|
Value Added Tax Act 1994
The Value Added Tax Act 1994c 23 is a UK tax law, concerning taxation of goods and services that fall within the scope of Value Added Tax (VAT). It came into force on 1 September 1994. The Value Added Tax Act 1983 was repealed and replaced by this legislation. Contents *Part I - The charge to tax *Part II - Reliefs, exemptions and repayments *Part III - Application of Act in particular cases. *Part IV - Administration, collection and enforcement *Part V - Appeals *Part VI - Supplementary provisions To encourage outsourcing it provides a mechanism through which government departments, including NHS trust An NHS trust is an organisational unit within the National Health Services of England and Wales, generally serving either a geographical area or a specialised function (such as an ambulance service). In any particular location there may be several ...s, can qualify for refunds on contracted out services. See also * Income and Corporation Taxes Act 1988 * Corporation Tax Act 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Tax Law
Taxation in the United Kingdom may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government (HM Revenue & Customs), devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion. History A uniform Land tax, originally was introduced in England during the late 17th century, formed the main source of government revenue throughout the 18th century and the early 19th century.Stephen Dowell, ''History of Taxation and Taxes in England'' (Routledge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
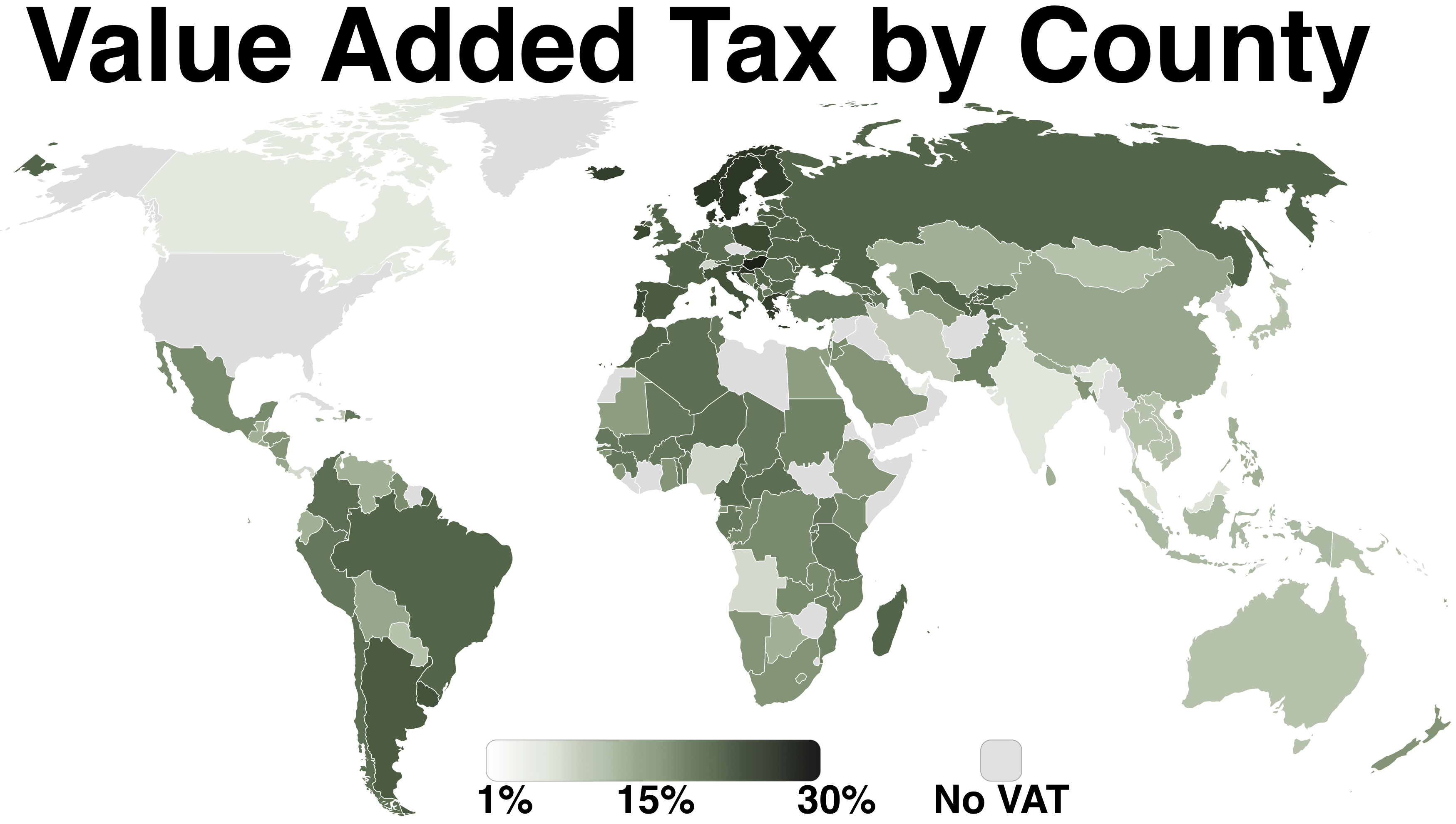
Value Added Tax (United Kingdom)
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities. Not all localities require VAT to be charged, and exports are often exempt. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. The terms VAT, GST, and the more general consumption tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NHS Trust
An NHS trust is an organisational unit within the National Health Services of England and Wales, generally serving either a geographical area or a specialised function (such as an ambulance service). In any particular location there may be several trusts involved in the different aspects of providing healthcare to the local population. there were altogether 217 trusts, and they employ around 800,000 of the NHS's 1.2 million staff. History NHS trusts were established under the National Health Service and Community Care Act 1990 and were set up in five waves. Each one was established by a Statutory Instrument. NHS trusts are not trusts in the legal sense but are in effect public sector corporations. Each trust is headed by a board consisting of executive and non-executive directors, and is chaired by a non-executive director. There were about 2,200 non-executives across 470 organisations in the NHS in England in 2015. Non-executive directors are recruited by open advertisement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income And Corporation Taxes Act 1988
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (e.g., mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a basis t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporation Tax Act 2010
The Corporation Tax Act 2010 (c.4) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that received Royal Assent on 3 March 2010. It was first presented ( first reading) in the House of Commons on 19 November 2009 and received its third reading on 4 February 2010. It was first read in the House of Lords The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminst ... on 4 February 2010 and received its second and third readings on 2 March 2010. Overview Section 1 of the Act gives a summary of the contents of the 2010 Act, and the changes it made, primarily to the Income and Corporation Taxes Act 1988. References External linksCorporation Tax Act 2010 on legislation.gov.uk United Kingdom Acts of Parliament 2010 Tax legislation in the United Kingdom {{UK-statute-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value-added Tax (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, the value added tax (VAT) was introduced in 1973, replacing Purchase Tax, and is the third-largest source of government revenue, after income tax and National Insurance. It is administered and collected by HM Revenue and Customs, primarily through the Value Added Tax Act 1994. VAT is levied on most goods and services provided by registered businesses in the UK and some goods and services imported from outside the UK. The default VAT rate is the standard rate, 20% since 4 January 2011. Some goods and services are subject to VAT at a reduced rate of 5% (such as domestic fuel) or 0% (such as most food and children's clothing). Others are exempt from VAT or outside the system altogether. VAT is an indirect tax because the tax is paid to the government by the seller (the business) rather than the person who ultimately bears the economic burden of the tax (the consumer). Opponents of VAT claim it is a regressive tax because the poorest people spend a highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)