|
Vesta Family
The Vesta family (adj. ''Vestian''; ) is a family of asteroids. The cratering family is located in the inner asteroid belt in the vicinity of its namesake and principal body, 4 Vesta. It is one of the largest asteroid families with more than 15,000 known members and consists of mostly bright V-type asteroids, so-called "vestoids". Characteristics The Vestian asteroids consist of 4 Vesta, the second-most-massive of all asteroids (mean diameter of 530 km), and many small asteroids below 10 km diameter. The brightest of these, 1929 Kollaa and 2045 Peking, have an absolute magnitude of 12.2, which would give them a radius of about 7.5 km assuming the same high albedo as 4 Vesta. The family originated from an impact on asteroid 4 Vesta, with the giant south-polar crater the likely impact site. The family are thought to be the source of the HED meteorites. The Vesta family also includes a few J-type asteroids (related to the V-type), which are thought to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Identification Number
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity (orbit), eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be Collisional family, fragments of past asteroid collisions. An asteroid family is a more specific term than list of minor-planet groups, asteroid group whose members, while sharing some broad orbital characteristics, may be otherwise unrelated to each other. General properties Large prominent families contain several hundred recognized asteroids (and many more smaller objects which may be either not-yet-analyzed, or not-yet-discovered). Small, compact families may have only about ten identified members. About 33% to 35% of asteroids in the main belt are family members. There are about 20 to 30 reliably recognized families, with several tens of less certain groupings. Most asteroid families are found in the main belt, main asteroid belt, although several famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical Clustering Method (asteroids)
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions. An asteroid family is a more specific term than asteroid group whose members, while sharing some broad orbital characteristics, may be otherwise unrelated to each other. General properties Large prominent families contain several hundred recognized asteroids (and many more smaller objects which may be either not-yet-analyzed, or not-yet-discovered). Small, compact families may have only about ten identified members. About 33% to 35% of asteroids in the main belt are family members. There are about 20 to 30 reliably recognized families, with several tens of less certain groupings. Most asteroid families are found in the main asteroid belt, although several family-like groups such as the Pallas family, Hungaria family, and the Phocaea family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1697 Koskenniemi
Events January–March * January 8 – Thomas Aikenhead is hanged outside Edinburgh, becoming the last person in Great Britain to be executed for blasphemy. * January 11 – French writer Charles Perrault releases the book ''Histoires ou contes du temps passé'' (literally "Tales of Past Times", known in England as "Mother Goose tales") in Paris, a collection of popular fairy tales, including ''Cinderella'', ''Puss in Boots'', ''Red Riding Hood'', ''The Sleeping Beauty'' and ''Bluebeard''. * February 8 – The English infantry regiment of Arthur Chichester, 3rd Earl of Donegall is disbanded four years after it was first raised. * February 22 – Gerrit de Heere becomes the new Governor of Dutch Ceylon, succeeding Thomas van Rhee and administering the colony for almost six years until his death. * February 26 – Conquistador Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi and 114 soldiers arrive at Lake Petén Itzá in what is now Guatemala and begin the Spanish conquest of Guatemala with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
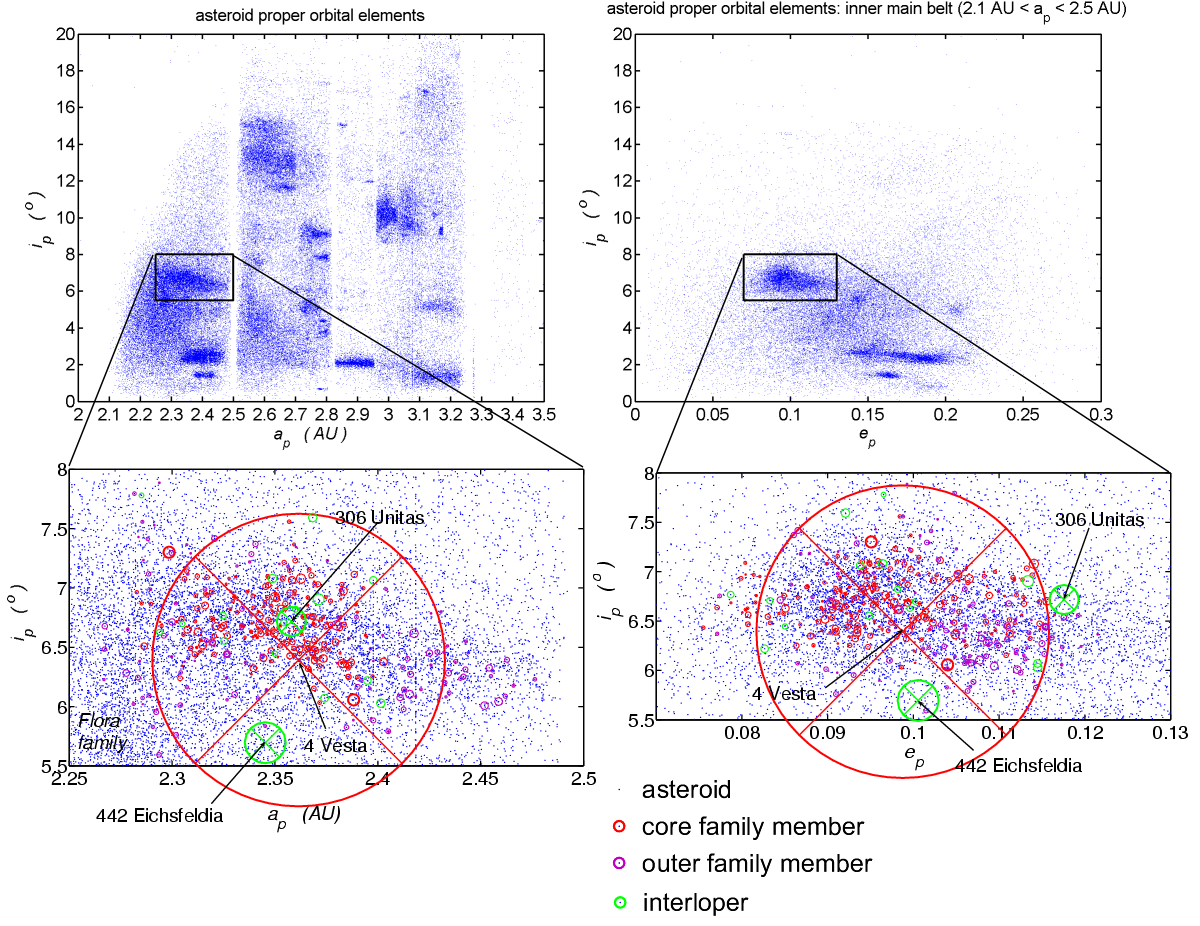
442 Eichsfeldia
Eichsfeldia (minor planet designation: 442 Eichsfeldia) is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomers Max Wolf and A. Schwassmann on 15 February 1899 in Heidelberg. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. Although Eichsfeldia has an orbit similar to the Vesta family asteroids, it was found to be an unrelated interloper on the basis of its non-matching spectral type In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati .... References External links Lightcurve plot of (442) Eichsfeldia Antelope Hills Observatory * * 000442 Discoveries by Max Wolf Discoveries by Friedrich Karl Arnold Schwassmann Named minor planets 000442 000442 18990215 {{C-beltasteroid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
306 Unitas
Unitas (minor planet designation: 306 Unitas) is a typical main belt asteroid that was discovered by Elia Millosevich on 1 March 1891 in Rome. The asteroid was named by the director of the Modena Observatory in honor of the Italian astronomer Angelo Secchi. It is classified as an S-type asteroid. In the late 1990s, a network of astronomers worldwide gathered light curve data that was ultimately used to derive the spin states and shape models of 10 new asteroids, including (306) Unitas. The computed shape model for this asteroid is regular, while the light curve displays two maxima per rotation. Lightcurve data has also been recorded by observers at the Antelope Hill Observatory, which has been designated as an official observatory by the Minor Planet Center. Measurements of the thermal inertia of 306 Unitas give an estimate range from 100 to 260 m−2 K−1 s−1/2, compared to 50 for lunar regolith and 400 for coarse sand in an atmosphere. Although 306 Unitas has an orbit simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include asteroids ( |
Eccentricity (orbit)
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit and its elements change over time due to gravitational perturbations by other objects and the effects of general relativity. A Kepler orbit is an idealized, mathematical approximation of the orbit at a particular time. Keplerian elements The traditional orbital elements are the six Keplerian elements, after Johannes Kepler and his laws of planetary motion. When viewed from an inertial frame, two orbiting bodies trace out distinct trajectories. Each of these trajectories has its focus at the common center of mass. When viewed from a non-inertial frame centered on one of the bodies, only the traj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osculating Orbit
In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space at a given moment in time is the gravitational Kepler orbit (i.e. an elliptic or other conic one) that it would have around its central body if perturbations were absent. That is, it is the orbit that coincides with the current orbital state vectors (position and velocity). Etymology The word '' osculate'' is Latin for "kiss". In mathematics, two curves osculate when they just touch, without (necessarily) crossing, at a point, where both have the same position and slope, i.e. the two curves "kiss". Kepler elements An osculating orbit and the object's position upon it can be fully described by the six standard Kepler orbital elements (osculating elements), which are easy to calculate as long as one knows the object's position and velocity relative to the central body. The osculating elements would remain constant in the absence of perturbations. Real astronomical orbits experience pert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits the Sun, from a maximum (aphelion) to a minimum (perihelion) and back again once each year. The astronomical unit was originally conceived as the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion; however, since 2012 it has been defined as exactly (see below for several conversions). The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degree (angle), degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |