|
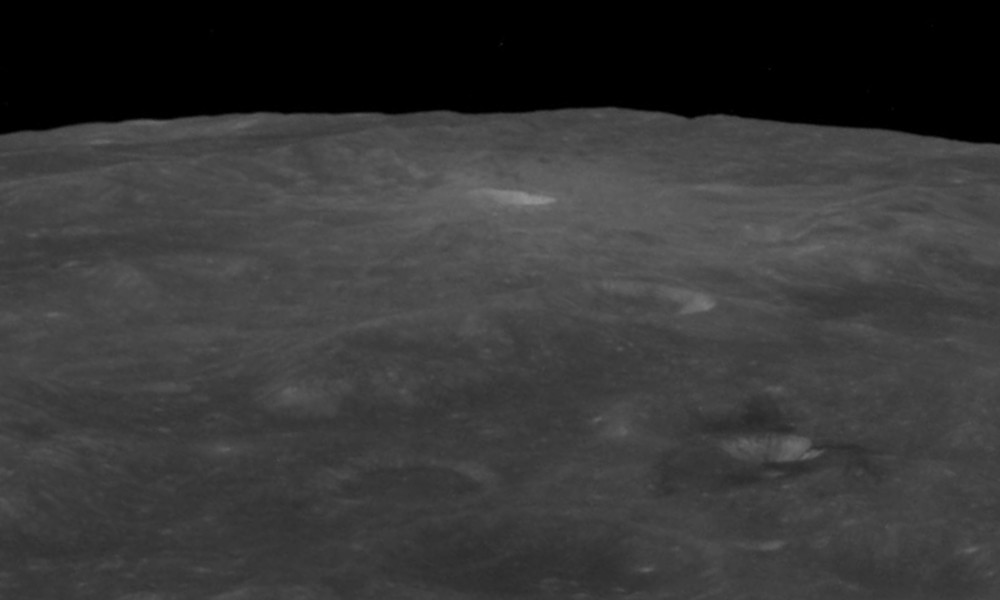
Vallis Planck
Vallis Planck is a long, linear valley located on the far side of the Moon. It is oriented radially to the huge Schrödinger basin, and was most likely formed by that impact. The selenographic coordinates of this feature are , and it has a length of 451 km. This cleft in the surface crosses the western part of the huge walled plain Planck, and it was named after that feature (which has an eponym of Max Planck Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (, ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918. Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical p ...). The southern edge closest to Schrödinger begins near the northeastern outer rampart of the crater Grotrian. It then continues to the north-northwest, where it suffers a disruption where it crosses the crater Fechner. The remainder of the feature continues to the northwestern outer rim of the walled plain Planck, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far Side (Moon)
The far side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces away from Earth, opposite to the near side, because of synchronous rotation in the Moon's orbit. Compared to the near side, the far side's terrain is rugged, with a multitude of impact craters and relatively few flat and dark lunar maria ("seas"), giving it an appearance closer to other barren places in the Solar System such as Mercury and Callisto. It has one of the largest craters in the Solar System, the South Pole–Aitken basin. The hemisphere is sometimes called the "dark side of the Moon", where "dark" means "unknown" instead of "lacking sunlight" each side of the Moon experiences two weeks of sunlight while the opposite side experiences two weeks of night. About 18 percent of the far side is occasionally visible from Earth due to libration. The remaining 82 percent remained unobserved until 1959, when it was photographed by the Soviet Luna 3 space probe. The Soviet Academy of Sciences published the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel. as a function of axial position ../nowiki>" Spherical coordinates In a spherical coordinate system, the radius describes the distance of a point from a fixed origin. Its position if further defined by the polar angle measured between the radial direction and a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuth angle, the angle between the orthogonal projection of the radial direction on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, and a fixed reference direction in that plane. See also *Bend radius *Filling radius in Riemannian geometry *Radius of convergence * Radius of convexity *Radius of curvature *Radius of gyration ''Radius of gyration'' or gyradius of a body about the axis of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrödinger (crater)
Schrödinger is a large lunar impact crater of the form traditionally called a walled plain and is named after Erwin Schrödinger. It is located near the south lunar pole on the far side of the Moon, and can only be viewed from orbit. The smaller crater Ganswindt is attached to the southwestern rim of Schrödinger, and intrudes slightly into the inner wall. Adjacent to the south is the crater Nefed'ev. Farther to the southwest is the crater Amundsen. Schrödinger is perhaps the moon's best example of a peak-ring basin. It possesses a wide outer rim that has been slightly rounded due to subsequent impacts. But the rim remains well-defined, and traces of terraces can be seen along the inner surface. The ejecta on the exterior forms an irregular outer rampart that extends for up to 100 kilometers. Within the interior is a second ring approximately half the diameter of the outer rim. This forms a circular range of rugged mountains that surrounds the center, with the exceptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenographic Coordinates
The selenographic coordinate system is used to refer to locations on the surface of Earth's moon. Any position on the lunar surface can be referenced by specifying two numerical values, which are comparable to the latitude and longitude of Earth. The longitude gives the position east or west of the Moon's prime meridian, which is the line passing from the lunar north pole through the point on the lunar surface directly facing Earth to the lunar south pole. (See also Earth's prime meridian.) This can be thought of as the midpoint of the visible Moon as seen from the Earth. The latitude gives the position north or south of the lunar equator. Both of these coordinates are given in degrees. Astronomers defined the fundamental location in the selenographic coordinate system by the small, bowl-shaped satellite crater ' Mösting A'. The coordinates of this crater are defined as: : Later, the coordinate system has become more precisely defined due to the Lunar Laser Ranging E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck (crater)
Planck is a large lunar impact crater, approximately 319 kilometers in diameter, that is located in the southern hemisphere of the Moon, on the far side as seen from the Earth. It lies to the west of the walled plain Poincaré, another enormous formation only slightly larger than Planck. Lying across the southeast rim of Planck is the crater Prandtl, to the northeast is Hildegard, and to the west is Fechner. Planck is located within the South Pole–Aitken basin. Formation According to a 2012 study, Planck formed roughly 4.09 Ga (billion years) ago, partially resurfacing the area of the South Pole-Aitken basin that it impacted. Description Like many lunar formations of this size, the outer rim has been damaged and eroded by lesser impacts, leaving a rugged ring of peaks and ridges that is notched and incised by small craters. The western rim of this walled plain is neatly overlain by a long lunar valley designated the Vallis Planck. Despite its name, however, this valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''. Usage of the word The term ''eponym'' functions in multiple related ways, all based on an explicit relationship between two named things. A person, place, or thing named after a particular person share an eponymous relationship. In this way, Elizabeth I of England is the eponym of the Elizabethan era. When Henry Ford is referred to as "the ''eponymous'' founder of the Ford Motor Company", his surname "Ford" serves as the eponym. The term also refers to the title character of a fictional work (such as Rocky Balboa of the Rocky film series, ''Rocky'' film series), as well as to ''self-titled'' works named after their creators (such as the album The Doors (album), ''The Doors'' by the band the Doors). Walt Disney created the eponymous The Walt Disney Company, Walt Disney Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (, ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918. Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical physics, but his fame as a physicist rests primarily on his role as the originator of quantum theory, which revolutionized human understanding of atomic and subatomic processes. In 1948, the German scientific institution Kaiser Wilhelm Society (of which Planck was twice president) was renamed Max Planck Society (MPG). The MPG now includes 83 institutions representing a wide range of scientific directions. Life and career Planck came from a traditional, intellectual family. His paternal great-grandfather and grandfather were both theology professors in Göttingen; his father was a law professor at the University of Kiel and Munich. One of his uncles was also a judge. Planck was born in 1858 in Kiel, Holstein, to Johann Julius Wilhelm Plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotrian (crater)
Grotrian is a lunar impact crater that is located on the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the north of the huge walled plain Schrödinger, within the radius of that formation's outer blanket of ejecta. The long Vallis Planck Vallis Planck is a long, linear valley located on the far side of the Moon. It is oriented radially to the huge Schrödinger basin, and was most likely formed by that impact. The selenographic coordinates of this feature are , and it has a length ... formation begins just to the north of Grotrian, and continues to the north-northwest towards Pikel'ner. The outer wall of this crater forms a very nearly circular shape, with the smaller crater Hawke across the southern rim breaking up the symmetry. The interior surfaces form relatively smooth slopes that continue down to the material deposited across the bottom. Apart from Hawke and a small crater on the northern edge of the rim, this formation has not been significantly eroded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fechner (crater)
Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim. Attached to the western rim of Fechner is Fechner T, a small, bowl-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo ray system. This satellite crater is surrounded by a blanket of light-hued ejecta that spills across the southwestern half of Fechner's interior floor. The crater rim of Fechner is relatively worn and eroded, with the eastern half of the rim reshaped due to the valley and proximity to Planck. The interior floor is marked by several small craters. The crater is named after Gustav Theodor Fechner, a German physicist, psychologist, and philosopher (1801-1887 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |