|
Vedic People
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indic religions. From the second or first millennium BCE, Indo-Aryan migrations, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent – Indus Valley (roughly today's Punjab), Western India, Northern India, Central India, and also in areas of the southern part like Sri Lanka and the Maldives through and after a complex process of migration, assimilation of other peoples and language shift.Mallory, J.P.; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. . Ancestors *Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European speakers) **Proto-Indo-Iranians (common ancestors of the Iranian peoples, Iranian, Nuristani people, Nuristani and Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan peoples) (Proto-Indo-Iranian language, Proto-Indo-Iranian speakers) ***Proto-Indo-Ary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced Proto-Indo-Aryan language. The Indo-Aryan language speakers are found across South Asia. History Proto-Indo-Iranians The introduction of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent was the result of a migration of Indo-Aryan people from Central Asia into the northern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka). These migrations started approximately 1,800 BCE, after the invention of the war chariot, and also brought Indo-Aryan languages into the Levant and possibly Inner Asia. Another group of the Indo-Aryans migrated further westward and founded the Mitanni kingdom in northern Syria; (c. 1500–1300 BC) the other group were the Vedic people. Christopher I. Beckwith sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
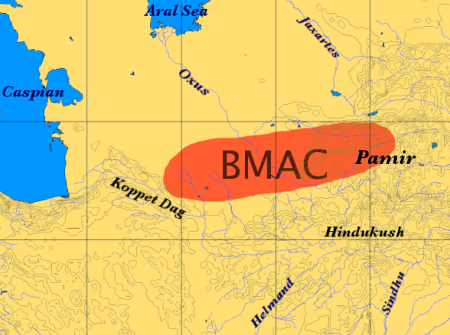
Proto-Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family, to major parts of Eurasia in the second part of the 3rd millennium BCE. They eventually branched out into Iranian peoples and Indo-Aryan peoples, predominantly in the geographical subregion of Southern Asia. Nomenclature The term ''Aryan'' has long been used to denote the ''Indo-Iranians'', because ''Arya'' is indeed the self-designation of the ancient speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages, specifically the Iranian and the Indo-Aryan peoples, collectively known as the Indo-Iranians. Despite this, some scholars use the term Indo-Iranian to refer to this group, though the term "Aryan" remains widely used by most scholars, such as Josef Wiesehofer, Will Durant, and Jaakko Häkkinen. Population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuru Kingdom
Kuru (Sanskrit: ) was a Vedic Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan tribal union in northern Iron Age India, Iron Age India, encompassing parts of the modern-day states of Haryana, Delhi, and some parts of western Uttar Pradesh, which appeared in the Middle Vedic period (c. 1200 – c. 900 BCE). The Kuru Kingdom was the first recorded State (polity), state-level society in the Indian subcontinent. The Kuru kingdom decisively changed the religious heritage of the early Vedic period, arranging their ritual hymns into collections called the Vedas, and developing new rituals which gained their position over Indian civilization as the Śrauta, Srauta rituals, which contributed to the so-called "classical synthesis" or Hinduism#Roots of Hinduism, "Hindu synthesis". It became the dominant political and cultural center of the middle Vedic Period during the reigns of Parikshit and Janamejaya, but declined in importance during the late Vedic period (c. 900 – c. 500 BCE) and had become "somethin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikshvaku Dynasty
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is also known as ("Solar dynasty" or "Descendants of the Sun") which means that this dynasty prays to the Sun as their God and their originator (the Gayatri Mantra is a prayer offered to the Sun God as the Sun is the main deity of the Solar Dynasty), and along with Lunar dynasty comprises one of the main lineages of the Kshatriya Varna. The first ''Tirthankara'' of Jainism, Rishabhdeva himself was King Ikshvaku. Further, 21 Tirthankaras of Jainism were born in this dynasty. According to Buddhist texts and tradition, Gautama Buddha descended from this dynasty. Many later kings of the Indian subcontinent claimed to be of Suryavamsha descent. The important personalities belonging to this royal house are Mandhatri, Muchukunda, Ambarisha, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhara Kingdom
Gandhāra ( sa, गन्धार) was an Ancient Indian kingdom mentioned in the Indian epics Mahabharata and Ramayana. Gandhara prince Shakuni was the root of all the conspiracies of Duryodhana against the Pandavas, which finally resulted in the Kurukshetra War. Shakuni's sister was the wife of the Kuru king Dhritarashtra and was known as Gandhari after the area of Gandhāra (which is in modern Afghanistan and Pakistan). Puskalavati, ''Takshasila'' (Taxila) and ''Purushapura'' (Peshawar) were cities in this Gandhara kingdom. Takshasila was founded by Raghava Rama's brother Bharata. Bharata's descendants ruled this kingdom afterwards. During the epic's period, the kingdom was ruled by Shakuni's father ''Suvala'', Shakuni and Shakuni's son. Arjuna defeated Shakuni's son during his post-war military campaign for Yudhishthira's Aswamedha Yagna. Janamejaya, a Kuru king in Arjuna's line, conquered Takshasila, probably then ruled by the Naga Takshaka. He conducted a massacre ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasa
''Dasa'' ( sa, दास, Dāsa) is a Sanskrit word found in ancient Indian texts such as the ''Rigveda'' and ''Arthasastra''. It usually means "enemy" or "servant" but ''dasa'', or ''das'', also means a "servant of God", "devotee," "votary" or "one who has surrendered to God". Dasa may be a suffix of a given name to indicate a "servant" of a revered person or a particular deity. ''Dasa'', in some contexts, is also related to ''dasyu'' and ''asura'', which have been translated by some scholars as "demon", "harmful supernatural forces", "slave", "servant" or "barbarian", depending on the context in which the word is used.Wash Edward Hale (1999), Ásura- in Early Vedic Religion, Motilal Barnarsidass, , pages 159-169 Etymology ''Dāsa'' first appears in Vedic texts from the second millennium BCE. There is no consensus on its origins. Karl Heinrich Tzschucke in 1806, in his translations of the Roman geographer Pomponius Mela, noted etymological and phonological parallels between '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chedi Kingdom
Chedi ( sa, चेदी) was a kingdom which fell roughly in the Bundelkhand division of Madhya Pradesh regions to the south of river Yamuna along the river Ken. Its capital city was called Suktimati in Sanskrit. According to the Mahabharata, the Chedi Kingdom was ruled by Shishupala, an ally of Jarasandha of Magadha and Duryodhana of Kuru. He was a rival of Vasudeva Krishna who was his uncle's son. He was killed by Vasudeva Krishna during the Rajasuya sacrifice of the Pandava king Yudhishthira. Bhima's wife was from Chedi. Prominent Chedis during the Kurukshetra War included Damaghosha, Shishupala, Dhrishtaketu, Suketu, Sarabha, Bhima's wife, Nakula's wife Karenumati, Dhrishtaketu's sons. Other Chedis included King Uparichara Vasu, his children, King Suvahu, King Sahaja. It was ruled during early periods by ''Paurava'' kings and later by Yadava kings in the central part of the country. Puranic History The Chedi clan and kingdom was founded by Chidi, the son of Vidarb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Ten Kings
The Battle of the Ten Kings ( sa, दाशराज्ञ युद्ध, translit=Dāśarājñá yuddhá) is a battle, first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV), between a Bharata king and a confederation of tribes. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Bharatas and subsequent formation of the Kuru polity. Background In Book 3, the Bharatas are noted to have crossed Beas and Sutlej, in their progress towards Kurukshetra where they came across a nascent (and temporary) inter-tribal alliance. This led to the battle, which is described in the 18th hymn (verses 5-21) of Book 7; the exact motivations are doubtful — Michael Witzel argues that it might have been a product of intratribal resentment or intrigues of an ousted family-priest while Ranabir Chakravarti argues that the battle was probably fought for controlling the rivers, which were a lifeline for irrigation. The hymns also mention of the tribes seeking to steal cows from the Bharatas. Battle Hanns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharatas (tribe)
The Bharatas were an early Vedic tribe that existed in the latter half of the second millennium B.C.E. The earliest mentioned location of the Bharatas was on the first Sarasvati River in southern Afghanistan. Under the tribal king Divodāsa, the Bharatas moved through the Hindu Kush mountains and defeated Śambara. Divodāsa's descendant, Sudās, won the Battle of the Ten Kings against a Puru-led coalition, which set the scene for the initial compilation of hymns of the Rigveda. After the battle, the Bharatas and other Puru clans would eventually form the Kuru Kingdom, which was the first attested state in Indian history. Etymology The name ''Bharata'' is of Indo-Aryan and Indo-Iranian origin, meaning "the ones who carry". History Two Bharatas, Devaśravas Bhārata and Devavāta Bhārata, are mentioned as living near the Āpayā, Sarasvatī and Dṛṣadvatī rivers. Devavāta's son, Sṛñjaya Daivavāta, defeated the Turvaśas, and is mentioned alongside Abhyāvar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Āndhra (tribe)
Āndhra (Sanskrit: ) () was an ancient Dravidian tribe of south-central South Asia whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. Location The Āndhras lived around the deltas of the Godāvarī and Kṛṣṇa rivers, and their neighbours to the north was the Indo-Aryan Kaliṅga kingdom. The political centre of the Āndhras was Andhapura, or Dhaññakaḍa, which corresponds to modern-day Vijayawada. History The Āndhras were the ancestors of the present-day Telugu people Telugu people ( te, తెలుగువారు, Teluguvāru), or Telugus, or Telugu vaaru, are the largest of the four major Dravidian ethnolinguistic groups in terms of population. Telugus are native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh .... References Further reading * {{refend Ancient peoples of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-Aryan Language
Proto-Indo-Aryan (sometimes Proto-Indic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Indo-Aryan languages. It is intended to reconstruct the language of the Proto-Indo-Aryans. Being descended from Proto-Indo-Iranian (which in turn is descended from Proto-Indo-European), it has the characteristics of a Satem language. History Proto-Indo-Aryan is meant to be the predecessor of Old Indo-Aryan (1500–300 BCE), which is directly attested as Vedic and Classical Sanskrit, as well as by the Indo-Aryan superstrate in Mitanni. Indeed, Vedic Sanskrit is very close to Proto-Indo-Aryan. Some of the Prakrits display a few minor features derived from Proto-Indo-Aryan that had already disappeared in Vedic Sanskrit. Today, numerous modern Indo-Aryan languages are extant. Differences from Vedic Despite the great archaicity of Vedic, the other Indo-Aryan languages preserve a small number of conservative features lost in Vedic. One of these is the representation of Proto-Indo-European *l an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-Aryans
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Indo-Aryan population movements into the region from Central Asia are considered to have started after 2000 BCE, as a slow diffusion during the Late Harappan period, which led to a language shift in the northern Indian subcontinent. Several hundred years later, the Iranian languages were brought into the Iranian plateau by the Iranians, who were closely related to the Indo-Aryans. The Proto-Indo-Iranian culture, which gave rise to the Indo-Aryans and Iranians, developed on the Central Asian steppes north of the Caspian Sea as the Sintashta culture (2050Lindner, Stephan, (2020)"Chariots in the Eurasian Steppe: a Bayesian approach to the emergence of horse-drawn transport in the early second millennium BC" in Antiquity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


