|
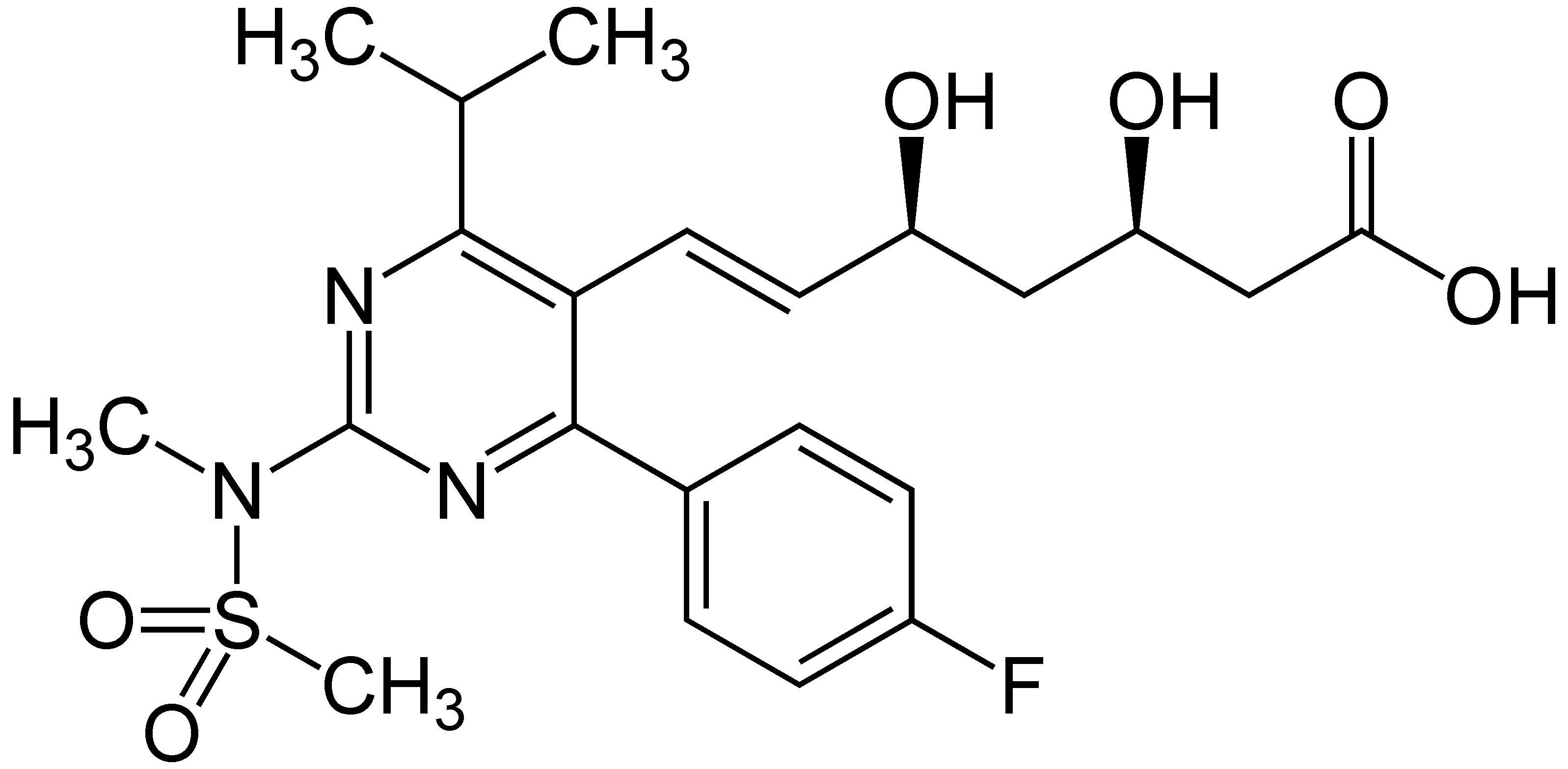
Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec
Valoctocogene roxaparvovec, sold under the brand name Roctavian, is a gene therapy used for the treatment of hemophilia A. It was developed by BioMarin Pharmaceutical. Valoctocogene roxaparvovec is made of a virus (AAV5) that has been modified to contain the gene for factor VIII, which is lacking in people with hemophilia A. It is given by intravenous infusion. The most common side effects include increased levels of the liver enzymes alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase (signs of possible liver problems), increased levels of the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (sign of possible tissue damage), nausea (feeling sick), and headache. Valoctocogene roxaparvovec was approved for medical use in the European Union in August 2022, and in the United States in June 2023. Medical uses Valoctocogene roxaparvovec is indicated for the treatment of severe haemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency) in adults without a history of factor VIII inhibitors and without dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. Factor VIII is produced in liver sinusoidal cells and endothelial cells outside the liver throughout the body. This protein circulates in the bloodstream in an inactive form, bound to another molecule called von Willebrand factor, until an injury that damages blood vessels occurs. In response to injury, coagulation factor VIII is activated and separates from von Willebrand factor. The active protein (sometimes written as coagulation factor VIIIa) interacts with another coagulation factor called factor IX. This interaction sets off a chain of additional chemical reactions that form a blood clot. Factor VIII participates in blood coagulation; it is a cofactor for factor IXa, which, in the presence of Ca2+ and phospholipids, forms a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. It is thought to be able to cure many genetic disorders or treat them over time. Between 1989 and December 2018, over 2,900 clinical trials were conducted, with more than half of them in phase I.Gene Therapy Cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs That Are A Gene Therapy
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee For Medicinal Products For Human Use
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), formerly known as Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products (CPMP), is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding medicinal products for human use. See also * Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use The Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) is the European Medicines Agency's committee responsible for elaborating the agency's opinions on all issues regarding veterinary medicines. Text was copied from this source which is © ... References External links Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Health and the European Union {{eu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priority Review
Priority review is a program of the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expedite the review process for drugs that are expected to have a particularly great impact on the treatment of a disease. The priority review voucher program is a program that grants a voucher for priority review to a drug developer as an incentive to develop treatments for disease indications with limited profitability. Priority review vouchers are currently earned by pharmaceutical companies for the development and approval of drugs treating neglected tropical diseases, rare pediatric diseases, and "medical countermeasures" for terrorism. The voucher can be used for future drugs that could have wider indications for use, but the company is required to pay a fee (approximately $2.8 million) to use the voucher. When seeking approval for a drug, manufacturers can apply to the FDA for priority review. This is granted when a drug is intended to treat a serious condition and would "provide a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone (). (Note that cortisone and aldosterone are isomers.) The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, anti-proliferative, and vasoconstrictive effects. Anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by blocking the action of inflammatory medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phases Of Clinical Research
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Summary Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV trials are 'post-marketing' or 'surveillance' studies conducted to monitor safety over sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis), which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures. Coagulopathies are sometimes erroneously referred to as "clotting disorders", but a clotting disorder is the opposite, defined as a predisposition to excessive clot formation (thrombus), also known as a hypercoagulable state or thrombophilia. Signs and symptoms Coagulopathy may cause uncontrolled internal or external bleeding. Left untreated, uncontrolled bleeding may cause damage to joints, muscles, or internal organs and may be life-threatening. People should seek immediate medical care for serious symptoms, including heavy external bleeding, blood in the urine or stool, double vision, severe head or neck pain, repeated vomiting, difficulty walking, convulsions, or se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologics License Application
A biologics license application (BLA) is defined by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as follows: The biologics license application is a request for permission to introduce, or deliver for introduction, a biologic product into interstate commerce (21 CFR 601.2). The BLA is regulated under 21 CFR 600 – 680. A BLA is submitted by any legal person or entity who is engaged in manufacture or an applicant for a license who takes responsibility for compliance with product and establishment standards. Form 356h specifies the requirements for a BLA. This includes: * Applicant information * Product/manufacturing information * Pre-clinical studies * Clinical studies * Labeling Some biological products are regulated by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) while others are regulated by Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) is one of six main centers for the Food and Drug Administration, U.S. Food and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |