|
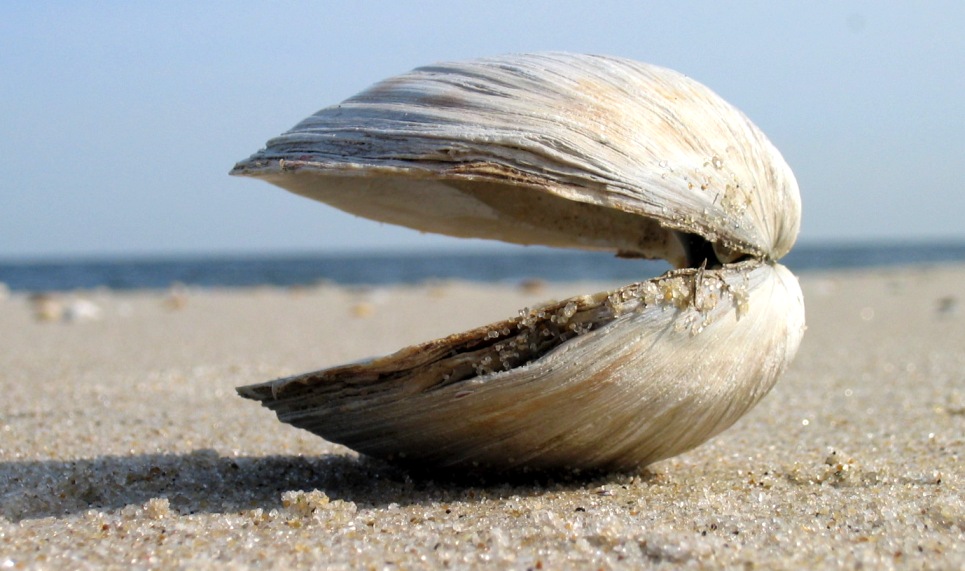
Venerida
Venerida (formerly Veneroida) is an order of mostly saltwater but also some freshwater bivalve molluscs. This order includes many familiar groups such as many clams that are valued for food and a number of freshwater bivalves. Since the 2000s, the taxonomy currently represented in the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) classifies several taxa contained in the former Veneroida into other orders, such as the new Cardiida (for Cardioidea and Tellinoidea) and Carditida (cockles and their allies). Description Venerids are generally thick-valved, equal-valved and isomyarian (that is, their adductor muscles are of equal size). Three main hinge teeth are characteristic of the subclass Heterodonta, to which this order belongs. Many species are active rather than sessile. However, they tend to be filter feeders, feeding through paired siphons, with a characteristic folded gill structure adapted to that way of life. In 2002, Gonzalo Giribet and Ward Wheeler suggested that the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodonta
Heteroconchia is a taxonomic infraclass of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs, belonging to the subclass Autobranchia This infraclass includes the edible clams, the cockles and the Venus clams. Description These bivalves are distinguished by having the two halves of the shell equally sized (i.e, they are ''equivalved'') and having a few cardinal teeth separated from a number of long lateral teeth. Their shells lack a nacreous layer, and the gills are lamellibranch in form. Most species have a siphon. Orders and families The following tree is their info which has been updated with the latest information from the World Register of Marine Species: Infraclass: Heteroconchia *Unclassified family: † Lipanellidae *Subterclass: Archiheterodonta **Order: † Actinodontida ***Superfamily: † Amnigenioidea ****Family: † Amnigeniidae ****Family: † Montanariidae ****Family: † Zadimerodiidae *** Superfamily: † Anodontopsoidea **** Family: † Actinodontidae **** Fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalve
Bivalvia (), in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances. The shell of a bivalve is composed of calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon (mollusks)
A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda (members of these classes include saltwater and freshwater snails, clams, octopus, squid and relatives). Siphons in molluscs are tube-like structures in which water (or, more rarely, air) flows. The water flow is used for one or more purposes such as locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction. The siphon is part of the mantle of the mollusc, and the water flow is directed to (or from) the mantle cavity. A single siphon occurs in some gastropods. In those bivalves which have siphons, the siphons are paired. In cephalopods, there is a single siphon or funnel which is known as a hyponome. In gastropods In some (but not all) sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon, or inhalant siphon, through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill for respiration.Ör ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
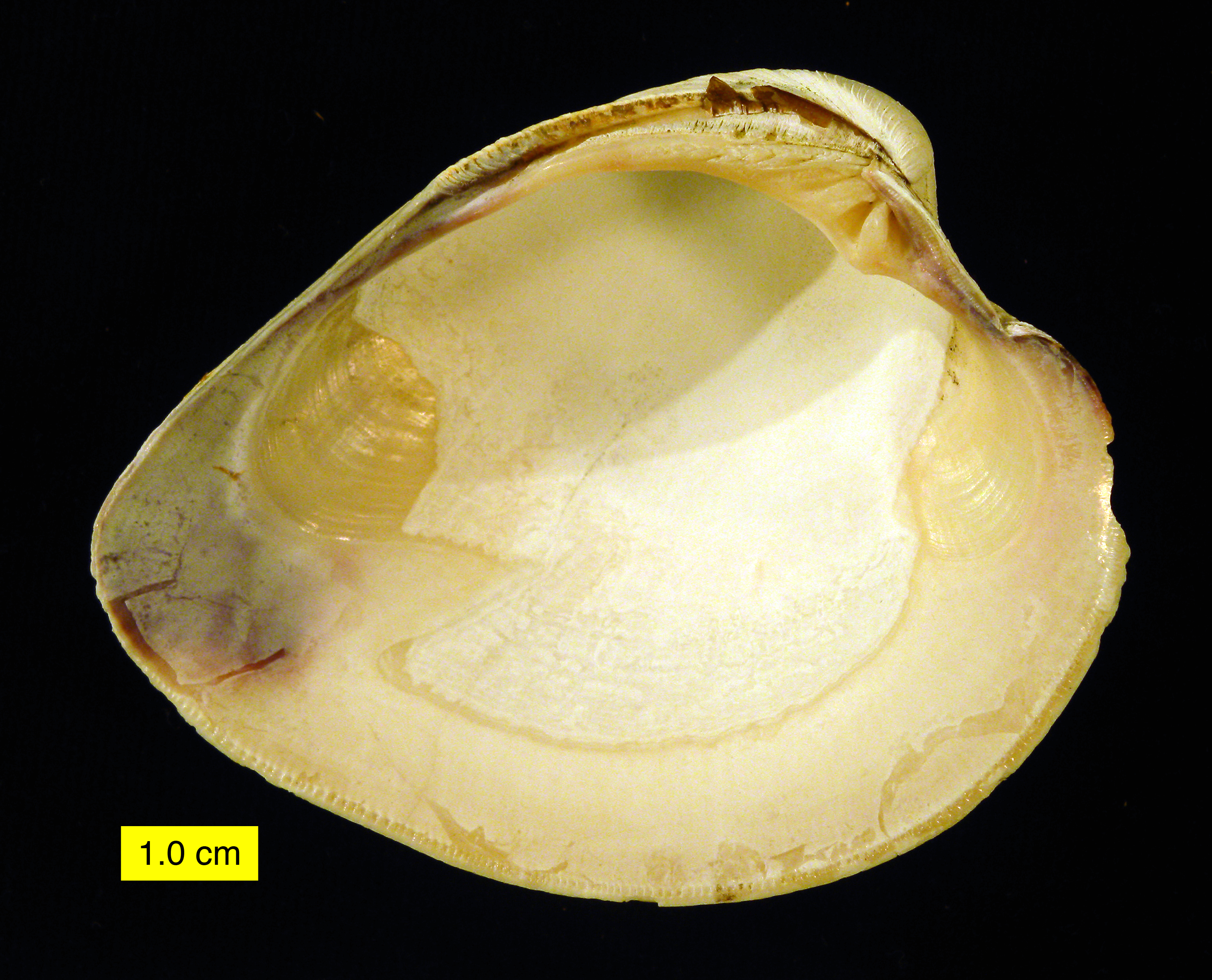
Mercenaria Mercenaria
The hard clam (''Mercenaria mercenaria''), also known as the round clam, hard-shell (or hard-shelled) clam, or the quahog, is an edible marine bivalve mollusk that is native to the eastern shores of North America and Central America from Prince Edward Island to the Yucatán Peninsula. It is one of many unrelated edible bivalves that in the United States are frequently referred to simply as clams, as in the expression "clam digging". Older literature sources may use the systematic name ''Venus mercenaria''; this species is in the family Veneridae, the venus clams. Confusingly, the "ocean quahog" is a different species, ''Arctica islandica'', which, although superficially similar in shape, is in a different family of bivalves: it is rounder than the hard clam, usually has black periostracum, and there is no pallial sinus in the interior of the shell. Alternative names The hard clam has many alternative common names. It is also known as the Northern quahog, round clam, or chowder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezidae
Trapezidae is a family of bivalves belonging to the superfamilt Arcticoidea of the order Venerida. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Trapezidae Lamy, 1920 (1895). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=23130 on 2021-09-19 Genera: * '' Coralliophaga'' Blainville, 1824 * '' Fluviolanatus'' Iredale, 1924 * '' Langvophorus'' Vu Khuc, 1977 * '' Neotrapezium'' Habe, 1951 * ''Pronoe Pronoe (; Ancient Greek: Προνόη ''Pronóē'' means 'forethought') refers to six characters in Greek mythology. * Pronoe, one of the 50 Nereids, marine-nymph daughters of the 'Old Man of the Sea' Nereus and the Oceanid Doris. Her name means "t ...'' Agassiz, 1843 * '' Pronoella'' Fischer, 1887 * '' Pseudotrapezium'' Fischer, 1887 * '' Straelenotrapezium'' Glibert & van de Poel, 1970 * '' Trapezium'' Megerle von Mühlfeld, 1811 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3788321 Venerida Bivalve families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcticidae
The Arcticidae are a family of marine clams in the order Venerida. The only living species in the family is ''Arctica islandica''. There are also many fossil species classified in a number of genera Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat .... Fossilworks. References External links *https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309181676_Behavioral_responses_of_Arctica_islandica_Bivalvia_Arcticidae_to_simulated_leakages_of_carbon_dioxide_from_sub-sea_geological_storage * *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carditida
Carditida is an order of marine bivalve clams. Superfamilies and families According to the World Register of Marine Species: * Family: † Archaeocardiidae *Superfamily: Carditoidea ** Family: Carditidae ** Family: Condylocardiidae *Superfamily: Crassatelloidea ** Family: Crassatellidae ** Family: Astartidae * Family: † Eodonidae Notes: * Previously in 2010, Condylocardiidae was classified in its own superfamily, Condylocardioidea. * Carditida does not yet exist in the ITIS classification, with its families instead being included in Venerida Venerida (formerly Veneroida) is an order of mostly saltwater but also some freshwater bivalve molluscs. This order includes many familiar groups such as many clams that are valued for food and a number of freshwater bivalves. Since the 2000s, .... References External links * * * Bivalve orders {{bivalve-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tellinoidea
Tellinoidea is a taxonomic superfamily of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the order Cardiida. Families These families are assigned to Tellinoidea: *Donacidae Fleming, 1828 *Psammobiidae Fleming, 1828 *Semelidae Stoliczka, 1870 (1825) *Solecurtidae d'Orbigny, 1846 *Tellinidae The Tellinidae are a family of marine bivalve molluscs of the order Cardiida. Commonly known as tellins or tellens, they live fairly deep in soft sediments in shallow seas and respire using long siphons that reach up to the surface of the sedime ... Blainville, 1814 References Venerida Mollusc superfamilies {{Bivalve-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamoidea
Chamidae, common name the jewel boxes or jewel box clams, is a taxonomic family of saltwater clams, a group of marine bivalve mollusks in the order Venerida.Abbott, R.T. & Morris, P.A. ''A Field Guide to Shells: Atlantic and Gulf Coasts and the West Indies.'' New York: Houghton Mifflin, 1995. 53. Genera and species Genera and species in the family Chamidae: *''Arcinella'' Schumacher, 1817 **''Arcinella arcinella'' (Linnaeus, 1767) – spiny jewelbox **''Arcinella cornuta'' Conrad, 1866 – Florida spiny jewelbox *'' Chama'' Linnaeus, 1758 **'' Chama arcana'' Bernard, 1976 – secret jewelbox **''Chama congregata'' Conrad, 1833 – corrugate jewelbox **''Chama echinata'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama florida'' Lamarck, 1819 – pretty jewelbox **''Chama frondosa'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama hicksi'' Valentich-Scott & Coan, 2010 **'' Chama lactuca'' Dall, 1886 – milky jewelbox **'' Chama macerophylla'' Gmelin, 1791 – leafy jewelbox **'' Chama pellucida'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama sar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Bivalves
Freshwater bivalves are one kind of freshwater mollusc, along with freshwater snails. They are bivalves that live in fresh water as opposed to salt water, which is the main habitat type for bivalves. The majority of species of bivalve molluscs live in the sea, but in addition, a number of different families live in fresh water (and in some cases, also in brackish water). These families belong to two different evolutionary lineages (freshwater mussels and freshwater clams), and the two groups are not closely related. Freshwater bivalves have a simple morphology that varies among taxa, and are distributed around most regions of the world. Species in the two groups vary greatly in size. Some pea clams (''Pisidium'' species) have an adult size of only 3 mm. In contrast, one of the largest species of freshwater bivalves is the swan mussel, in the family Unionidae; it can grow to a length of 20 cm, and usually lives in lakes or slow rivers. Freshwater pearl mussels are econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clam
Clam is a common name for several kinds of bivalve molluscs. The word is often applied only to those that are edible and live as infauna, spending most of their lives halfway buried in the sand of the seafloor or riverbeds. Clams have two shells of equal size connected by two adductor muscles and have a powerful burrowing foot. They live in both freshwater and marine environments; in salt water they prefer to burrow down into the mud and the turbidity of the water required varies with species and location; the greatest diversity of these is in North America. Clams in the culinary sense do not live attached to a substrate (whereas oysters and mussels do) and do not live near the bottom (whereas scallops do). In culinary usage, clams are commonly eaten marine bivalves, as in clam digging and the resulting soup, clam chowder. Many edible clams such as palourde clams are ovoid or triangular; however, razor clams have an elongated parallel-sided shell, suggesting an old-fashioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamidae
Chamidae, common name the jewel boxes or jewel box clams, is a taxonomic family of saltwater clams, a group of marine bivalve mollusks in the order Venerida.Abbott, R.T. & Morris, P.A. ''A Field Guide to Shells: Atlantic and Gulf Coasts and the West Indies.'' New York: Houghton Mifflin, 1995. 53. Genera and species Genera and species in the family Chamidae: *''Arcinella'' Schumacher, 1817 **''Arcinella arcinella'' (Linnaeus, 1767) – spiny jewelbox **''Arcinella cornuta'' Conrad, 1866 – Florida spiny jewelbox *'' Chama'' Linnaeus, 1758 **'' Chama arcana'' Bernard, 1976 – secret jewelbox **''Chama congregata'' Conrad, 1833 – corrugate jewelbox **''Chama echinata'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama florida'' Lamarck, 1819 – pretty jewelbox **''Chama frondosa'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama hicksi'' Valentich-Scott & Coan, 2010 **'' Chama lactuca'' Dall, 1886 – milky jewelbox **'' Chama macerophylla'' Gmelin, 1791 – leafy jewelbox **'' Chama pellucida'' Broderip, 1835 **''Chama sar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |