|
Venera-D
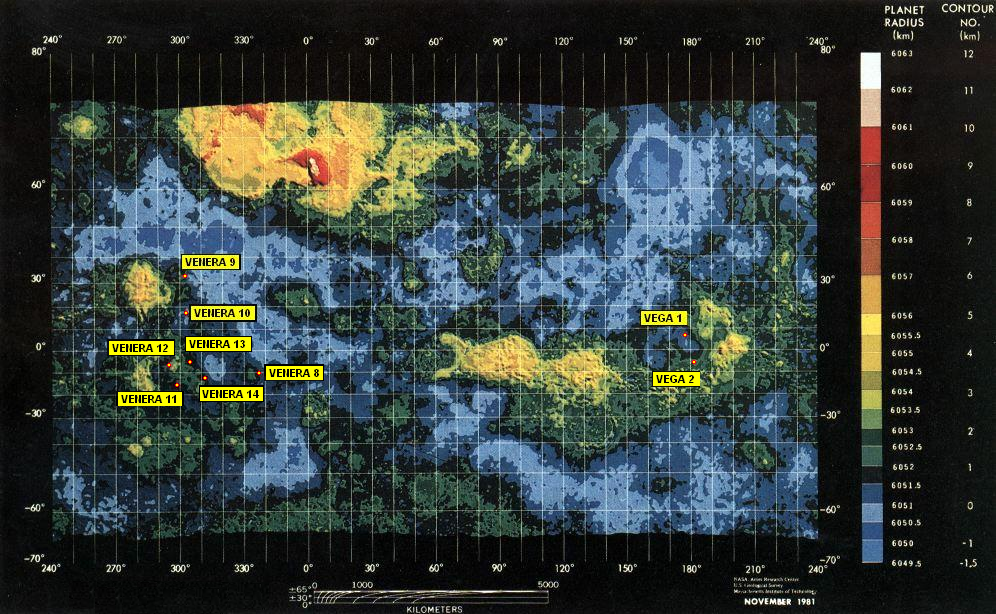
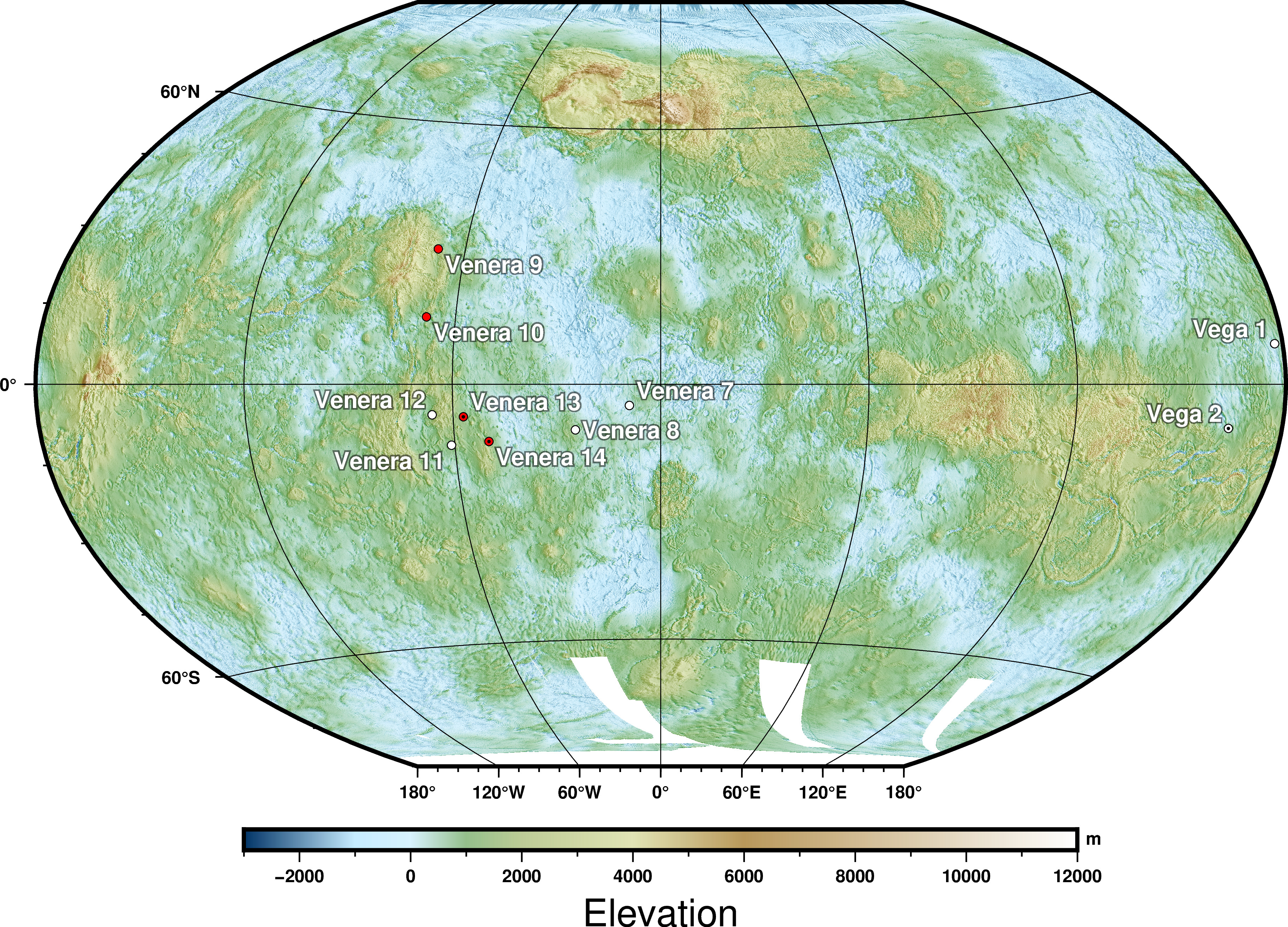
Venera-D (russian: Венера-Д, ) is a proposed Russian space mission to Venus that would include an orbiter and a lander to be launched in 2029. The orbiter's prime objective is to perform observations with the use of a radar. The lander, based on the Venera design, would be capable of operating for a long duration (≈3 h) on the planet's surface. The "D" in Venera-D stands for "dolgozhivushaya," which means "long lasting" in Russian. Venera-D will be the first Venus probe launched by the Russian Federation (the earlier Venera probes were launched by the former Soviet Union). Venera-D will serve as the flagship for a new generation of Russian-built Venus probes, culminating with a lander capable of withstanding the harsh Venusian environment for more than the 1 hours logged by the Soviet probes. The surface of Venus experiences average temperatures of 462° Celsius (864 Fahrenheit), crushing pressures, and corroding clouds of carbon dioxide laced with sulfuric acid. Venera- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the surface of the planet, including the two Vega program and Venera-Halley probes, while thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere. Due to the extreme surface conditions on Venus, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, with times ranging from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet (Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet (Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface (Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet (Venera 13 on 30 October 1981) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera Program
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the surface of the planet, including the two Vega program and Venera-Halley probes, while thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere. Due to the extreme surface conditions on Venus, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, with times ranging from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet (Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet (Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface (Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet (Venera 13 on 30 October 1981) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To Venus ...
There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have conducted missions to Venus. ;Mission Type Legend: Future missions Under development Venus Missions by Organization/Company Proposed missions References External links * {{Venus Venus * Venus Missions to Venus There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venera 16
Venera 16 (russian: Венера-16 meaning ''Venus 16'') was a spacecraft sent to Venus by the Soviet Union. This uncrewed orbiter was to map the surface of Venus using high resolution imaging systems. The spacecraft was identical to Venera 15 and based on modifications to the earlier Venera space probes. The latest data from the spacecraft were received on June 13, 1985, when it responded to the signal sent from Earth for Vega 1. Mission profile Venera 16 was launched on June 7, 1983, at 02:32:00 UTC and reached Venus' orbit on October 11, 1983. The spacecraft was inserted into Venus orbit a day apart from Venera 15, with its orbital plane shifted by an angle of approximately 4° relative to one another probe. This made it possible to reimage an area if necessary. The spacecraft was in a nearly polar orbit with a periapsis ~1000 km, at 62°N latitude, and apoapsis ~65000 km, with an inclination ~90°, the orbital period being ~24 hours. Together with Venera 15, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body, the magnetic field resembles a magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation, that also protects all living organisms from potentially detrimental and dangerous consequences. This is studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly to space, resulting in a warmer planet. Earth's natural greenhouse effect makes life as we know it possible and carbon dioxide plays a significant role in providing for the relatively high temperature on Earth. The greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary atmosphere warms the planet's surface beyond the temperature it would have in the absence of its atmosphere.A concise description of the greenhouse effect is given in the ''Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report,'' "What is the Greenhouse Effect?FAQ 1.3 – AR4 WGI Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change Science, IPCC Fourth Assessment Report, Chapter 1, p. 115: "To balance the absorbed incoming olarenergy, the Earth m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have almost the same chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in 1913 in a suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six naturally occurring noble gases are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn). Oganesson (Og) is a synthetically produced highly radioactive element. Although IUPAC has used the term "noble gas" interchangeably with "group 18" and thus included oganesson, it may not be significantly chemically noble and is predicted to break the trend and be reactive due to relativistic effects. Because of the extremely short 0.7 ms half-life of its only known isotope, its chemistry has not yet been investigated. For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Research Institute
The Russian Space Research Institute (russian: Институт космических исследований Российской академии наук, Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, SRI RAS, Russian abbreviation: ИКИ РАН, IKI RAN) is the leading organization of the Russian Academy of Sciences on space exploration to benefit fundamental science. It was formerly known as the Space Research Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences (Russian abbr.: ИКИ АН СССР, IKI AN SSSR). It is usually known by the shorter name Space Research Institute and especially by the initialism IKI. The institute is located in Moscow with a staff of 289 scientists. It conducts scientific research in the fields of astrophysics, planetary science, solar physics, Sun-Earth relations, cosmic plasma, and geophysics. IKI also develops and tests space technologies in collaboration with the Russian Academy of Sciences and the Federal Space Agency. History I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |