|
VSIA
{{redirect, VSIA, the airport in Port Blair, Veer Savarkar International Airport Virtual Socket Interface Alliance (VSIA) is a body of SIP (Semiconductor / Silicon intellectual property) standards. History VSIA was founded in 1996 and dissolved in 2008, and was an open, international organization of companies such as Mentor Graphics, Cadence Design Systems, Magma Design Automation, ARM Holdings, and Synopsys, from various segments of the SoC ( System-on-a-chip) industry. Importance of VSIA VSIA's mission was to enhance the productivity of the SoC design community dramatically. VSIA has developed an international standard, the QIP metric (Quality Intellectual Property Metric) for measuring SIP quality and examining the practices used to design, integrate and support the IP. This is important and, to have a measure of the quality, VSIA also works on other issues such as IP protection, IP transfer, IP integration and IP reuse standards (IP hardening is required for easy IP reuse) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Intellectual Property Metric
The quality intellectual property metric (QIP) is an international standard, developed by Virtual Socket Interface Alliance ( VSIA) for measuring Intellectual Property (IP) or Silicon intellectual property (SIP) quality and examining the practices used to design, integrate and support the SIP. SIP hardening is required to facilitate the reuse of IP in integrated circuit design. Background and importance Many computer processors use a system-on-a-chip (SoC) design, which is intended to include all of a device's functions on a single chip. As a result, these chips need to include numerous technical standards that the device will use. One solution to designing such a chip is the reuse of high quality IP. Reusing IP from others means that the chip designer does not need to redesign these elements. IP quality is the key to successful SoC designs, but it is one of the SoC’s most challenging problems. * QIP metric allows both the IP designers and IP integrators to measure the qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QIP Metric
The quality intellectual property metric (QIP) is an international standard, developed by Virtual Socket Interface Alliance ( VSIA) for measuring Intellectual Property (IP) or Silicon intellectual property (SIP) quality and examining the practices used to design, integrate and support the SIP. SIP hardening is required to facilitate the reuse of IP in integrated circuit design. Background and importance Many computer processors use a system-on-a-chip (SoC) design, which is intended to include all of a device's functions on a single chip. As a result, these chips need to include numerous technical standards that the device will use. One solution to designing such a chip is the reuse of high quality IP. Reusing IP from others means that the chip designer does not need to redesign these elements. IP quality is the key to successful SoC designs, but it is one of the SoC’s most challenging problems. * QIP metric allows both the IP designers and IP integrators to measure the qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
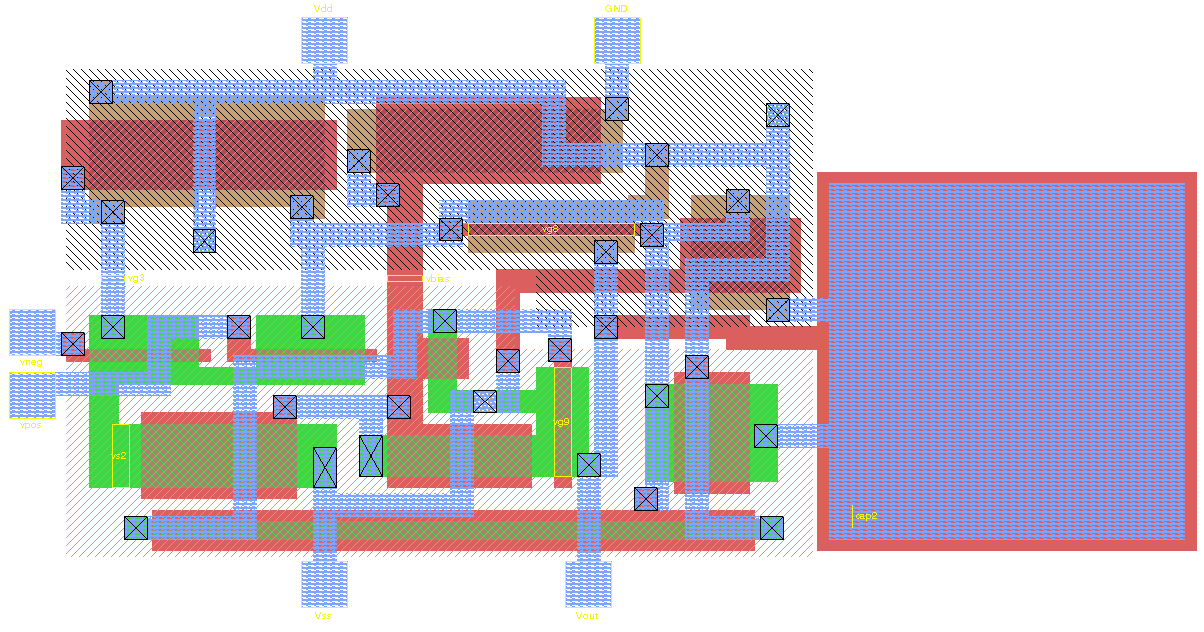
Silicon Intellectual Property
In electronic design, a semiconductor intellectual property core (SIP core), IP core, or IP block is a reusable unit of logic, cell, or integrated circuit layout design that is the intellectual property of one party. IP cores can be licensed to another party or owned and used by a single party. The term comes from the licensing of the patent or source code copyright that exists in the design. Designers of application-specific integrated circuits (ASIC) and systems of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) logic can use IP cores as building blocks. History The licensing and use of IP cores in chip design came into common practice in the 1990s. There were many licensors and also many foundries competing on the market. In 2013, the most widely licensed IP cores are from Arm Holdings (43.2% market share), Synopsys Inc. (13.9% market share), Imagination Technologies (9% market share) and Cadence Design Systems (5.1% market share). Types of IP cores The use of an IP core in chip d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentor Graphics
Siemens EDA is a US-based electronic design automation (EDA) multinational corporation for electrical engineering and electronics, headquartered in Wilsonville, Oregon. Founded in 1981 as Mentor Graphics, the company was acquired by Siemens in 2017. The company distributes products that assist in electronic design automation, simulation tools for analog mixed-signal design, VPN solutions, and fluid dynamics and heat transfer tools. The company leveraged Apollo Computer workstations to differentiate itself within the computer-aided engineering (CAE) market with its software and hardware. History Siemens EDA was founded as Mentor Graphics in 1981 by Tom Bruggere, Gerry Langeler, and Dave Moffenbeier, all formerly of Tektronix. The company raised $55 million in funding through an initial public offering in 1984. Mentor initially wrote software that ran only in Apollo workstations. When Mentor entered the CAE market the company had two technical differentiators: the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence Design Systems
Cadence Design Systems, Inc. (stylized as cādence), headquartered in San Jose, California, is an American multinational corporation, multinational computational software company, founded in 1988 by the merger of SDA Systems and ECAD, Inc. The company produces software, Electronic hardware, hardware and silicon structures for designing integrated circuits, System on chip, systems on chips (SoCs) and printed circuit boards. History Origins Cadence Design Systems began as an Electronic design automation, electronic design automation (EDA) company, formed by the 1988 merger of Solomon Design Automation (SDA), co-founded in 1983 by A. Richard Newton, Richard Newton, Alberto Sangiovanni-Vincentelli and James Solomon, and ECAD, Inc., ECAD, a public company co-founded by Ping Chao, Glen Antle and Paul Huang in 1982. SDA's CEO Joseph Costello (software executive), Joseph Costello was appointed as CEO of the newly combined company. Executive leadership Following the resignation of Cadenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma Design Automation
Magma headquarters at Santa Clara Magma Design Automation was a software company in the electronic design automation (EDA) industry. The company was founded in 1997 and maintained headquarters in San Jose, California, with facilities throughout North America, Europe and Asia. Magma software products were used in major elements of Integrated circuit design, including: synthesis, placement, routing, power management, circuit simulation, verification and analog/mixed-signal design. Magma was acquired by Synopsys in a merger finalized February 22, 2012 at a cash value of about $523 million, or $7.35 per share. History Magma was founded in 1997 by a team including Rajeev Madhavan, who served as chairman, CEO and president from the company's inception. The company initially competed primarily with Cadence and Avanti Corporation in physical design but eventually broadened its product portfolio and competed with all three of the largest established EDA companies: Cadence, Mentor Grap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Holdings
Arm is a British semiconductor and software design company based in Cambridge, England. Its primary business is in the design of ARM processors (CPUs). It also designs other chips, provides software development tools under the DS-5, RealView and Keil brands, and provides systems and platforms, system-on-a-chip (SoC) infrastructure and software. As a "holding" company, it also holds shares of other companies. Since 2016, it has been owned by Japanese conglomerate SoftBank Group. While ARM CPUs first appeared in the Acorn Archimedes, a desktop computer, today's systems include mostly embedded systems, including ARM CPUs used in virtually all smartphones. Systems such as iPhones and Android smartphones frequently include many chips, from many different providers, that include one or more licensed Arm cores, in addition to those in the main Arm-based processor. Arm's core designs are also used in chips that support all the most common network-related technologies. Processors ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synopsys
Synopsys is an American electronic design automation (EDA) company that focuses on silicon design and verification, silicon intellectual property and software security and quality. Products include tools for logic synthesis and physical design of integrated circuits, simulators for development and debugging environments that assist in the design of the logic for chips and computer systems. In recent years, Synopsys has expanded its products and services to include application security testing. Synopsys has gained attention due to its relationship with various Chinese state entities. In 2018, Synopsys formed a partnership with the People's Liberation Army National Defence University and, in 2022, the company came under investigation by the United States Department of Justice for technology transfers to sanctioned entities in China. History Synopsys was founded by Aart J de Geus and David Gregory in 1986 in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. The company was initially est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System-on-a-chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, on-chip input/output devices, input/output interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. It may contain digital, analog, mixed-signal, and often radio frequency signal processing functions (otherwise it is considered only an application processor). Higher-performance SoCs are often paired with dedicated and physically separate memory and secondary storage (such as LPDDR and eUFS or eMMC, respectively) chips, that may be layered on top of the SoC in what's known as a package on package (PoP) configuration, or be placed close to the SoC. Additionally, SoCs may use separate wireless modems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IP Hardening
In electronic design, a semiconductor intellectual property core (SIP core), IP core, or IP block is a reusable unit of logic, cell, or integrated circuit layout design that is the intellectual property of one party. IP cores can be licensed to another party or owned and used by a single party. The term comes from the licensing of the patent or source code copyright that exists in the design. Designers of application-specific integrated circuits (ASIC) and systems of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) logic can use IP cores as building blocks. History The licensing and use of IP cores in chip design came into common practice in the 1990s. There were many licensors and also many foundries competing on the market. In 2013, the most widely licensed IP cores are from Arm Holdings (43.2% market share), Synopsys Inc. (13.9% market share), Imagination Technologies (9% market share) and Cadence Design Systems (5.1% market share). Types of IP cores The use of an IP core in ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit Design
Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography. IC design can be divided into the broad categories of digital and analog IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGAs, memories (RAM, ROM, and flash) and digital ASICs. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and RF IC design. Analog IC design is used in the design of op-amps, linear regulators, phase locked loops, oscillators and active filters. Analog design is more concerned with the physics of the semiconductor devices such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong Science And Technology Parks Corporation
The Hong Kong Science and Technology Parks Corporation (HKSTP) is a public corporation set up by the Hong Kong Government in 2001 to foster innovation and technology development in Hong Kong Roles and responsibilities HKSTP manages facilities and provides value-added services for the technology, research and development sector in Hong Kong.GovHK Website. Hong Kong Science & Technology Parks Corporation (HKSTPC). Retrieved 21 November 2017 from https://www.gov.hk/en/business/supportenterprises/innovation/index.htm These facilities include Hong Kong Science Park (for technology companies), InnoCentre (for design enterprises), and three industrial estates at Tai Po, Yuen Long and Tseung Kwan O (for a range of skill-intensive business sectors). According to the Government, Hong Kong Science Park is the 'flagship technology infrastructure' in Hong Kong.Report of the Advisory Committee on Innovation and Technology, p15. March 2017. Advisory Committee on Innovation and Tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |