|
Valveless Pulsejet
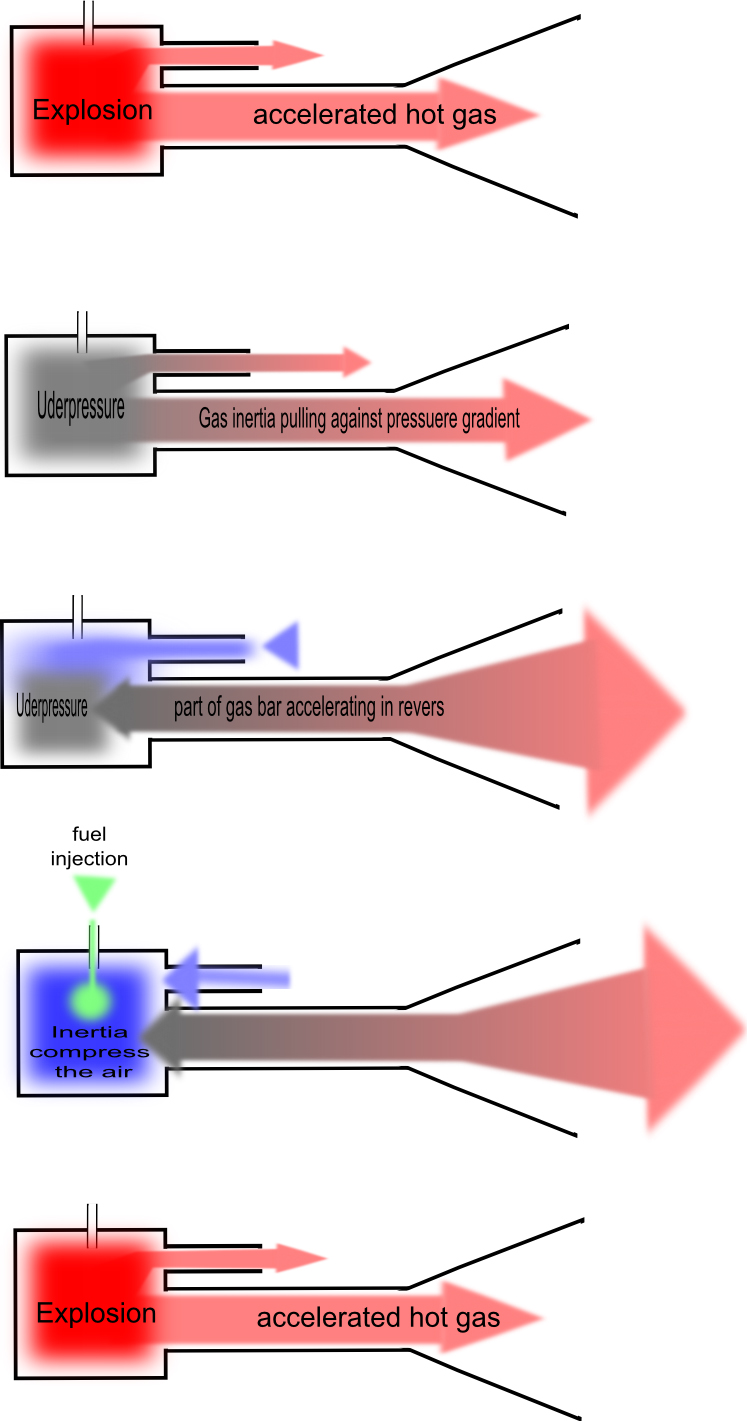
A valveless pulsejet (or pulse jet) is the simplest known jet propulsion device. Valveless pulsejets are low in cost, light weight, powerful and easy to operate. They have all the advantages (and most of the disadvantages) of conventional valved pulsejets, but without the reed valves that need frequent replacement - a valveless pulsejet can operate for its entire useful life with practically zero maintenance. They have been used to power model aircraft, experimental go-karts, and unmanned military aircraft such as cruise missiles and target drones. Basic characteristics A pulsejet engine is an air-breathing reaction engine that employs an ongoing sequence of discrete combustion events rather than one sustained combustion event. This clearly distinguishes it from other reaction engine types such as rockets, turbojets, and ramjets, which are all constant combustion devices. All other reaction engines are driven by maintaining high internal pressure; pulsejets are driven by an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrol
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lead and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet of hydrogen". It was an accidental discovery while attempting to isolate potassium metal. By heating potassium carbonate with carbon at very high temperatures, he produced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recuperator
A recuperator is a special purpose counter-flow energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air handling system, or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the waste heat. Generally, they are used to extract heat from the exhaust and use it to preheat air entering the combustion system. In this way they use waste energy to heat the air, offsetting some of the fuel, and thereby improve the energy efficiency of the system as a whole. Description In many types of processes, combustion is used to generate heat, and the recuperator serves to recuperate, or reclaim this heat, in order to reuse or recycle it. The term recuperator refers as well to liquid-liquid counterflow heat exchangers used for heat recovery in the chemical and refinery industries and in closed processes such as ammonia-water or LiBr-water absorption refrigeration cycle. Recuperators are often used in association with the burner portion of a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radicals
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition System
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol (gasoline) road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles. Compression ignition Diesel engines ignite the fuel-air mixture by the heat of compression and do not need a spark. They usually have glowplugs that preheat the combustion chamber to allow starting in cold weather. Other engines may use a flame, or a heated tube, for ignition. While this was common for very early engines it is now rare. The first electric spark ignition was probably Alessandro Volta's toy electric pistol from the 1780s. Siegfried Marcus patented his "Electrical igniting device for gas engines" on 7 October 1884. History Magneto systems The simplest form of spark ignition is that using a magneto. The engine spins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rarefaction
Rarefaction is the reduction of an item's density, the opposite of compression. Like compression, which can travel in waves (sound waves, for instance), rarefaction waves also exist in nature. A common rarefaction wave is the area of low relative pressure following a shock wave (see picture). Rarefaction waves expand with time (much like sea waves spread out as they reach a beach); in most cases rarefaction waves keep the same overall profile ('shape') at all times throughout the wave's movement: it is a ''self-similar expansion''. Each part of the wave travels at the local speed of sound, in the local medium. This expansion behaviour contrasts with that of pressure increases, which gets narrower with time until they steepen into shock waves. When angle of incidence is greater than angle of refraction, then light travels from denser to rarer medium. When angle of incidence is smaller than angle of refraction then light travels from rarer to denser medium Physical examples A nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Wave
Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. Mechanical longitudinal waves are also called ''compressional'' or compression waves, because they produce compression and rarefaction when traveling through a medium, and pressure waves, because they produce increases and decreases in pressure. A wave along the length of a stretched Slinky toy, where the distance between coils increases and decreases, is a good visualization. Real-world examples include sound waves (vibrations in pressure, a particle of displacement, and particle velocity propagated in an elastic medium) and seismic P-waves (created by earthquakes and explosions). The other main type of wave is the transverse wave, in which the displacements of the medium are at right angles to the direction of propagation. Transverse waves, for instance, describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |