|
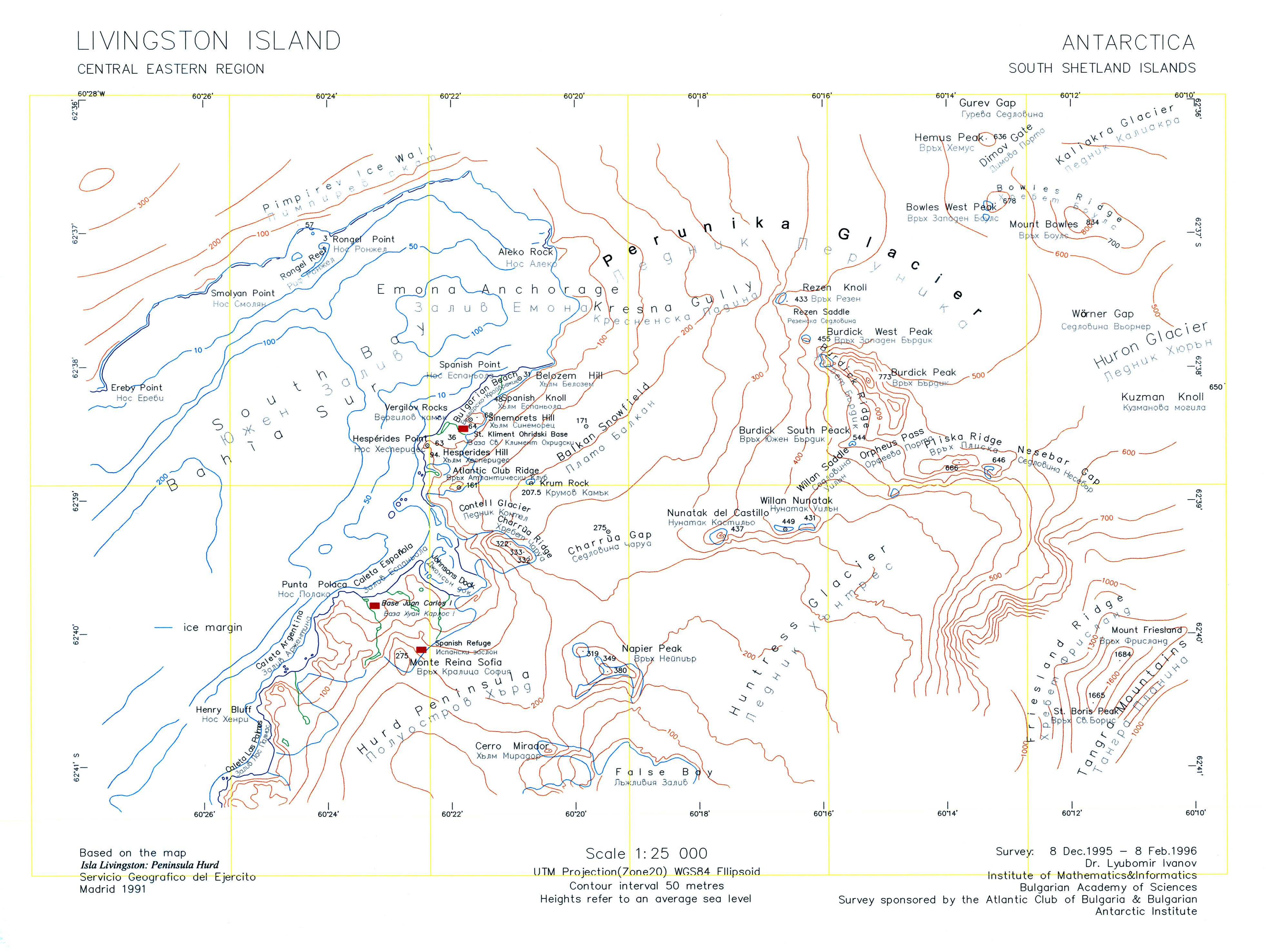
Vergilov Ridge
Vergilov Ridge ( bg, Вергилов хребет, 'Vergilov Hrebet' \ver-'gi-lov 'hre-bet\) is a submarine ridge in South Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It extends 3.5 km in a southeast-northwest direction between the Vergilov Rocks and the opposite Pimpirev Beach at a depth of over 50 m, with depths exceeding 100 m on both sides of the ridge. It was formed as a frontal moraine of Perunika Glacier between the 13th and 17th centuries. The feature takes its name from the Vergilov Rocks. Location Vergilov Ridge is centred at . Spanish mapping in 1991. See also * Vergilov Rocks Maps Isla Livingston: Península Hurd.Mapa topográfico de escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991. (Map reproduced on p. 16 of the linked work) * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. * Antarctica, South Shetland Islands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Bay, Livingston Island
South Bay () is a wide bay indenting for the south coast of Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The bay is lying northwest of False Bay and east of Walker Bay, and is entered between Hannah Point and Miers Bluff. The glaciers Kamchiya, Pimpirev, Perunika, Contell, Johnsons and Hurd Ice Cap feed the bay. South Bay was known to both American and British sealers as early as 1820, and the name has been well established in international usage for over 100 years. Maps Chart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. South Shetland Islands.Scale 1:200000 topographic map No. 5657. DOS 610 – W 62 60. Tolworth, UK, 1968. * Islas Livingston y Decepción. Mapa topográfico a escala 1:100000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991. * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes. The islands have been claimed by the United Kingdom since 1908 and as part of the British Antarctic Territory since 1962. They are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province) and Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries maintain research stations on the islands. Most of them are situated on King George Island, benefitting from the airfield of the Chilean base Eduardo Frei. There are sixteen research stations in different parts of the islands, with Chilean stations being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vergilov Rocks
Vergilov Rocks (Vergilov Kamak ver-'gi-lov 'ka-m&k) are a group of rocks off Bulgarian Beach on Hurd Peninsula in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, consisting of one main rock and two adjacent smaller ones submerging at high water. The rocks are named after Zlatil Vergilov, a member of the 1988 Bulgarian party on Livingston Island, base commander at St. Kliment Ohridski in the 1996–99 seasons. Location The rocks are located at which is northeast of Hespérides Point, west by south of Greenpeace Rock, and from the coast in front of the Bulgarian base (British mapping in 1968, Bulgarian mapping from a 1995-1996 topographic survey). Maps Isla Livingston: Península Hurd.Mapa topográfico de escala 1:25000. Madrid: Servicio Geográfico del Ejército, 1991. (Map reproduced on p. 16 of the linked work) * L.L. Ivanov. St. Kliment Ohridski Base, Livingston Island. Scale 1:1000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pimpirev Beach
Pimpirev Beach ( bg, Пимпирев бряг, Pimpirev bryag, ) is the portion of the northwest coast of South Bay, Livingston Island, Antarctica bounded to the southwest by Ereby Point and to the northeast by the north corner of the bay marked by an ice sea cave located 5.8 km east-northeast of Ereby Point and 1.45 km northwest of Aleko Point. The shoreline, extending 6.5 km in a west-southwest to east-northeast direction, is formed by a narrow beach under the Pimpirev Glacier’s terminus; a number of minor disruptions occur with segments of the ice cap penetrating the sea. Featuring Smolyan Point, a cape located 1.9 km northeast of Ereby Point and ending up with a 25 m wide and 4 m high rock, with conspicuous radial crevasses spreading inland. The central portion of the coast is indented for 250 m by a nameless 710 m wide cove behind Rongel Reef. The beach takes its name from the adjacent Pimpirev Ice Wall, respectively Pimpirev Glacier. Locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders (in which case it is often referred to as boulder clay) down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines were formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines (till-covered areas forming sheets on flat or irregular topography) and medial moraines (moraines formed where two glaciers meet). Etymology The word ''moraine'' is borrowed from French , which in turn is derived from the Savoyard Italian ("mound of earth"). ''Morena'' in this case was derived from Proven� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perunika Glacier
Perunika Glacier ( bg, ледник Перуника, lednik Perunika, ) is an 8 km long and 3 km wide (average) roughly crescent-shaped glacier in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated east of Pimpirev Glacier, south of Saedinenie Snowfield, southwest of Kaliakra Glacier, west of Huron Glacier, and north of Balkan Snowfield and the head of Huntress Glacier."Perunika Glacier " SCAR Its head is bounded by to the south-southwest, |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |