|
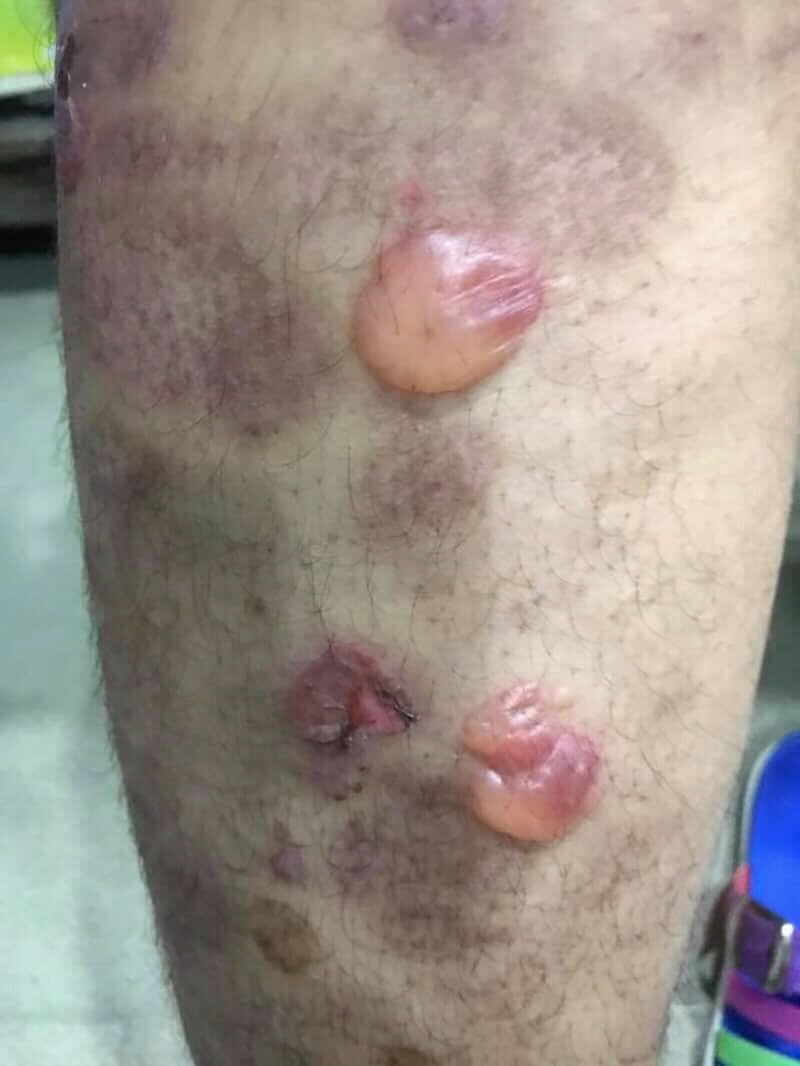
Vesiculobullous Disease
A vesiculobullous disease is a type of mucocutaneous disease characterized by Vesicle (dermatology)#Primary lesions, vesicles and Bulla (dermatology), bullae (i.e. blisters). Both vesicles and bullae are fluid-filled lesions, and they are distinguished by size (vesicles being less than 5–10 mm and bulla being larger than 5–10 mm, depending upon which definition is used). In the case of vesiculobullous diseases which are also immune disorders, the term ''immunobullous'' is sometimes used. Examples of vesiculobullous diseases include: * ''Infectious disease, Infectious: (virus, viral)'' ** Herpes simplex ** Varicella-Zoster infection ** Hand, foot and mouth disease ** Herpangina ** Measles (Rubeola) * ''Immunobullous:'' ** Pemphigus vulgaris ** Pemphigoid ** Dermatitis herpetiformis** Linear IgA disease, Linear immunoglobulin-A disease (linear IgA disease) * ''Genetic disease, Genetic:'' ** Epidermolysis bullosa Some features are as follows: References External link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucocutaneous Disease
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Pemphigus vulgaris is a rare chronic blistering skin disease and the most common form of pemphigus. Pemphigus was derived from the Greek word ''pemphix'', meaning blister. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction in which antibodies are formed against desmosomes, components of the skin that function to keep certain layers of skin bound to each other. As desmosomes are attacked, the layers of skin separate and the clinical picture resembles a blister. These blisters are due to acantholysis, or breaking apart of intercellular connections through an autoantibody-mediated response. Over time the condition inevitably progresses without treatment: lesions increase in size and distribution throughout the body, behaving physiologically like a severe burn. Before the advent of modern treatments, mortality for the disease was close to 90%. Today, the mortality rate with treatment is between 5-15% due to the introduction of corticosteroids as primary treatment. Nevertheless, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not known. DH is neither related to nor caused by herpes virus; the name means that it is a skin inflammation having an appearance (Latin: '' -formis'') similar to herpes. The age of onset is usually about 15–40, but DH also may affect children and the elderly. Men are slightly more affected than women. Estimates of DH prevalence vary from 1 in 400 to 1 in 10,000. It is most common in patients of northern European and northern Indian ancestry, and is associated with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) haplotype HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 along with coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity. Dermatitis herpetiformis was first described by Louis Adolphus Duhring in 1884. A connection between DH and coeliac disease was recognized in 1967. Signs and symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid (type of pemphigoid) is an autoimmune pruritic skin disease which typically occurs in people aged over 60, that may involve the formation of blisters ( bullae) in the space between the epidermal and dermal skin layers. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction, which involves formation of anti-hemidesmosome antibodies, causing a loss of keratinocytes to basement membrane adhesion. Signs and symptoms Clinically, the earliest lesions may appear as a hives-like red raised rash, but could also appear dermatitic, targetoid, lichenoid, nodular, or even without a rash ( essential pruritus). Tense bullae eventually erupt, most commonly at the inner thighs and upper arms, but the trunk and extremities are frequently both involved. Any part of the skin surface can be involved. Oral lesions are present in a minority of cases. The disease may be acute, but can last from months to years with periods of exacerbation and remission. Several other skin diseases m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermolysis Bullosa
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare medical conditions that result in easy blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. Blisters occur with minor trauma or friction and are painful. Its severity can range from mild to fatal. Inherited EB is a rare disease with a prevalence in the United States of 8.2 per million live births. Those with mild cases may not develop symptoms until they start to crawl or walk. Complications may include esophageal narrowing, squamous cell skin cancer, and the need for amputations. EB is due to a mutation in at least one of 16 different genes. Some types are autosomal dominant while others are autosomal recessive. The underlying mechanism is a defect in attachment between or within the layers of the skin. Loss or diminished function of C7 leads to weakness in the structural architecture of the dermal–epidermal junction (DEJ) and mucosal membranes. There are four main types: epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), dystrophic epidermolysis bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acantholysis
Acantholysis is the loss of intercellular connections, such as desmosomes, resulting in loss of cohesion between keratinocytes,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease'' (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. . seen in diseases such as pemphigus vulgaris. It is absent in bullous pemphigoid, making it useful for differential diagnosis. This histological feature is also seen in herpes simplex infections (HSV 1 and 2) and varicella zoster infections (chicken pox and shingles). See also * Skin lesion * Skin disease * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against t ... References External links Dermatologic terminology {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermolysis Bullosa
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare medical conditions that result in easy blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. Blisters occur with minor trauma or friction and are painful. Its severity can range from mild to fatal. Inherited EB is a rare disease with a prevalence in the United States of 8.2 per million live births. Those with mild cases may not develop symptoms until they start to crawl or walk. Complications may include esophageal narrowing, squamous cell skin cancer, and the need for amputations. EB is due to a mutation in at least one of 16 different genes. Some types are autosomal dominant while others are autosomal recessive. The underlying mechanism is a defect in attachment between or within the layers of the skin. Loss or diminished function of C7 leads to weakness in the structural architecture of the dermal–epidermal junction (DEJ) and mucosal membranes. There are four main types: epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), dystrophic epidermolysis bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be Heredity, inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y linkage, Y chromosome or Mitochondrial disease#Causes, mitochondrial DNA (due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear IgA Disease
Linear IgA bullous dermatosis is a rare immune-mediated blistering skin disease frequently associated with medication exposure, especially vancomycin, with men and women being equally affected.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . It was first described by Tadeusz Chorzelski in 1979 and may be divided into two types:Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . * ''Adult linear IgA disease'' is an acquired, autoimmune blistering disease that may present with a clinical pattern of vesicles indistinguishable from dermatitis herpetiformis, or with vesicles and bullae in a bullous pemphigoid-like appearance. This disease can often be difficult to treat even with usually effective medications such as rituximab. * ''Childhood linear IgA disease'' (also known as "Chronic bullous disease of childhood") is an acquired, self-limited bullous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not known. DH is neither related to nor caused by herpes virus; the name means that it is a skin inflammation having an appearance (Latin: '' -formis'') similar to herpes. The age of onset is usually about 15–40, but DH also may affect children and the elderly. Men are slightly more affected than women. Estimates of DH prevalence vary from 1 in 400 to 1 in 10,000. It is most common in patients of northern European and northern Indian ancestry, and is associated with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) haplotype HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 along with coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity. Dermatitis herpetiformis was first described by Louis Adolphus Duhring in 1884. A connection between DH and coeliac disease was recognized in 1967. Signs and symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pemphigoid
Pemphigoid is a group of rare autoimmune blistering diseases of the skin, and mucous membranes. As its name indicates, pemphigoid is similar in general appearance to pemphigus, but, unlike pemphigus, pemphigoid does not feature acantholysis, a loss of connections between skin cells. Pemphigoid is more common than pemphigus, and is slightly more common in women than in men. It is also more common in people aged over 70 years than it is in younger people. Classification IgG The forms of pemphigoid are considered to be connective tissue autoimmune skin diseases. There are several types: * Gestational pemphigoid (PG) (formerly called ''Herpes gestationis'') * Bullous pemphigoid (BP) Rarely affects the mouth * Mucous membrane pemphigoid (MMP) or (cicatricial pemphigoid), (No skin involvement) Bullous and mucous membrane pemphigoid usually affect persons who are over age 60. Gestational pemphigoid occurs during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester, or immediate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''red measles'', and ''English measles''. Both rubella, also known as ''German measles'', and roseola are different diseases caused by unrelated viruses. Mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |