|
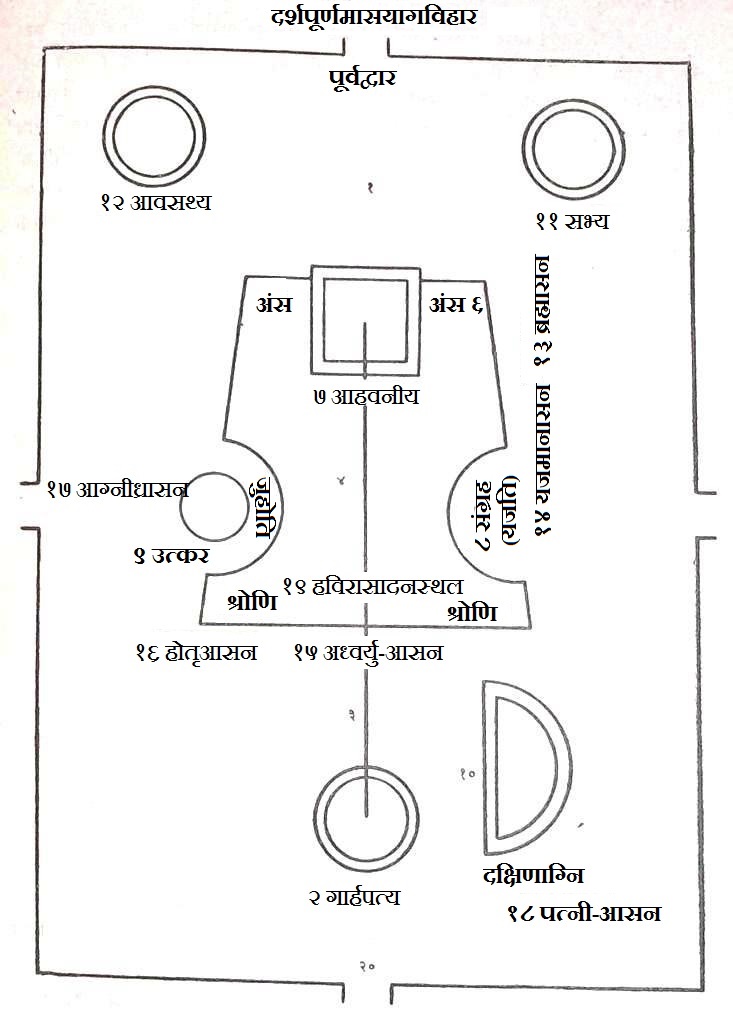
Vedic Fire Altar
''Vedi'' () is the sacrificial altar in the Vedic religion. Such altars were an elevated outdoor enclosure, generally strewed with Kusha grass, and having receptacles for the sacrificial fire; it was of various shapes, but usually narrow in the middle. They were used in various types of Yajna rituals, of which the lengthiest was the ''agnicayana'', lasting twelve days. In Vedic times, offerings, often including animals, were burnt in the fire, and fully consumed by it. This contrasts with modern Hindu offerings to gods, which are all vegetable, and are preserved to be consumed by the devotees (which was also the case in other religions, such as ancient Greek religion). Fire altars remain part of the rituals in some Hindu festivals and rites of passage; in particular circling around a sacred fire ('' saptapadi'') remains an essential part of Hindu weddings. Although Agni, the Vedic god of fire, has an important place in the mandala setting out the plan in Hindu temple archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homa During Sri Thimmaraya Swamy Pratishthapana
Homa may refer to: Places Ethiopia * Homa (woreda), a district in Oromia Region, Ethiopia Kenya * Homa Bay, a town and a bay on the shore of Lake Victoria in Kenya * Homa Mountain, a volcano near Homa Bay, Kenya Iran * Chal Homa, Markazi, Iran * Homa, Iran, a village in Lorestan Province, Iran * Homa, North Khorasan, Iran, a village * Homa-ye Bala (other), places in Iran * Homag (other), various places in Iran * Homay, Iran (other), various places in Iran Israel * Har Homa, East Jerusalem neighborhood, Israel United States * Homa Hills, Wyoming * La Homa, Texas, U.S. People People with the given name Homa * Homa Arjomand (born 1952), Iranian political activist * Homa Darabi (1994–1940), Iranian pediatrician, academic, and political activist * Homa Vafaie Farley, Iranian-born potter and ceramist * Homa Hoodfar, Canadian-Iranian sociocultural anthropologist * Homa Katouzian (born 1942), Iranian economist, historian, sociologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identified as being established in the triangle of land at the confluence of Drishadvati and Sarasvati Rivers. The prehistoric and pre-Mauryan character of Indus Valley civilization was first identified by Luigi Tessitori at this site. Kalibangan's excavation report was published in its entirety in 2003 by the Archaeological Survey of India, 34 years after the completion of excavations. The report concluded that Kalibangan was a major provincial capital of the Indus Valley Civilization. Kalibangan is distinguished by its unique fire altars and "world's earliest attested ploughed field". It is around 2900 BC that the region of Kalibangan developed into what can be considered a planned city. Indus Valley Civilization The Kalibangan pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaring The Circle
Squaring the circle is a problem in geometry first proposed in Greek mathematics. It is the challenge of constructing a square with the area of a circle by using only a finite number of steps with a compass and straightedge. The difficulty of the problem raised the question of whether specified axioms of Euclidean geometry concerning the existence of lines and circles implied the existence of such a square. In 1882, the task was proven to be impossible, as a consequence of the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem, which proves that pi (\pi) is a transcendental number. That is, \pi is not the root of any polynomial with rational coefficients. It had been known for decades that the construction would be impossible if \pi were transcendental, but that fact was not proven until 1882. Approximate constructions with any given non-perfect accuracy exist, and many such constructions have been found. Despite the proof that it is impossible, attempts to square the circle have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristubh
''Trishtubh'' ( sa, त्रिष्टुभ्, , IAST: ) is a Vedic metre of 44 syllables (four padas of eleven syllables each), or any hymn composed in this metre. It is the most prevalent metre of the Rigveda, accounting for roughly 40% of its verses. The Trishtubh pada contains a "break" or caesura, after either four or five syllables, necessarily at a word-boundary and if possible at a syntactic break, followed by either three or two short syllables. The final four syllables form a trochaic cadence. For example RV 2.3.1: :' :' :' :' :"Agni is set upon the earth well kindled :he standeth in the presence of all beings. :Wise, ancient, God, the Priest and Purifier :let Agni serve the Gods for he is worthy." :(trans. Griffith; the translator attempts to imitate the meter in English) This is to be read metrically as follows, with marking the caesura and separating the cadence: : : : : The Avesta has a parallel stanza of 4x11 syllables with a caesura after the fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Meter
Vedic metre refers to the poetic metre in the Vedic literature. The study of Vedic metre, along with post-Vedic metre, is part of Chandas, one of the six Vedanga disciplines. Overview In addition to these seven, there are fourteen less frequent ones syllable-based metres (''Varna-vritta'' or ''Akshara-chandas''): :- 8. ''Atijagati'' (13x4); 9. ''Śakkarī'' (14x4); 10. ''Atiśakarī '' (15x4); 11. ''Ashṭi'' (16x4); :- 12. ''Atyashti'' (17x4); 13. ''Dhritī '' (18x4); 14. ''Atidhritī'' (19x4); 15. ''Kṛiti'' (20x4); :- 16. ''Prakṛiti'' (21x4); 17. ''Ākṛiti'' (22x4): 18. ''Vikṛiti'' (23x4); 19. '' Śankṛiti'' (24x4); :- 20. ''Atikṛiti'' (25x4); 21. ''Utkṛiti'' (26x4). (Note: all metres have several varieties (from 2 to 30 depending on the case). :There is also the metre called ''Dandaka'' which is the general name given to other metres of this class exceeding the measure (26x4) of ''Utkriti'' (''Dandaka'' is the No. 22 on the list compiled by H.H. Wilson). Fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taittiriya Samhita
The ''Taittirīya Shakha'' (Sanskrit, loosely meaning 'Branch or School of the sage Tittiri'), is a ''shakha'' (i.e. 'branch', 'school', or rescension) of the Krishna (black) Yajurveda. Most prevalent in South India, it consists of the ''Taittirīya Samhita'' ('TS'), ''Taittirīya Brahmana'' ('TB'), ''Taittirīya Aranyaka'' ('TA'), and ''Taittirīya Pratisakhya'' ('TP'). Nomenclature The 'Taittiriya Shakha' can be loosely translated as 'Branch or School of (the sage) Tittri' or 'Branch or School of Taittiriya' or 'School of the pupils of Tittiri'. *'Taittiriya' is derived from the name of the sage Taittiri (or Tittiri). *'Shakha' means 'branch' or 'school'. Origin Monier-Williams According to Monier-Williams ''Sanskrit-English Dictionary'', Taittiri was a pupil of Yaska (estimated 4th-5th century BCE). According to the Vishnu Purana, Yaska was in turn a pupil of Vaiśampáyana, (estimated 6th century BCE). Taittiri is also stated in the Mahabharata to have atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. The sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted since the 2nd millennium BCE. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the bulk of the ''Rigveda'' Samhita was composed in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent (see) Rigvedic rivers), most likely between 1500 and 1000 BCE, although a wider approximation of 19001200 BCE has also been given. The text is layered, consisting of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulbasutras
The ''Shulva Sutras'' or ''Śulbasūtras'' (Sanskrit: शुल्बसूत्र; ': "string, cord, rope") are sutra texts belonging to the Śrauta ritual and containing geometry related to fire-altar construction. Purpose and origins The Shulba Sutras are part of the larger corpus of texts called the Shrauta Sutras, considered to be appendices to the Vedas. They are the only sources of knowledge of Indian mathematics from the Vedic period. Unique fire-altar shapes were associated with unique gifts from the Gods. For instance, "he who desires heaven is to construct a fire-altar in the form of a falcon"; "a fire-altar in the form of a tortoise is to be constructed by one desiring to win the world of Brahman" and "those who wish to destroy existing and future enemies should construct a fire-altar in the form of a rhombus"., p. 387, "Certain shapes and sizes of fire-altars were associated with particular gifts that the sacrificer desired from the gods: 'he who desires heaven i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana ( sa, शतपथब्राह्मणम् , Śatapatha Brāhmaṇam, meaning 'Brāhmaṇa of one hundred paths', abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Śukla (white) Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the Vedas), it contains detailed explanations of Vedic sacrificial rituals, symbolism, and mythology. Particularly in its description of sacrificial rituals (including construction of complex fire-altars), the Shatapatha Brahmana (SB) provides scientific knowledge of geometry (e.g. calculations of pi and the root of the Pythagorean theorem) and observational astronomy (e.g. planetary distances and the assertion that the Earth is circular) from the Vedic period. The Shatapatha Brahmana is also considered to be significant in the development of Vaishnavism as the origin of several Puranic legends and avatars of the RigVedic god Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalpa (Vedanga)
Kalpa ( sa, कल्प) means "proper, fit" and is one of the six disciplines of the Vedānga, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas – the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study is focused on the procedures and ceremonies associated with Vedic ritual practice.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Kalpa" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 339. The major texts of Kalpa Vedanga are called ''Kalpa Sutras'' in Hinduism. The scope of these texts includes Vedic rituals, rites of passage rituals associated with major life events such as birth, wedding and death in family, as well as personal conduct and proper duties in the life of an individual. Most Kalpasutras texts have experienced interpolation, changes and consequent corruption over their history, and Apasthamba Kalpasutra ancillary to the Yajurveda may be the best preserved text in this genre. Kalpa Sutras are also found in other Indian traditions, such as Jainism. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)