|
Vanaspara
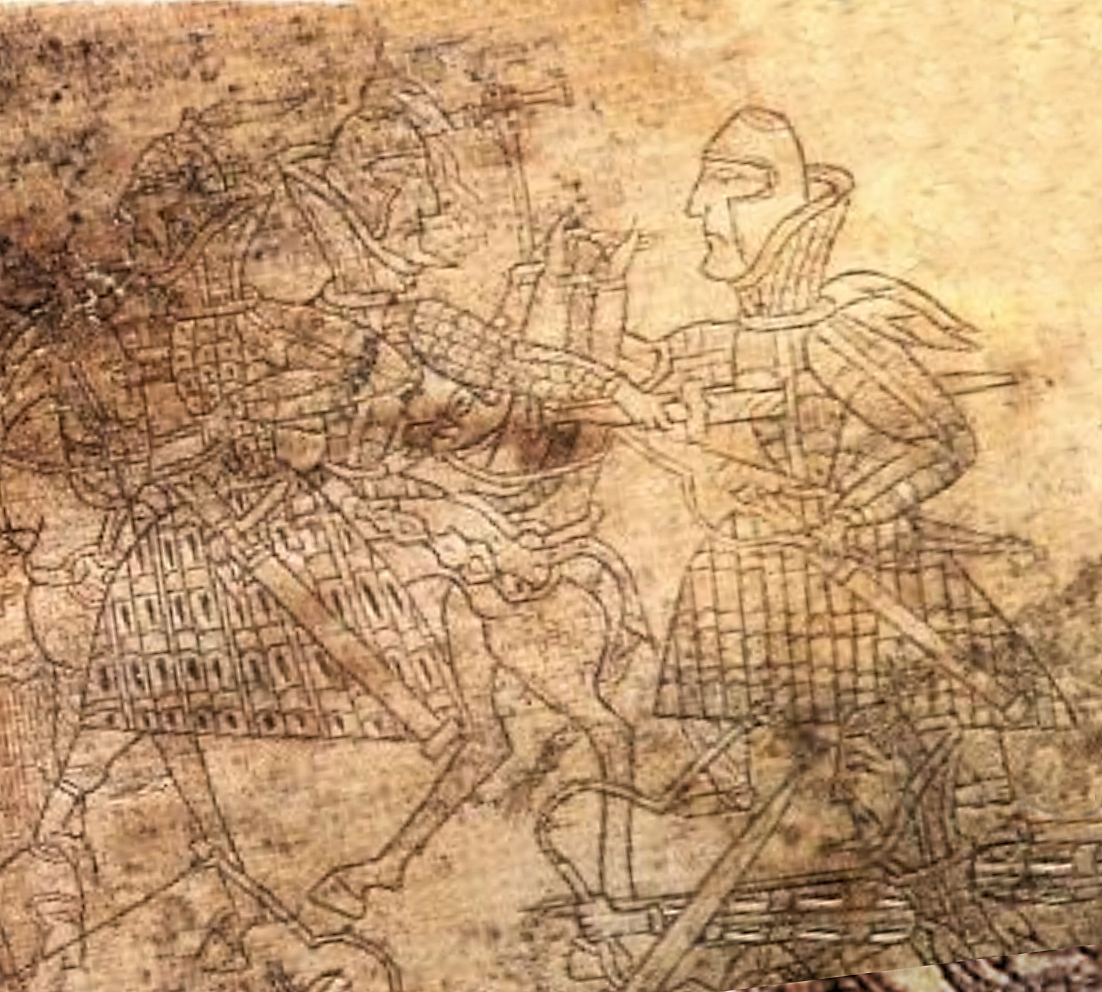
Vanaspara (ruled circa 130 CE) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap (''kshtrapa''). He is mentioned as a "Satrap" (Brahmi:, ''Kṣatrapa'', "Satrap") of Kushan ruler Kanishka I on an inscription discovered in Sarnath, and dated to the 3rd year of Kanishka (c. 130 CE), in which Kanishka mentions he was, together with "Great Satrap" Kharapallana, governor of the eastern parts of his Empire. The inscription was discovered on an early statue of a Boddhisattva, the Sarnath Bala Boddhisattva, now in the Sarnath Museum .Papers on the Date of Kaniṣka, Arthur Llewellyn Basham, Brill Archive, 1969, p.27/ref> References External linksDates of Kanishka and the Indo-Scythians {{authority control Indo-Scythian kings 2nd-century monarchs in Asia 2nd-century Iranian people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharapallana
Kharapallana (Brahmi script, Brahmi: , ; Greek alphabet, Greek: Ancient Greek: ) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap who ruled around c. 130 CE. Name Kharapallana's name is attested in the Greek alphabet, Greek form ( grc, wiktionary:Χαροβαλανο, Χαροβαλανο) and in the Brahmi script, Brahmi form , which are derived from the Saka language, Saka name , meaning "splendid youth". Reign He is mentioned as a "Great Satrap" (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satrap") of Kushan ruler Kanishka I on an inscription discovered in Sarnath, and dated to the 3rd year of Kanishka (c. 130 CE), in which Kanishka mentions he was, together with Satrap Vanaspara, governor of the eastern parts of his Empire. The inscription was discovered on an early statue of a Boddhisattva, the Sarnath Bala Boddhisattva, now in the Sarnath Museum . Vanaspara and Kharapallana were ruling for Kanishka over the eastern provinces of the Empire, including the Benares region. References Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythian Kings
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE. The first Saka king of India was Maues/Moga (1st century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, Pakistan and the Indus Valley. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over north-western India, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local kingdoms. The Indo-Scythians were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire, by either Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. Yet the Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by the Satavahana emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni. Indo-Scythian rule in the northwestern Indian subcontinent ceased when the last Western Satrap Rudrasimha III was defeated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythian
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE. The first Saka king of India was Maues/Moga (1st century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, Pakistan and the Indus Valley. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over north-western India, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local kingdoms. The Indo-Scythians were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire, by either Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. Yet the Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by the Satavahana emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni. Indo-Scythian rule in the northwestern Indian subcontinent ceased when the last Western Satrap Rudrasimha III was defeated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Satrap
The Northern Satraps (Brahmi: , ''Kṣatrapa'', "Satraps" or , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps"), or sometimes Satraps of Mathura, or Northern Sakas, are a dynasty of Indo-Scythian rulers who held sway over the area of Eastern Punjab and Mathura after the decline of the Indo-Greeks, from the end of the 1st century BCE to the 2nd century CE. They are called "Northern Satraps" in modern historiography to differentiate them from the "Western Satraps", who ruled in Gujarat and Malwa at roughly the same time and until the 4th century CE. They are thought to have replaced the last of the Indo-Greek kings in the Eastern Punjab, as well as the Mitra dynasty and the Datta dynasty of local Indian rulers in Mathura. The Northern Satraps were probably displaced by, or became vassals of, the Kushans from the time of Vima Kadphises, who is known to have ruled in Mathura in 90–100 CE, and they are known to have acted as Satraps and Great Satraps in the Mathura region for his successor Kan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarnath Bala Boddhisattva
The ''Bala Bodhisattva'' is an ancient Indian statue of a Bodhisattva, found in 1904-1905 by German archaeologist F.O. Oertel (1862-1942) in Sarnath, India. The statue has been decisive in matching the reign of Kanishka with contemporary sculptural style, especially the type of similar sculptures from Mathura, as its bears a dated inscription in his name.Papers on the Date of Kaniṣka, Arthur Llewellyn Basham, Brill Archive, 1969, p.27/ref> This statue is in all probability a product of the art of Mathura, which was then transported to the Ganges region. Inscription The inscription on the Bodhisattva explains that it was dedicated by a "Brother" (''Bhikshu'') named Bala, in the "Year 3 of Kanishka". This allows to be a rather precise date on the sculptural style represented by the statue, as year 3 is thought to be approximately 123 CE. The inscription further states that Kanishka (who ruled from his capital in Mathura) had several satraps under his commands in order to rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boddhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards Enlightenment in Buddhism, bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood. In the Early Buddhist schools as well as modern Theravada, Theravada Buddhism, a bodhisattva (Pali: ''bodhisatta'') refers to someone who has made a resolution to become a Buddha (title), Buddha and has also received a confirmation or prediction from a living Buddha that this will be so. In Mahayana, Mahayana Buddhism, a bodhisattva refers to anyone who has generated ''bodhicitta'', a spontaneous wish and compassionate mind to attain Buddhahood for the benefit of all Sentient beings (Buddhism), sentient beings. Mahayana bodhisattvas are spiritually heroic persons that work to attain awakening and are driven by a great compassion (''mahakaruṇā''). These beings are exemplified by important spiritual qualities such as the "four divine abodes" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanishka I
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian script, Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi script, Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadphises, founder of the Kushan Empire, Kushan empire, Kanishka came to rule an empire, extending from Central Asia and Gandhara to Pataliputra on the Gangetic plain. The main capital of his empire was located at history of Peshawar, ''Puruṣapura'' (Peshawar) in Gandhara, with another major capital at Mathura. Coins of Kanishka were found in Tripuri (present-day Jabalpur). His conquests and patronage of Buddhism played an important role in the development of the Silk Road, and in the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, transmission of Mahayana Buddhism from Gandhara across the Karakoram ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kushan
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of modern-day territory of, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, and northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath near Varanasi (Benares), where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan Emperor Kanishka the Great. The Kushans were most probably one of five branches of the Yuezhi confederation, an Indo-European nomadic people of possible Tocharian origin, who migrated from northwestern China (Xinjiang and Gansu) and settled in ancient Bactria. The founder of the dynasty, Kujula Kadphises, followed Greek religious ideas and iconography after the Greco-Bactrian tradition, and being a follower of Shaivism. The Kushans in general were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
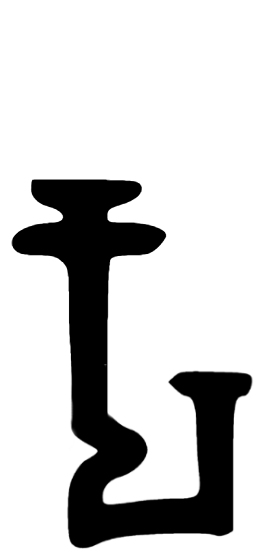
Gupta Ashoka Kss
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. In Bengal The Rāmpāl plate of Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. In Northern India The Gupta surname is also used by Banias and Jains in the northern part of India. Notables Monarchs *Gupta (king), founder of the Gupta dynasty *Ghatotkacha (king) * Chandragupta I *Samudragupta *Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya *Kumaragupta I *Skandagupta, last Gupta emperor *Vishnugupta (Gupta Empire) * Budhagupta Academic * Akhil Gupta (born 1959), professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the field of so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Ashoka P
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. In Bengal The Rāmpāl plate of Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. In Northern India The Gupta surname is also used by Banias and Jains in the northern part of India. Notables Monarchs *Gupta (king), founder of the Gupta dynasty *Ghatotkacha (king) *Chandragupta I *Samudragupta *Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya *Kumaragupta I *Skandagupta, last Gupta emperor *Vishnugupta (Gupta Empire) *Budhagupta Academic *Akhil Gupta (born 1959), professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the field of social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Ashoka Tr
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. In Bengal The Rāmpāl plate of Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. In Northern India The Gupta surname is also used by Banias and Jains in the northern part of India. Notables Monarchs *Gupta (king), founder of the Gupta dynasty *Ghatotkacha (king) * Chandragupta I * Samudragupta *Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya *Kumaragupta I * Skandagupta, last Gupta emperor * Vishnugupta (Gupta Empire) * Budhagupta Academic * Akhil Gupta (born 1959), professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the field o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |