|
Vasyl' Shakhrai
Vasyl' Matviyovych Shakhrai ( uk, Василь Матвійович Шахрай; February 11, 1888 – 1919) was a Ukrainian political activist and Bolshevik revolutionary during the Russian Revolution. He was а founder of what came to be called National Communism. Biography Shakhrai joined the Bolsheviks after completing his training at the Military Academy in Poltava in 1917, while some sources claim that he was a member and activist of Bolsheviks since 1913. He was one of the few Ukrainians amongst the Poltava Bolsheviks. At the time the Bolsheviks were in a unified organisation with the local Mensheviks, but Shakhrai supported Serhii Mazlakh, a Poltava Bolshevik who successfully ousted the Mensheviks by August 1917. Shakhrai and Mazlakh were then elected editors of the weekly newspaper. By this time Shakhrai was supporting Ukrainian national interests within the party. Although this caused concern amongst the predominantly Jewish local Mensheviks, he gained support amongst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Orthodox Christians. While under the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Austrian Empire, and then Austria-Hungary, the East Slavic population who lived in the territories of modern-day Ukraine were historically known as Ruthenians, referring to the territory of Ruthenia, and to distinguish them with the Ukrainians living under the Russian Empire, who were known as Little Russians, named after the territory of Little Russia. Cossack heritage is especially emphasized, for example in the Ukrainian national anthem. Ethnonym The ethnonym ''Ukrainians'' came into wide use only in the 20th century after the territory of Ukraine obtained distinctive statehood in 1917. From the 14th to the 16th centuries the western portions of the Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 Deaths
Events January * January 1 ** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Pressburg (now Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia. ** HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off the coast of the Hebrides; 201 people, mostly servicemen returning home to Lewis and Harris, are killed. * January 2– 22 – Russian Civil War: The Red Army's Caspian-Caucasian Front begins the Northern Caucasus Operation against the White Army, but fails to make progress. * January 3 – The Faisal–Weizmann Agreement is signed by Emir Faisal (representing the Arab Kingdom of Hejaz) and Zionist leader Chaim Weizmann, for Arab–Jewish cooperation in the development of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, and an Arab nation in a large part of the Middle East. * January 5 – In Germany: ** Spartacist uprising in Berlin: The Marxist Spartacus League, with the newly formed Communist Party of Germany and the Independent Social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1888 Births
In Germany, 1888 is known as the Year of the Three Emperors. Currently, it is the year that, when written in Roman numerals, has the most digits (13). The next year that also has 13 digits is the year 2388. The record will be surpassed as late as 2888, which has 14 digits. Events January–March * January 3 – The 91-centimeter telescope at Lick Observatory in California is first used. * January 12 – The Schoolhouse Blizzard hits Dakota Territory, the states of Montana, Minnesota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Texas, leaving 235 dead, many of them children on their way home from school. * January 13 – The National Geographic Society is founded in Washington, D.C. * January 21 – The Amateur Athletic Union is founded by William Buckingham Curtis in the United States. * January 26 – The Lawn Tennis Association is founded in England. * February 6 – Gillis Bildt becomes Prime Minister of Sweden (1888–1889). * February 27 &nda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteer Army
The Volunteer Army (russian: Добровольческая армия, translit=Dobrovolcheskaya armiya, abbreviated to russian: Добрармия, translit=Dobrarmiya) was a White Army active in South Russia during the Russian Civil War from 1917 to 1920. The Volunteer Army fought against Bolsheviks on the Southern Front and the Ukrainian War of Independence. In 1919 it was made part of the Armed Forces of South Russia, becoming the largest force of the White movement until it was merged with the Army of Wrangel in March 1920. History Formation The Volunteer Army began forming in November/December 1917 under the leadership of General Mikhail Alekseyev and General Lavr Kornilov in Novocherkassk, shortly after the Russian Civil War began following the October Revolution. It organized to fight against the Bolsheviks in South Russia. Alekseyev and Kornilov enlisted supporters, which initially included volunteering officers, cadets, students, and Cossacks. Of the first 3,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Denikin
Anton Ivanovich Denikin (russian: Анто́н Ива́нович Дени́кин, link= ; 16 December O.S. 4 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 4 December1872 – 7 August 1947) was a Russian Lieutenant General in the Imperial Russian Army (1916), who later served as the Deputy Supreme Ruler of Russia, Supreme Ruler of the Russian State during the Russian Civil War of 1917–1922. He was also a military leader of South Russia (as commander in chief). His slogan was “Russia - One and Indivisible”. Childhood Denikin was born on 16 December 1872, in the village of Szpetal Dolny, part of the city Włocławek in Warsaw Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Poland). His father, Ivan Efimovich Denikin, had been born a serf in the province of Saratov. Sent as a recruit to do 25 years of military service, the elder Denikin became an officer in the 22nd year of his army service in 1856. He retired from the army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saratov
Saratov (, ; rus, Сара́тов, a=Ru-Saratov.ogg, p=sɐˈratəf) is the largest city and administrative center of Saratov Oblast, Russia, and a major port on the Volga River upstream (north) of Volgograd. Saratov had a population of 901,361, making it the 17th-largest city in Russia by population. Saratov is from Volgograd, from Samara, and southeast of Moscow. The city stands near the site of Uvek, a city of the Golden Horde. Tsar Feodor I of Russia likely developed Saratov as a fortress to secure Russia's southeastern border. Saratov developed as a shipping port along the Volga and was historically important to the Volga Germans, who settled in large numbers in the city before they were expelled after World War II. Saratov is home to a number of cultural and educational institutions, including the Saratov Drama Theater, Saratov Conservatory, Radishchev Art Museum, Saratov State Technical University, and Saratov State University. Etymology The na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1924 and of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1924. Under his administration, Russia, and later the Soviet Union, became a one-party socialist state governed by the Communist Party. Ideologically a Marxist, his developments to the ideology are called Leninism. Born to an upper-middle-class family in Simbirsk, Lenin embraced revolutionary socialist politics following his brother's 1887 execution. Expelled from Kazan Imperial University for participating in protests against the Russian Empire's Tsarist government, he devoted the following years to a law degree. He moved to Saint Petersburg in 1893 and became a senior Marxist activist. In 1897, he was arrested for sedition and exiled to Shushenskoye in Siberia for three years, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Brest Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's participation in World War I. The treaty was signed at German-controlled Brest-Litovsk ( pl, Brześć Litewski; since 1945, Brest, now in modern Belarus), after two months of negotiations. The treaty was agreed upon by the Russians to stop further invasion. As a result of the treaty, Soviet Russia defaulted on all of Imperial Russia's commitments to the Allies and eleven nations became independent in eastern Europe and western Asia. Under the treaty, Russia lost all of Ukraine and most of Belarus, as well as its three Baltic republics of Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia (so-called Baltic governorates in the Russian Empire), and these three regions became German vassal states under German princelings. Russia also ceded its province of Kars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest Litovsk
Brest ( be, Брэст / Берасьце, Bieraście, ; russian: Брест, ; uk, Берестя, Berestia; lt, Brasta; pl, Brześć; yi, בריסק, Brisk), formerly Brest-Litovsk (russian: Брест-Литовск, lit=Lithuanian Brest; be, links=no, translit=Berastze Litouski (Berastze), Берасце Літоўскі (Берасце); lt, links=no, Lietuvos Brasta; pl, links=no, Brześć Litewski, ), Brest-on-the-Bug ( pl, links=no, Brześć nad Bugiem), is a city (population 350,616 in 2019) in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish city of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It is the capital city of the Brest Region. Brest is a historical site for many cultures, as it hosted important historical events, such as the Union of Brest and Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. Furthermore, the Brest Fortress was recognized by the Soviet Union as a Hero Fortress in honour of the defense of Brest Fortress in June 1941. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
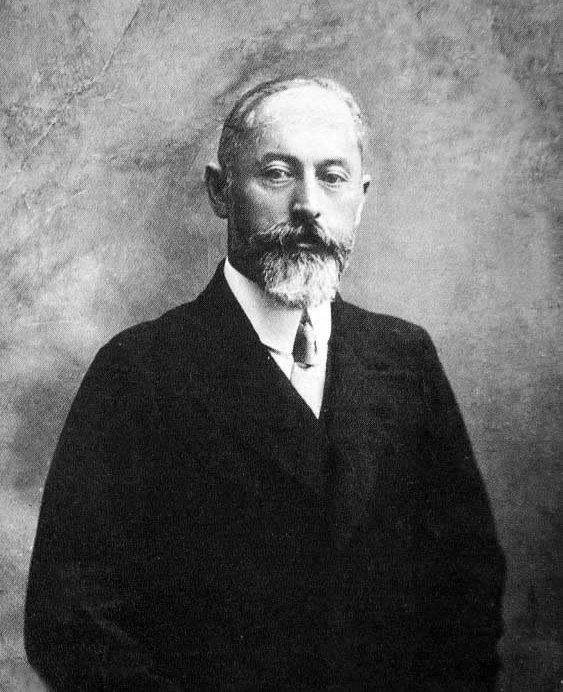


.png)


.jpg)
