; the Valdivian temperate rain forests of southwestern South America; the rain forests of New Zealand and southeastern Australia; northwest Europe (small pockets in Great Britain and larger areas in Ireland, southern Norway and northern Iberia); southern Japan; the Black Sea–Caspian Sea region from the southeasternmost coastal zone of the Bulgarian coast, through Turkey, to Georgia, and northern Iran. The moist conditions of temperate rain forests generally support an understory of mosses, ferns and some shrubs and berries. Temperate rain forests can be temperate coniferous forests or temperate broadleaf and mixed forests. Definition For temperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)