|
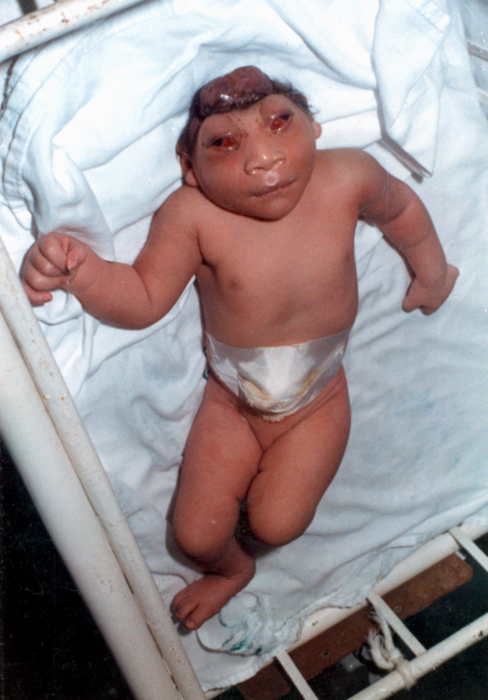
Vestigial Twin
A vestigial twin is a form of parasitic twinning, where the parasitic "twin" is so malformed and incomplete that it typically consists entirely of extra limbs or organs. It also can be a complete living being trapped inside the host person, however the parasitic twin is anencephalic and lacks consciousness. This phenomenon occurs when a fertilized ovum or partially formed embryo splits incompletely. The result can be anything from two whole people joined by a bit of skin (conjoined twins), to one person with extra body parts belonging to the vestigial twin. Most vestigial limbs are non-functional, and although they may have bones, muscles and nerve endings, they are not under the control of the host. The possession of six or more digits on the hands and feet (polydactyly) usually has a genetic or chromosomal A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Twin
A parasitic twin, also known as an asymmetrical or unequal conjoined twin, is the result of the processes that also produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two. Parasitic twins occur when a twin embryo begins developing in utero, but the pair does not fully separate, and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of its twin. Unlike conjoined twins, one ceases development during gestation and is vestigial to a mostly fully formed, otherwise healthy individual twin. The undeveloped twin is defined as parasitic, rather than conjoined, because it is incompletely formed or wholly dependent on the body functions of the complete fetus. The independent twin is called the autosite. Variants * Conjoined parasitic twins joined at the head are described as craniopagus or cephalopagus, and occipitalis if joined in the occipital region or parietalis if joined in the parietal region. * ''Craniopagus parasiticus'' is a general term f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anencephalic
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception. Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon, the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking. With very few exceptions, infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Signs and symptoms The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovum
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capable of movement (non-motile). If the male gamete (sperm) is capable of movement, the type of sexual reproduction is also classified as oogamous. A nonmotile female gamete formed in the oogonium of some algae, fungi, oomycetes, or bryophytes is an oosphere. When fertilized the oosphere becomes the oospore. When egg and sperm fuse during fertilisation, a diploid cell (the zygote) is formed, which rapidly grows into a new organism. History While the non-mammalian animal egg was obvious, the doctrine ''ex ovo omne vivum'' ("every living nimal comes froman egg"), associated with William Harvey (1578–1657), was a rejection of spontaneous generation and preformationism as well as a bold assumption that mammals also reproduced via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes). Signs and symptoms In humans/animals this condition can present itself on one or both hands or feet. The extra digit is usually a small piece of soft tissue that can be removed. Occasionally it contains bone without joints; rarely it may be a complete functioning digit. The extra digit is most common on the ulnar (little finger) side of the hand, less common on the radial (thumb) side, and very rarely within the middle three digits. These are respectively known as postaxial (little finger), preaxial (thumb), and central (ring, middle, index fingers) polydactyly. The extra digit is most commonly an abnormal fork in an existing digit, or it may rarely originate at the wrist as a normal digit does. The incidence of congenital deformities in newborns is approximately 2%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated (S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called sis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Disorders
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Twin
A parasitic twin, also known as an asymmetrical or unequal conjoined twin, is the result of the processes that also produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two. Parasitic twins occur when a twin embryo begins developing in utero, but the pair does not fully separate, and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of its twin. Unlike conjoined twins, one ceases development during gestation and is vestigial to a mostly fully formed, otherwise healthy individual twin. The undeveloped twin is defined as parasitic, rather than conjoined, because it is incompletely formed or wholly dependent on the body functions of the complete fetus. The independent twin is called the autosite. Variants * Conjoined parasitic twins joined at the head are described as craniopagus or cephalopagus, and occipitalis if joined in the occipital region or parietalis if joined in the parietal region. * ''Craniopagus parasiticus'' is a general term f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |