|
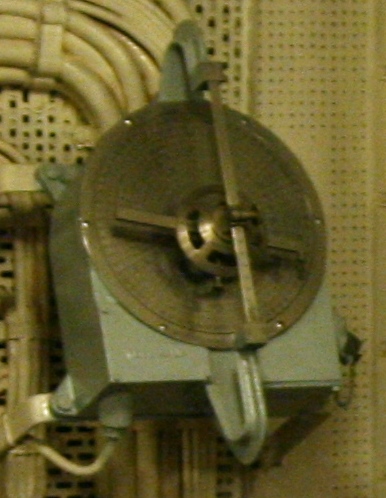
Vickers Range Clock
The Vickers Range Clock was a clockwork device used by the Royal Navy for continuously calculating the range to an enemy ship. Overview In 1903, Percy Scott described a device he'd invented which was similar to the Vickers clock. In April 1904, Vickers worked with Scott and patented their device, samples of which were available for trials in 1905. In 1906, the Royal Navy ordered 246 units for use on their ships. More than one might be installed, to allow for tracking multiple targets. The device consisted of a circular dial with a single central rotating pointer, like a clock. The dial was engraved with the ranges in yards. The clockwork motor drove the pointer at a constant rate determined by a control on the right hand side of the device. This had a handle and its own dial, on which the rate of change of range (or "range rate") could be selected. This was calculated by other means, often by use of a Dumaresq or a time-and-range plot. A second rotating handle was fitted to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Scott
Admiral Sir Percy Moreton Scott, 1st Baronet, (10 July 1853 – 18 October 1924) was a British Royal Navy officer and a pioneer in modern naval gunnery. During his career he proved to be an engineer and problem solver of some considerable foresight, ingenuity and tenacity. He did not, however, endear himself to the Navy establishment for his regular outspoken criticism of the Navy's conservatism and resistance to change and this undoubtedly slowed the acceptance of his most important ideas, notably the introduction of directed firing. In spite of this, his vision proved correct most of the time and he rose to the rank of admiral and amongst other honours was made baronet, a hereditary title. Early years Scott was educated at Eastman's Royal Naval Academy, Southsea, and entered the navy as a cadet in 1866, at the age of thirteen, and in 1868 received a post on HMS ''Forte'', a 50-gun frigate. He served in the Third Anglo-Ashanti War and was based at Cape Coast Castle. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumaresq
The Dumaresq is a mechanical calculating device invented around 1902 by Lieutenant John Dumaresq of the Royal Navy. It is an analogue computer that relates vital variables of the fire control problem to the movement of one's own ship and that of a target ship. It was often used with other devices, such as a Vickers range clock, to generate range and deflection data so the gun sights of the ship could be continuously set. A number of versions of the Dumaresq were produced of increasing complexity as development proceeded. Geometric principle The dumaresq relies on sliding and rotating bars and dials to represent the motion of the two ships. Normally the motion of the ship carrying the dumaresq is represented by a metal bar running above the instrument. Below the bar is a round metal plate inscribed with a coordinate plot, and an angle scale around its outer rim. The fixed bar is mounted on a bearing that allows it to be turned to represent the direction of motion of the ship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederic Charles Dreyer
Admiral Sir Frederic Charles Dreyer, (8 January 1878 – 11 December 1956) was an officer of the Royal Navy. A gunnery expert, he developed a fire control system for British warships, and served as flag captain to Admiral Sir John Jellicoe at the Battle of Jutland. He retired with the rank of admiral in 1943, having served through two world wars and having already retired once. Background and early life Frederic Dreyer was born on 8 January 1878 in the Irish town of Parsonstown (now Birr) in King's County (now County Offaly), the second son of the Danish-born astronomer John Louis Emil Dreyer who was director of the Armagh Observatory. Educated at The Royal School, Armagh, in 1891 Dreyer joined the Royal Navy and entered the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth. Royal Navy career Early years At Dartmouth Dreyer performed well in his examinations and was placed fifth in his term. He then served as a midshipman in HMS ''Anson'' (1893–1896) and HMS ''Barfleur'' (1896–1897) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Computers
This article specifically addresses U.S. armed forces military computers and their use. History Some of the earliest computers were military computers. Military requirements for portability and ruggedness led to some of the earliest transistorized computers, such as the 1958 AN/USQ-17, the 1959 AN/MYK-1 (MOBIDIC), the 1960 M18 FADAC, and the 1962 D-17B; the earliest integrated-circuit based computer, the 1964 D-37C; as well as one of the earliest laptop computers, the 1982 Grid Compass. Military requirements for a computer small enough to fit through a submarine's hatch led to the AN/UYK-1. Construction Typically a military computer is much more robust than an industrial computer enclosure. Most electronics will be protected with a layer of conformal coating. There will be more structure inside to support the components, the plug-in cards will be individually supported and secured to assure they do not pop out of their sockets, the processor and heat sink will be secured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Computers
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples are adding machines and mechanical counters, which use the turning of gears to increment output displays. More complex examples could carry out multiplication and division—Friden used a moving head which paused at each column—and even differential analysis. One model, the Ascota 170 accounting machine sold in the 1960s calculated square roots. Mechanical computers can be either analog, using smooth mechanisms such as curved plates or slide rules for computations; or digital, which use gears. Mechanical computers reached their zenith during World War II, when they formed the basis of complex bombsights including the Norden, as well as the similar devices for ship computations such as the US Torpedo Data Computer or British Admiralty Fire Control Table. Noteworthy are mechanical flight instruments for early spacecraft, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Computers
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude ( digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were typically much faster, but they started to become obsolete as early as the 1950s and 1960s, although they rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Artillery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for naval gunfire support, shore bombardment and anti-aircraft roles. The term generally refers to tube-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar indicates the use of ship-borne catapults against Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire, fire-throwers. From the late Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannon, cannons of various calibres. The Mongol invasion of Java introduced cannons to be used in naval warfare (e.g. Cetbang by the Majapahit). The Battle of Arnemuiden, fought between England and France in 1338 at the start of the Hundred Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |