|
Veigaiidae
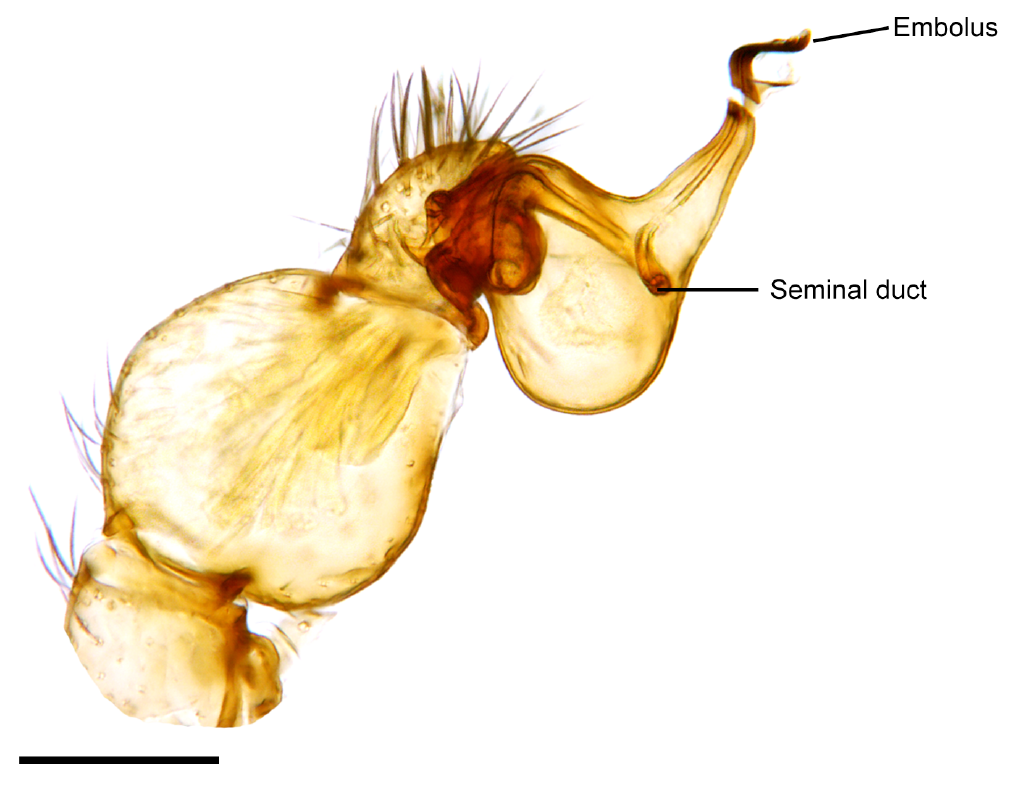
Veigaiidae is a family of mites belonging to the superorder Parasitiformes. However they are not parasitic but free-living and predatory and are found in soil and decaying organic matter. Some species are specialists of rocky shorelines. Members of this family can be distinguished by a hyaline appendage on the tarsus of the pedipalp. Genera * ''Cyrthydrolaelaps'' Berlese, 1904 * ''Gamasolaelaps'' Berlese, 1903 * ''Gorirossia'' Farrier, 1957 * ''Veigaia ''Veigaia'' is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae.Hallan, Joel, edVeigaiidae Species Listing. Biology Catalog. Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 27, 2010. Species * '' Veigaia agilis'' (Berlese, 1916) * ''Veigaia anmashanensis'' T ...'' Oudemans, 1905 References *Evans, G. Owen (1959): The genera ''Cyrthydrolaelaps'' Berlese and ''Gamasolaelaps'' Berlese (Acarina: Mesostigmata). ''Acarologia I''. *Joel Hallan's Biology CatalogVeigaiidae Mesostigmata Taxa named by Anthonie Cornelis Oudemans Acari famili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veigaia
''Veigaia'' is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae.Hallan, Joel, edVeigaiidae Species Listing. Biology Catalog. Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 27, 2010. Species * '' Veigaia agilis'' (Berlese, 1916) * ''Veigaia anmashanensis'' Tseng, 1994 * ''Veigaia ashizuriensis'' Ishikawa, 1978 * ''Veigaia belovae'' Davydova, 1979 * ''Veigaia benoiti'' Loots, 1980 * ''Veigaia bogdanovi'' Davydova, 1978 * ''Veigaia bregetovae'' Petrova & Makarova, 1989 * ''Veigaia capreolus'' (Berlese, 1905) * ''Veigaia carpillaris ''Veigaia carpillaris'' is a species of mite in the family Veigaiidae Veigaiidae is a family of mites belonging to the superorder Parasitiformes. However they are not parasitic but free-living and predator Predation is a biological ...'' Tseng, 1994 * '' Veigaia cerva'' (Kramer, 1876) * ''Veigaia clavata'' Ma-Liming & Wang-Shenron, 1998 * ''Veigaia cuneata'' Ma, 1996 * '' Veigaia exigua'' (Berlese, 1916) * '' Veigaia formosana'' Tseng, 1994 * ''Veiga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorirossia
''Gorirossia'' is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae.Hallan, Joel, edVeigaiidae Species Listing. Biology Catalog. Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 27, 2010. Species * ''Gorirossia whartoni ''Gorirossia'' is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae Veigaiidae is a family of mites belonging to the superorder Parasitiformes. However they are not parasitic but free-living and predator Predation is a biological interacti ...'' Farrier, 1957 References Mesostigmata {{Mesostigmata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrthydrolaelaps
''Cyrthydrolaelaps'' is a genus of mites in the family Veigaiidae Veigaiidae is a family of mites belonging to the superorder Parasitiformes. However they are not parasitic but free-living and predatory and are found in soil and decaying organic matter. Some species are specialists of rocky shorelines. Member ....Hallan, Joel, edVeigaiidae Species Listing. Biology Catalog. Texas A&M University. Retrieved on August 27, 2010. Species * '' Cyrthydrolaelaps hirtus'' Berlese, 1904 References Mesostigmata {{Mesostigmata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamasolaelaps
''Gamasolaelaps'' is a genus of mites belonging to the family Veigaiidae. Males of this genus can be distinguished from other members of the family by the lack of spurs on the second pair of legs and the fact the sclerotized shields on the underside of the body are never fused together. Females are more difficult to diagnose, a high powered microscope A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisibl ... being required. Species * '' Gamasolaelaps aurantiacus'' (Berlese, 1903) * '' Gamasolaelaps bellingeri'' Evans * '' Gamasolaelaps bidentis'' Tseng, 1994 * ''Gamasolaelaps bondwaensis'' Hurlbutt, 1983 * ''Gamasolaelaps cerviformis'' Berlese * ''Gamasolaelaps cornuum'' Karg, 1997 * ''Gamasolaelaps ctenisetiger'' Ishikawa, 1978 * ''Gamasolaelaps cuniculicola'' Wang, Zhou & Ji, 1990 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesostigmata
Mesostigmata is an order of mites belonging to the Parasitiformes. They are by far the largest group of Parasitiformes, with over 8,000 species in 130 families. Mesostigmata includes parasitic as well as free-living and predatory forms. They can be recognized by the single pair of spiracles positioned laterally on the body. The family with the most described species is Phytoseiidae. Other families of note are Diplogyniidae, Macrochelidae, Pachylaelapidae, Uropodidae and Veigaiidae. Amongst the best known species are ''Varroa destructor'', an economically important parasite of honey bees, as well as the red mite (''Dermanyssus gallinae'') a parasite of poultry, most commonly chickens. Description Mesostigmata are mites ranging from 0.12-4 mm long (0.2-4 mm according to another source). They have a pair of stigmatal openings above legs III-IV usually associated with a peritrematal groove. The gnathosoma has a sclerotised ring around the bases of the chelicerae (basis capitul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritivore
Detritivores (also known as detrivores, detritophages, detritus feeders, or detritus eaters) are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as feces). There are many kinds of invertebrates, vertebrates and plants that carry out coprophagy. By doing so, all these detritivores contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles. They should be distinguished from other decomposers, such as many species of bacteria, fungi and protists, which are unable to ingest discrete lumps of matter, but instead live by absorbing and metabolizing on a molecular scale (saprotrophic nutrition). The terms ''detritivore'' and ''decomposer'' are often used interchangeably, but they describe different organisms. Detritivores are usually arthropods and help in the process of remineralization. Detritivores perform the first stage of remineralization, by fragmenting the dead plant matter, allowing decomposers to perform the second stage of reminerali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from el, ὑάλινος, translit=hyálinos, lit=transparent, and el, ὕαλος, translit=hýalos, lit=crystal, glass, label=none. Histopathology Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellular matrix of hyaline cartilage looks homogeneously pink, and the term "hyaline" is used to describe similarly homogeneously pink material besides the cartilage. Hyaline material is usually acellular and proteinaceous. For example, arterial hyaline is seen in aging, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and in association with some drugs (e.g. calcineurin inhibitors). It is bright pink with PAS staining. Ichthyology and entomology In ichthyology and entomology, ''hyaline'' denotes a colorless, transparent substance, such as unpigmented fins of fishes or clear insect wings. Resh, Vincent H. and R. T. Cardé, Eds. Encyclo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_with_its_prey.jpg)
