|
Vacanti Mouse
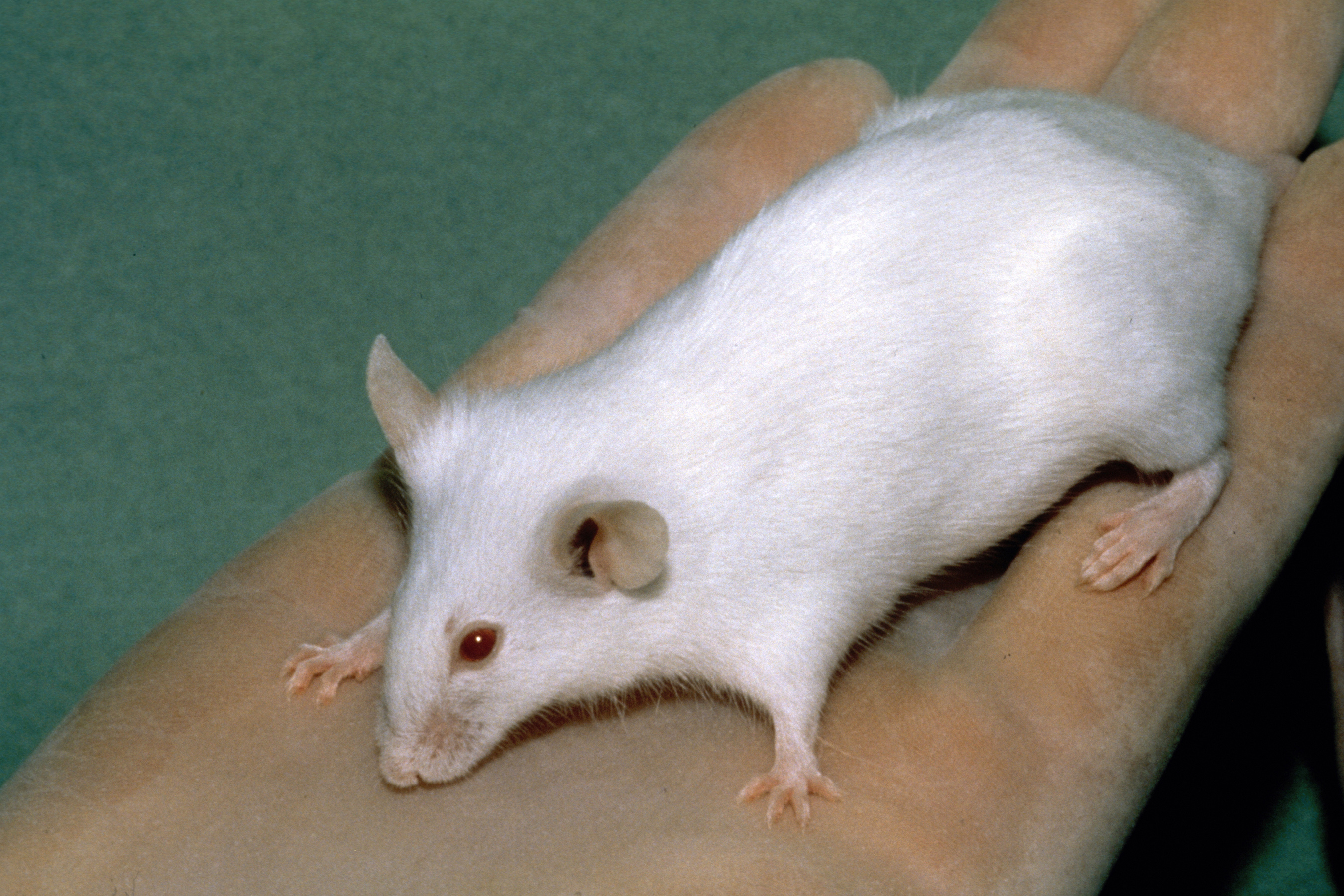
The Vacanti mouse was a laboratory mouse (circa 1996) that had what looked like a human ear grown on its back. The "ear" was actually an ear-shaped cartilage structure grown by seeding cow cartilage cells into biodegradable ear-shaped mold and then implanted under the skin of the mouse, with an external ear-shaped splint to maintain the desired shape. Then the cartilage naturally grew by itself within the restricted shape and size. The splint was removed briefly to take the publicity pictures, which is very controversial. The ''EMOUSE'', as it became known, was created by Charles A. Vacanti in the Department of Anesthesiology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Linda Griffith at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Joseph P. Vacanti in the Department of Surgery at Children's Hospital. Charles Vacanti later moved to the Department of Anesthesiology at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. The results were based on the works of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacanti Mouse
The Vacanti mouse was a laboratory mouse (circa 1996) that had what looked like a human ear grown on its back. The "ear" was actually an ear-shaped cartilage structure grown by seeding cow cartilage cells into biodegradable ear-shaped mold and then implanted under the skin of the mouse, with an external ear-shaped splint to maintain the desired shape. Then the cartilage naturally grew by itself within the restricted shape and size. The splint was removed briefly to take the publicity pictures, which is very controversial. The ''EMOUSE'', as it became known, was created by Charles A. Vacanti in the Department of Anesthesiology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Linda Griffith at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and Joseph P. Vacanti in the Department of Surgery at Children's Hospital. Charles Vacanti later moved to the Department of Anesthesiology at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. The results were based on the works of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Hospital (Boston)
A children's hospital is a hospital which offers its services exclusively to children. Children's Hospital may also refer to: * ''Childrens Hospital'', a 2008–2016 American TV series * ''Children's Hospital'' (Australian TV series), a 1997–1998 television series that aired on ABC * ''Children's Hospital'' (UK TV series), a 1993–2003 documentary television series * ''The Children's Hospital'', a 2006 novel by Chris Adrian See also *Children's Hospital Association *Foundling hospital * "In the Children's Hospital", an 1880 poem by Alfred, Lord Tennyson *List of children's hospitals **List of children's hospitals in the United States A children's hospital is a medical facility that offers its services exclusively to children and adolescents. Most children's hospitals can serve children from birth up to the age of 21. The number of children's hospitals proliferated in the 20th ... * :Children's hospitals * :Children's hospitals by country * :Children's hospitals in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the order Rodentia, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. Although a wild animal, the house mouse has benefited significantly from associating with human habitation to the point that truly wild populations are significantly less common than the semi-tame populations near human activity. The house mouse has been domesticated as the pet or fancy mouse, and as the laboratory mouse, which is one of the most important model organisms in biology and medicine. The complete mouse reference genome was sequenced in 2002. Characteristics House mice have an adult body length (nose to base of tail) of and a tail length of . The weight is typically . In the wild they vary in color from grey and light brown to black (individual hairs are actually agouti coloured), but domesticated fancy mice and laboratory mice ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Memes
An Internet meme, commonly known simply as a meme ( ), is an idea, behavior, style, or image that is spread via the Internet, often through social media platforms. What is considered a meme may vary across different communities on the Internet and is subject to change over time. Traditionally, the term mostly applied to images, concepts, or catchphrases, but it has since become broader and more multi-faceted, evolving to include more elaborate structures such as challenges, GIFs, videos, and viral sensations. The retronym derives from the earlier concept of a meme as any cultural idea, behavior or style that propagates through imitation. Internet memes are considered a part of Internet culture. They can spread from person to person via social networks, blogs, email, or news sources. Instant communication on the Internet facilitates word of mouth transmission, resulting in fads and sensations that tend to grow rapidly. For example, posting a photo of someone planking online bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (GM) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transplant Rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when Organ transplant, transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient and by use of immunosuppressant drugs after transplant. Types of transplant rejection Transplant rejection can be classified into three types: hyperacute, acute, and chronic. These types are differentiated by how quickly the recipient's immune system is activated and the specific aspect or aspects of immunity involved. Hyperacute rejection Hyperacute rejection is a form of rejection that manifests itself in the minutes to hours following transplantation. It is caused by the presence of pre-existing Antibody, antibodies in the recipient that recognize antigens in the donor organ. These antigens are located on the endothelial lining of blood vessels within the transplanted organ and, once antibodies bind, will lead to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scid Mouse
The severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is a severe immunodeficiency genetic disorder that is characterized by the complete inability of the adaptive immune system to mount, coordinate, and sustain an appropriate immune response, usually due to absent or atypical T cell, T and B cell, B lymphocytes. In humans, SCID is colloquially known as Severe combined immunodeficiency, "bubble boy" disease, as victims may require complete clinical isolation to prevent lethal infection from environmental microbes. Several forms of SCID occur in animal species. Not all forms of SCID have the same cause; different genes and modes of inheritance have been implicated in different species. Horses Equine SCID is an autosome, autosomal recessive gene, recessive disorder that affects the Arabian horse. Similar to the "bubble boy" condition in humans, an affected foal is born with no immune system, and thus generally dies of an opportunistic infection, usually within the first four to six months of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nude Mouse
A nude mouse is a laboratory mouse from a strain with a genetic mutation that causes a deteriorated or absent thymus, resulting in an inhibited immune system due to a greatly reduced number of T cells. The phenotype (main outward appearance) of the mouse is a lack of body hair, which gives it the "nude" nickname. The nude mouse is valuable to research because it can receive many different types of tissue and tumor grafts, as it mounts no rejection response. These xenografts are commonly used in research to test new methods of imaging and treating tumors. The genetic basis of the nude mouse mutation is a disruption of the FOXN1 gene. Nomenclature The nomenclature for the nude mouse has changed several times since their discovery. Originally they were described as ''nu'' and this was updated to ''Hfh11nu'' when the mutated gene was identified as a mutation in the HNF-3/forkhead homolog 11 gene. Then in 2000 the gene responsible for the mutation was identified as a member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Massachusetts Medical School
The University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School is a public medical school in Worcester, Massachusetts. It is part of the University of Massachusetts system. It is home to three schools: the T.H. Chan School of Medicine, the Morningside Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and the Tan Chingfen Graduate School of Nursing, as well as a biomedical research enterprise and a range of public-service initiatives throughout the state. History UMMS was established by the 162nd Massachusetts General Court in 1962 to provide residents of the commonwealth an opportunity to study medicine at an affordable cost and to increase the number of primary-care physicians practicing in the commonwealth's under-served areas. The School of Medicine accepted its first class of 16 students in 1970. Six years later a 371-bed hospital opened on campus; the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences opened in 1979, and the Graduate School of Nursing opened in 1986. In 1998 the UMMS system of hospitals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the most prestigious and highly ranked academic institutions in the world. Founded in response to the increasing industrialization of the United States, MIT adopted a European polytechnic university model and stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT is one of three private land grant universities in the United States, the others being Cornell University and Tuskegee University. The institute has an urban campus that extends more than a mile (1.6 km) alongside the Charles River, and encompasses a number of major off-campus facilities such as the MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the Bates Center, and the Haystack Observatory, as well as affiliated laboratories such as the Broad and Whitehead Institutes. , 98 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Mouse
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species ''Mus musculus''. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues. Other mouse species sometimes used in laboratory research include two American species, the white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') and the North American deer mouse (''Peromyscus maniculatus''). History as a biological model Mice have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linda Griffith
Linda Gay Griffith (born August 30, 1960 Atlanta, Georgia) is an American biological engineer, and Professor of Biological Engineering and Mechanical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where she also directs the Center for Gynepathology Research. She is a 2006 recipient of a MacArthur Fellowship, commonly referred to as the "MacArthur genius award." In 2011, Griffith was elected a member of the National Academy of Engineering for contributions to 3D functional biomaterials, engineered hepatic tissues, and cell transplant devices. In 2021, she was elected into the National Academy of Medicine for "long-standing leadership in research, education, and medical translation; for pioneering work in tissue engineering, biomaterials, and systems biology, including developing the first “liver chip” technology; inventing 3D biomaterials printing and organotypic models for systems gynopathology; and for the establishment of the MIT Biological Engineering Department." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)