|
Vesical Veins
The vesical veins are veins in the pelvis that drain blood from the urinary bladder. The vesical veins receive blood from the vesical venous plexus The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is f ... and are tributaries of the internal iliac veins. References External links Venous drainage of the urinary bladder Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
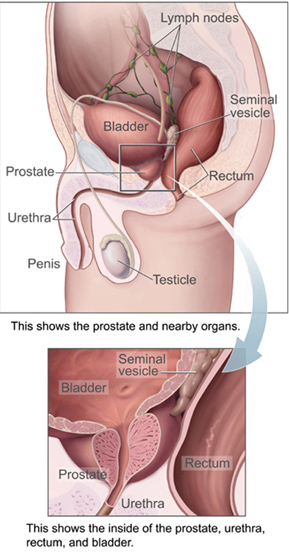
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesical Venous Plexus
The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate and communicates with the pudendal and prostatic plexuses. It is drained, by means of several vesical veins The vesical veins are veins in the pelvis that drain blood from the urinary bladder. The vesical veins receive blood from the vesical venous plexus The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate The ..., into the internal iliac veins. References External links Anatomy at umich.edu Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vesical Artery
The superior vesical artery supplies numerous branches to the upper part of the bladder. This artery often also gives branches to the vas deferens and can provide minor collateral circulation for the testicles. Anatomy The superior vesical artery is a branch of the umbilical artery. The vesiculo-prostatic artery usually arises from the superior vesical artery in men. Distribution Other branches supply the ureter. Variation The middle vesical artery, usually a branch of the superior vesical artery, is distributed to the fundus of the bladder and the seminal vesicles. This artery is not usually described in modern anatomy textbooks. Instead, it is described that the superior vesical artery may exist as multiple vessels that arise from a common origin. Development The first part of the superior vesical artery represents the terminal section of the previous portion of the umbilical artery (fetal hypogastric artery The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vesical Artery
The inferior vesical artery (or inferior vesicle artery) is an artery of the pelvis which arises from the internal iliac artery and supplies parts of the urinary bladder as well as other structures of the urinary system and structures of the male reproductive system. Some sources consider this vessel to be present only in males, and cite the vaginal artery as the homologous structure in females; others consider it to be present in both sexes, with the vessel taking the form of a small branch of a vaginal artery in females. Structure Origin The inferior vesical artery is a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It frequently has a common origin with the middle rectal artery. Course The inferior vesical artery passes medially across the pelvic floor. Distribution The inferior vesical artery is distributed to the trigone and inferior portion of the urinary bladder, the ureter, prostate, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles.vas deferens The branches to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesical Venous Plexus
The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate and communicates with the pudendal and prostatic plexuses. It is drained, by means of several vesical veins The vesical veins are veins in the pelvis that drain blood from the urinary bladder. The vesical veins receive blood from the vesical venous plexus The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate The ..., into the internal iliac veins. References External links Anatomy at umich.edu Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |