|
VPEC-T
VPEC-T analysis (value, policies, events, content and trust) is a thinking framework comprising a collection of mental filters or guides. It provides a "simplified 'language' for preventing loss in translation from business needs to IT solutions" and is used when analyzing the expectations of multiple parties having different views of a system in which they all have an interest in common, but have different priorities and different responsibilities. System, here is used in the broad sense of a set of interacting or interdependent entities, real or abstract, forming an integrated whole. It is applied to 'systems' that range from those as small as a performance appraisal, to ones as large as a criminal justice system. VPEC-T ("vee-pec-tee") is used where interaction between agents and communication between parties can easily result in ambiguity. This form of analysis is particularly applicable where it is likely that the interaction and communication context is unordered, comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
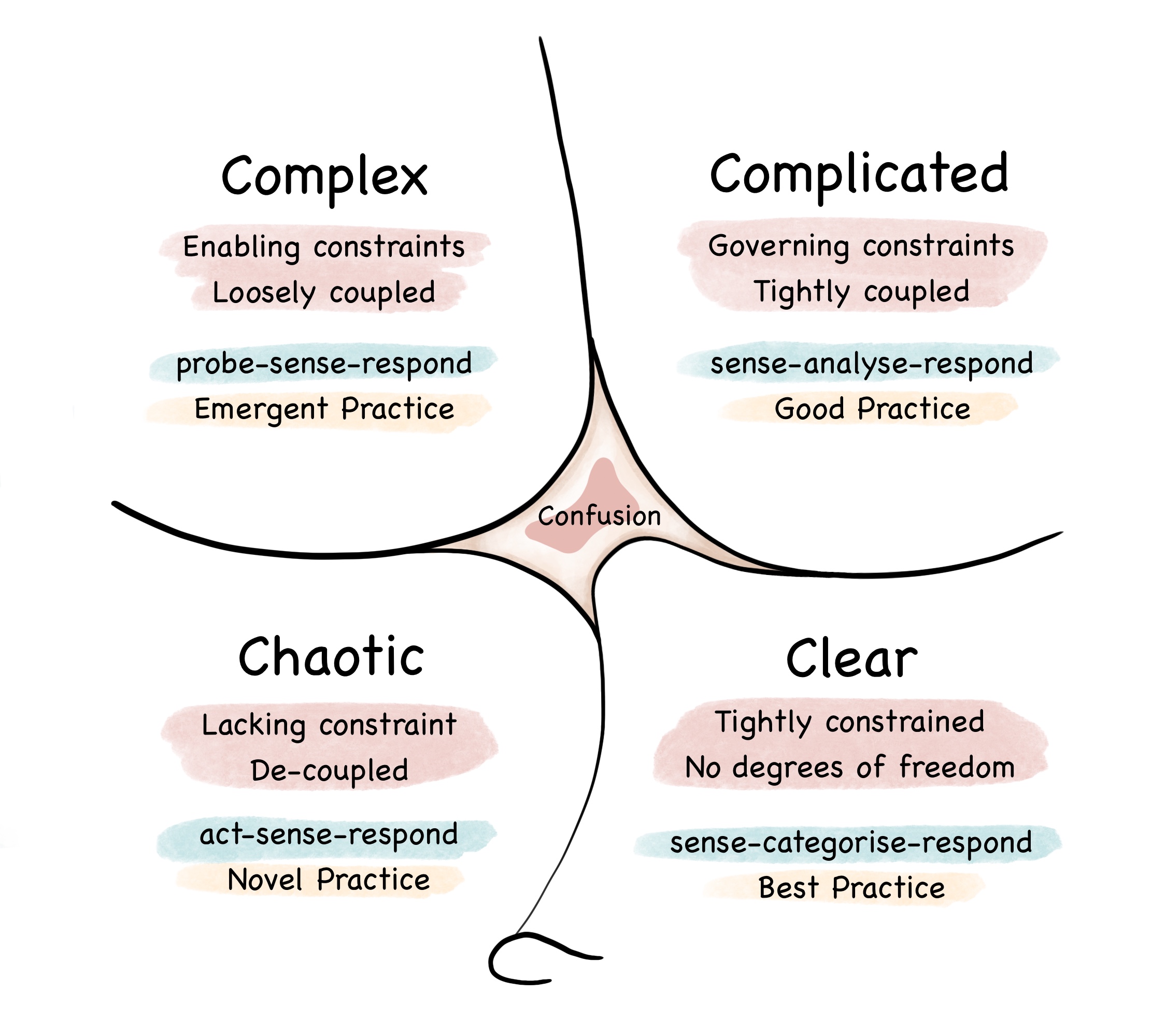
Cynefin Framework
The Cynefin framework ( ) is a conceptual framework used to aid decision-making. Created in 1999 by Dave Snowden when he worked for IBM Global Services, it has been described as a " sense-making device". ''Cynefin'' is a Welsh word for ''habitat''. Cynefin offers five decision-making contexts or "domains"—''clear'' (known as ''simple'' until 2014, then ''obvious'' until being recently renamed), ''complicated'', ''complex'', ''chaotic'', and ''confusion''—that help managers to identify how they perceive situations and make sense of their own and other people's behaviour. The framework draws on research into systems theory, complexity theory, network theory and learning theories. Background Terminology The idea of the Cynefin framework is that it offers decision-makers a "sense of place" from which to view their perceptions. ''Cynefin'' is a Welsh word meaning ''habitat'', ''haunt'', ''acquainted'', ''familiar''. Snowden uses the term to refer to the idea that we all have c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek language, Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek–English Lexicon'', on Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capgemini
Capgemini SE is a multinational information technology (IT) services and consulting company, headquartered in Paris, France. History Capgemini was founded by Serge Kampf in 1967 as an enterprise management and data processing company. The company was founded as the ''Société pour la Gestion de l'Entreprise et le Traitement de l'Information'' (Sogeti). In 1974, Sogeti acquired Gemini Computers Systems, an American company based in New York. In 1975, having made two major acquisitions of CAP (Centre d'Analyse et de Programmation) and Gemini Computer Systems, and following resolution of a dispute with the similarly named CAP UK over the international use of the name 'CAP', Sogeti renamed itself as CAP Gemini Sogeti. Cap Gemini Sogeti launched US operations in 1981, following the acquisition of Milwaukee-based DASD Corporation, specializing in data conversion and employing 500 people in 20 branches throughout the US. Following this acquisition, The U.S. Operation was known as Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value (economics)
In economics, economic value is a measure of the benefit provided by a goods, good or service (economics), service to an Agent (economics), economic agent. It is generally measured through units of currency, and the interpretation is therefore "what is the maximum amount of money a specific actor is Willingness to pay, willing and able to pay for the good or service"? Among the competing schools of economic theory there are differing Theory of value (economics), theories of value. Economic value is ''not'' the same as Price, market price, nor is economic value the same thing as market value. If a consumer is willing to buy a good, it implies that the customer places a higher value on the good than the market price. The difference between the value to the consumer and the market price is called "Economic surplus, consumer surplus". It is easy to see situations where the actual value is considerably larger than the market price: purchase of drinking water is one example. Overvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts. It has been used as a way of exploring and developing effective action in complex contexts, enablinsystems change Systems thinking draws on and contributes to systems theory and the system sciences. History Frameworks and methodologies Frameworks and methodologies for systems thinking include: * Critical systems thinking * Soft systems methodology * Systemic design * System dynamics * Viable system model Multi-method approach See also * Management cybernetics * Operational research Operations research ( en-GB, operational research) (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a discipline that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve deci ... References Systems science Cybernetics Systems theory Systems th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensemaking
Sensemaking or sense-making is the process by which people give meaning to their collective experiences. It has been defined as "the ongoing retrospective development of plausible images that rationalize what people are doing" ( Weick, Sutcliffe, & Obstfeld, 2005, p. 409). The concept was introduced to organizational studies by Karl E. Weick in the 1970s and has affected both theory and practice. Weick intended to encourage a shift away from the traditional focus of organization theorists on decision-making and towards the processes that constitute the meaning of the decisions that are enacted in behavior. Definition There is no single agreed upon definition of sensemaking, but there is consensus that it is a process that allows people to understand ambiguous, equivocal or confusing issues or events. Disagreements about the meaning of sensemaking exist around whether sensemaking is a mental process within the individual, a social process or a process that occurs as part of discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Systems
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication systems, complex software and electronic systems, social and economic organizations (like cities), an ecosystem, a living cell, and ultimately the entire universe. Complex systems are systems whose behavior is intrinsically difficult to model due to the dependencies, competitions, relationships, or other types of interactions between their parts or between a given system and its environment. Systems that are "complex" have distinct properties that arise from these relationships, such as nonlinearity, emergence, spontaneous order, adaptation, and feedback loops, among others. Because such systems appear in a wide variety of fields, the commonalities among them have become the topic of their independent area of research. In many cases, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Event Processing
Event processing is a method of tracking and analyzing (processing) streams of information (data) about things that happen (events), and deriving a conclusion from them. Complex event processing, or CEP, consists of a set of concepts and techniques developed in the early 1990s for processing real-time events and extracting information from event streams as they arrive. The goal of complex event processing is to identify meaningful events (such as opportunities or threats) in real-time situations and respond to them as quickly as possible. These events may be happening across the various layers of an organization as sales leads, orders or customer service calls. Or, they may be news items, text messages, social media posts, stock market feeds, traffic reports, weather reports, or other kinds of data. An event may also be defined as a "change of state," when a measurement exceeds a predefined threshold of time, temperature, or other value. Analysts have suggested that CEP will give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Adaptive Systems
A complex adaptive system is a system that is ''complex'' in that it is a dynamic network of interactions, but the behavior of the ensemble may not be predictable according to the behavior of the components. It is ''adaptive'' in that the individual and collective behavior mutate and self-organize corresponding to the change-initiating micro-event or collection of events. It is a "complex macroscopic collection" of relatively "similar and partially connected micro-structures" formed in order to adapt to the changing environment and increase their survivability as a macro-structure. The Complex Adaptive Systems approach builds on replicator dynamics. The study of complex adaptive systems, a subset of nonlinear dynamical systems, is an interdisciplinary matter that attempts to blend insights from the natural and social sciences to develop system-level models and insights that allow for heterogeneous agents, phase transition, and emergent behavior. Overview The term ''complex a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediation
Mediation is a structured, interactive process where an impartial third party neutral assists disputing parties in resolving conflict through the use of specialized communication and negotiation techniques. All participants in mediation are encouraged to actively participate in the process. Mediation is a "party-centered" process in that it is focused primarily upon the needs, rights, and interests of the parties. The mediator uses a wide variety of techniques to guide the process in a constructive direction and to help the parties find their optimal solution. A mediator is facilitative in that she/he manages the interaction between parties and facilitates open communication. Mediation is also evaluative in that the mediator analyzes issues and relevant norms ("reality-testing"), while refraining from providing prescriptive advice to the parties (e.g., "You should do..."). Mediation, as used in law, is a form of alternative dispute resolution resolving disputes between two o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Interaction
A social relation or also described as a social interaction or social experience is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more individuals within and/or between groups. The group can be a language or kinship group, a social institution or organization, an economic class, a nation, or gender. Social relations are derived from human behavioral ecology, and, as an aggregate, form a coherent social structure whose constituent parts are best understood relative to each other and to the ecosystem as a whole. Fundamental inquiries into the nature of social relations feature in the work of sociologists such as Max Weber in his theory of social action. Social relationships are composed of both positive (affiliative) and negative (agonistic) interactions, representing opposing effects. Categorizing social interactions enables observational and other social research, such as Gemeinsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Systems
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, information storage, store, and information distribution, distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure (or roles), and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and data processing, processing of data of which the data is used to provide information, contribute to knowledge as well as digital products that facilitate decision making. A computer information system is a system that is composed of people and computers that processes or interprets information. The term is also sometimes used to simply refer to a computer, computer system with software installed. "Information systems" is also an academic field study about systems with a specific reference to information and the complementary networks of computer hardware and soft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |