|
Verb–object–subject Word Order
In linguistic typology, a verb–object–subject or verb–object–agent language, which is commonly abbreviated VOS or VOA, is one in which most sentences arrange their elements in that order. That would be the equivalent in English to "Drank cocktail Sam." The relatively rare default word order accounts for only 3% of the world's languages. It is the fourth-most common default word order among the world's languages out of the six. It is a more common default permutation than OVS and OSV but is significantly rarer than SOV (as in Hindi and Japanese), SVO (as in English and Mandarin), and VSO (as in Filipino and Irish). Families in which all or many of their languages are VOS include the following: * the Algonquian family (including Ojibwa) * the neighbouring families of the Oregon Coast (including Alsea, Suislaw, Hanis Coos and Miluk Coos) * the Arawakan family (including Baure) * the Austronesian family (including Malagasy, Toba Batak, Belauan, Gilbertese, Fijian and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Typology
Linguistic typology (or language typology) is a field of linguistics that studies and classifies languages according to their structural features to allow their comparison. Its aim is to describe and explain the structural diversity and the common properties of the world's languages. Its subdisciplines include, but are not limited to phonological typology, which deals with sound features; syntactic typology, which deals with word order and form; lexical typology, which deals with language vocabulary; and theoretical typology, which aims to explain the universal tendencies. Linguistic typology is contrasted with genealogical linguistics on the grounds that typology groups languages or their grammatical features based on formal similarities rather than historic descendence. The issue of genealogical relation is however relevant to typology because modern data sets aim to be representative and unbiased. Samples are collected evenly from different language families, emphasizing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquian Languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term ''Algonquin'' has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (), "they are our relatives/allies". A number of Algonquian languages are considered extinct languages by the modern linguistic definition. Speakers of Algonquian languages stretch from the east coast of North America to the Rocky Mountains. The proto-language from which all of the languages of the family descend, Proto-Algonquian, was spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago. There is no scholarly consensus about where this language was spoken. Family division This subfamily of around 30 languages is divided into three groups acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumashan Languages
Chumashan was a family of languages that were spoken on the southern California coast by Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo to Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and canyons east to bordering the San Joaquin Valley, to three adjacent Channel Islands: San Miguel, Santa Rosa, and Santa Cruz. The Chumashan languages may be, along with Yukian and perhaps languages of southern Baja such as Waikuri, one of the oldest language families established in California, before the arrival of speakers of Penutian, Uto-Aztecan, and perhaps even Hokan languages. Chumashan, Yukian, and southern Baja languages are spoken in areas with long-established populations of a distinct physical type. The population in the core Chumashan area has been stable for the past 10,000 years. However, the attested range of Chumashan is recent (within a couple thousand years). There is internal evidence that Obispeño replaced a Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsou Language
Tsou () is a divergent Austronesian language spoken by the Tsou people of Taiwan. Tsou is a threatened language; however, this status is uncertain. Its speakers are located in the west-central mountains southeast of the Chiayi/ Alishan area in Taiwan. Name The name ''Tsou'' literally means "person", from Proto-Austronesian ''*Cau'' through regular sound changes. It is therefore cognate with the name of the Thao. Classification Tsou has traditionally been considered part of a Tsouic branch of Austronesian. However, several recent classifications, such as Chang (2006)Chang, Henry Yungli. 2006. "Rethinking the Tsouic Subgroup Hypothesis: A Morphosyntactic Perspective." In Chang, H., Huang, L. M., Ho, D. (eds.). ''Streams converging into an ocean: Festschrift in honor of Professor Paul Jen-Kuei Li on his 70th birthday.'' Taipei: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica. and Ross (2009)Ross, Malcolm. 2009. "Proto Austronesian verbal morphology: A reappraisal." In Alexander Ade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fijian Language
Fijian (') is an Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian family spoken by some 350,000–450,000 ethnic Fijians as a native language. The 2013 Constitution established Fijian as an official language of Fiji, along with English and Fiji Hindi and there is discussion about establishing it as the "national language". Fijian is a VOS language. Standard Fijian is based on the speech of Bau, which is an East Fijian language. A pidginized form is used by many Indo-Fijians and Chinese on the islands, while Pidgin Hindustani is used by many rural ethnic Fijians and Chinese in areas dominated by Indo-Fijians. History Phonology The consonant phonemes of Fijian are as shown in the following table: The consonant written has been described as a prenasalized trill or trilled affricate . However, it is only rarely pronounced with a trilled release; the primary feature distinguishing it from is that it is postalveolar, , rather than dental/alveolar. The sounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbertese Language
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages. The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the islands, is the local adaptation of the previous European name "Gilberts" to Gilbertese phonology. Early European visitors, including Commodore John Byron, whose ships happened on Nikunau in 1765, had named some of the islands the Kingsmill or Kings Mill Islands or for the Northern group ''les îles Mulgrave'' in French but in 1820 they were renamed, in French, ''les îles Gilbert'' by Admiral Adam Johann von Krusenstern, after Captain Thomas Gilbert, who, along with Captain John Marshall, had passed through some of these islands in 1788. Frequenting of the islands by Europeans, Americans and Chinese dates from whaling and oil trading from the 1820s, when no doubt Europeans learnt to speak it, as Gilbertese learnt to speak English and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palauan Language
Palauan () is a Malayo-Polynesian language native to the Republic of Palau, where it is one of the two official languages An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ..., alongside English language, English. It is widely used in day-to-day life in the country. Palauan is not closely related to other Malayo-Polynesian languages and its exact classification within the branch is unclear. Classification It is a member of the Austronesian languages, Austronesian family of languages, and is one of only two indigenous languages in Micronesia that are not part of the Oceanic languages, Oceanic branch of that family, the other being Chamorro language, Chamorro (see , , , and ). Roger Blench (2015) argues that based on evidence from fish names, Palauan had early contact with Oceanic la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
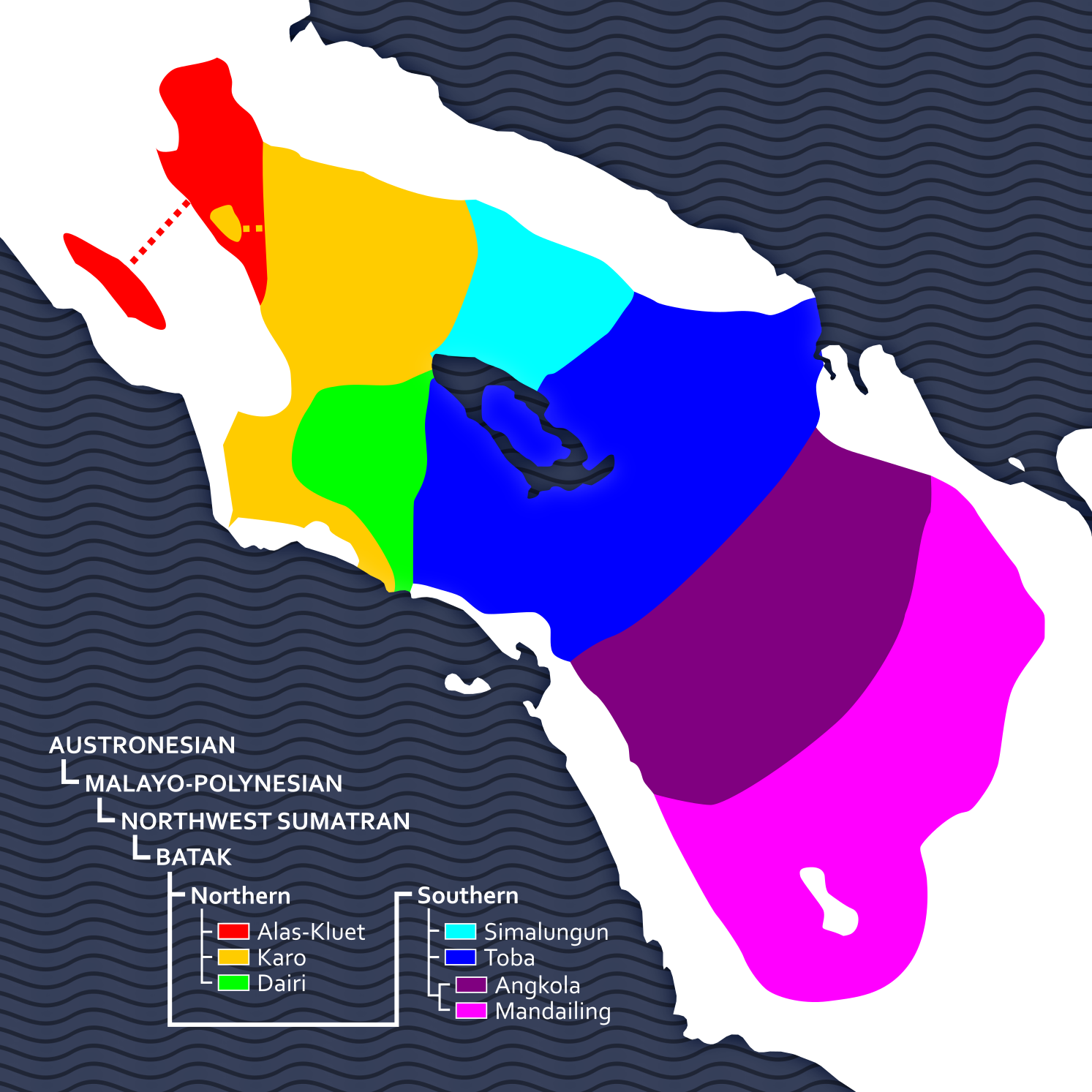
Toba Batak Language
Toba Batak () is an Austronesian language spoken in North Sumatra province in Indonesia. It is part of a group of languages called Batak. There are approximately 1,610,000 Toba Batak speakers, living to the east, west and south of Lake Toba. Historically it was written using Batak script, but the Latin script is now used for most writing. Nomenclature The name of this language arises from a rich and complex history of ethnic identity in colonial and post-colonial Indonesia. It is a generic name for the common language used by the people of the districts of Toba, Uluan, Humbang, Habinsaran, Samosir, and Silindung, centered upon the Island of Sumatra; more particularly, at Lake Toba. Linguistically and culturally these tribes of people are closely related. Other nearby communities such as Silalahi and Tongging may also be classified as speakers of Toba Batak. The term ''Toba Batak'' is, itself, a derivation of the Toba Batak language. As such, it is used both as a noun a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malagasy Language
Malagasy (; ) is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th century AD. The Malagasy language is one of the Barito languages and is most closely related to the Ma'anyan language, still spoken on Borneo to this day. Malagasy also includes numerous Malay loanwords, from the time of the early Austronesian settlement and trading between Madagascar and the Sunda Islands. After c. 1000 AD, Malagasy incorporated numerous Bantu and Arabic loanwords, brought over by traders and new settlers. Malagasy is spoken by around 25 million people in Madagascar and the Comoros. Most people in Madagascar speak it as a first language, as do some people of Malagasy descent elsewhere. Malagasy is divided between two main dialect groups; Eastern and Western. The central plateau of the island, where the capital Antananari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baure Language
Bauré is an endangered Arawakan language spoken by only 40 of the thousand Baure people of the Beni Department of northwest of Magdalena, Bolivia. Some Bible portions have been translated into Bauré. Most speakers have been shifting to Spanish. Orthography Vowels * a - * e - �/e* i - /ɪ* o - /ɔ/u Consonants * ch/č/z - _[d͡ʒ.html" ;"title="͡ʃ[, [d͡ʒ">͡ʃ[, [d͡ʒafter n * h/j - [h* k/c/qu/g - [k], [g] after n * m - [m] * n - [n] * p/b - [p], [b] after m * r/l - [r/l] * s - [s] * sh/š/x - [ʃ] * t/d - [t], [d] after n * v/b - [β/b] * w/hu/u - [w] * y - [j] * '/h - [ʔ] Grammar Baure has an active–stative syntax.Aikhenvald, "Arawak", in Dixon & Aikhenvald, eds., ''The Amazonian Languages'', 1999. See also *Llanos de Moxos (archaeology) The Llanos (Spanish ''Los Llanos'', "The Plains"; ) is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the tropical and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawakan Languages
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawaka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |