|
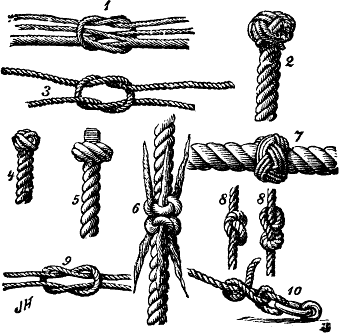
Vibration-proof Hitch
The vibration-proof hitch is a knot used for fastening a line or rope to a solid object. This particular hitch is designed to tighten when subjected to vibration and functions best when the object is fairly large compared to the diameter of the rope. Knot expert Geoffrey Budworth credits the knot to Amory Bloch Lovins. See also *List of knots This list of knots includes many alternative names for common knots and lashings. Knot names have evolved over time, and there are many conflicting or confusing naming issues. The overhand knot, for example, is also known as the thumb knot. The ... References {{Knot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clove Hitch
The clove hitch is a type of knot. Along with the bowline and the sheet bend, it is often considered one of the most important knots. A clove hitch is two successive half-hitches around an object. It is most effectively used as a crossing knot. It can be used as a binding knot, but is not particularly secure in that role. A clove hitch made around the rope's own standing part is known as either two half-hitches or buntline hitch, depending on whether the turns of the clove hitch progress away from or towards the hitched object. Usage This knot is particularly useful where the length of the running end needs to be adjustable, since feeding in rope from either direction will loosen the knot to be tightened at a new position. With certain types of cord, the clove hitch can slip when loaded. In modern climbing rope, the clove hitch will slip to a point, and then stop slipping. When tied around a carabiner, the load should pull on the end closest to its spine. With smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-line Hitch
The ground-line hitch is a type of knot used to attach a rope to an object. Worked-up and dressed properly, it is more secure than the simpler clove hitch and has less tendency to jam, but does not respond well to swinging. It can also be used as a simple binding knot and is classed among several knots known as the miller's knot.Clifford W. Ashley, ''The Ashley Book of Knots'' (New York: Doubleday, 1944), 62. The Ground-line hitch is also the start of a three-lead four-bight Turk's head.Ashley, 291. The knot is named for its use to attach a net to the groundline, a weighted or lead cored rope on the bottom of the net (especially a gillnet). See also *List of binding knots *List of knots This list of knots includes many alternative names for common knots and lashings. Knot names have evolved over time, and there are many conflicting or confusing naming issues. The overhand knot, for example, is also known as the thumb knot. The ... References External links An Introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snuggle Hitch
The snuggle hitch is a modification of the clove hitch, and is stronger and more secure. Owen K. Nuttall of the International Guild of Knot Tyers came up with this unique hitch, and it was first documented in the Guild's ''Knotting Matters'' magazine issue of January, 1987. Generally, hitches are used to attach a line to another rope or spar, pole, etc., and are usually temporary. Thus, they should be relatively easy to untie. Joseph A. MacDonald, ''Handbook of Rigging'' (New York : McGraw Hill, 2009), 201. Tying Start by tying a clove hitch around the spar or pole. Then make an additional turn around with the working end, in the same direction as the turns forming the clove hitch. Now, tuck the working end under the standing part of the original clove hitch. Pull up tight to complete the hitch. Image:bobmcgrsnuggle1.jpg, 1. Almost a clove hitch... Image:bobmcgrsnuggle2.jpg, 2. Clove hitch complete... Image:bobmcgrsnuggle3.jpg, 3. Make another turn around... Image:bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ''bend'' fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a ''loop knot'' is any knot creating a loop; and ''splice'' denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory. History Knots and knotting have been used and studied throughout history. For example, Chinese knotting is a decorative handicraft art that began as a form of Chinese folk art in the Tang and Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD) in China, later popularized in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hitch Knots
A hitch knot is a type of knot used to secure a rope to an object or another rope. It is used in a variety of situations, including climbing, sailing, and securing loads. Hitch knots are classified based on their ability to be tightened or released, their resistance to slipping, and their strength. Some common types of hitch knots include the fisherman's knot, the water knot, and the clove hitch. Hitch knots are important because they allow a rope to be securely fastened to an object, enabling the rope to support weight or transmit force. Physical theory of hitches A simple mathematical theory of hitches has been proposed by Bayman and extended by Maddocks and Keller. It makes predictions that are approximately correct when tested empirically. Alphabetical list of hitch knots See also * List of knots * Single hitch References {{Knots Hitch knots, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amory Bloch Lovins
Amory Bloch Lovins (born November 13, 1947) is an American writer, physicist, and former chairman/chief scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute. He has written on energy policy and related areas for four decades, and served on the US National Petroleum Council, an oil industry lobbying group, from 2011 to 2018. Lovins has promoted energy efficiency, the use of renewable energy sources, and the generation of energy at or near the site where the energy is actually used. Lovins has also advocated a "negawatt revolution" arguing that utility customers don't want kilowatt-hours of electricity; they want energy services. In the 1990s, his work with Rocky Mountain Institute included the design of an ultra-efficient automobile, the Hypercar. He has provided expert testimony and published 31 books, including ''Reinventing Fire'', ''Winning the Oil Endgame'', '' Small is Profitable'', ''Brittle Power'', and ''Natural Capitalism''. Early life and education Lovins was born in Washingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |