|
VL-Bus
The VESA Local Bus (usually abbreviated to VL-Bus or VLB) is a short-lived expansion bus introduced during the i486 generation of x86 IBM-compatible personal computers. Created by VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association), the VESA Local Bus worked alongside the then-dominant ISA bus to provide a standardized high-speed conduit intended primarily to accelerate video (graphics) operations. VLB provides a standardized fast path that add-in (video) card makers could tap for greatly accelerated memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while still using the familiar ISA bus to handle basic device duties such as interrupts and port-mapped I/O. Some high-end 386dx motherboards also had a VL-Bus slot. Historical overview In the early 1990s, the I/O bandwidth of the prevailing ISA bus, 8.33 MB/s for standard 16 bit 8.33 MHz slots, had become a critical bottleneck to PC video and graphics performance. The need for faster graphics was driven by increased adoption of graphical user interfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Bus
In computer architecture, a local bus is a computer bus that connects directly, or almost directly, from the central processing unit (CPU) to one or more slots on the expansion bus. The significance of direct connection to the CPU is avoiding the bottleneck created by the expansion bus, thus providing fast throughput. There are several local buses built into various types of computers to increase the speed of data transfer (i.e. bandwidth). Local buses for expanded memory and video boards are the most common. VESA Local Bus and Processor Direct Slot were examples of a local bus design. Although VL-Bus was later succeeded by AGP, it is not correct to categorize AGP as a local bus. Whereas VL-Bus operated on the CPU's memory bus In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This ex ... a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 80486
The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386. It was the first tightly- pipelined x86 design as well as the first x86 chip to include more than one million transistors. It offered a large on-chip cache and an integrated floating-point unit. A typical 50 MHz i486 executes around 40 million instructions per second (MIPS), reaching 50 MIPS peak performance. It is approximately twice as fast as the i386 or i286 per clock cycle. The i486's improved performance is thanks to its five-stage pipeline with all stages bound to a single cycle. The enhanced FPU unit on the chip was significantly faster than the i387 FPU per cycle. The intel 80387 FPU ("i387") was a separate, optional math coprocessor that was installed in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OPTi
OPTi Inc. was a fabless semiconductor company based in Milpitas, California, that primarily manufactured chipsets for personal computers. The company dissolved in 2001 and transferred its assets to the unaffiliated non-practicing entity OPTi Technologies (itself later renamed OPTi Inc.) History OPTi Inc. was formed in 1989 in Milpitas, California, by former employees of Chips and Technologies. Cash-strapped on a "shoe-string udget, among the company's first products was a trio of VLSI chipsets for i386SX- and i486-equipped AT motherboards. The first was a direct-mapped CPU cache for 386SX motherboards; the second was a burst-mode CPU cache for 486 motherboards; and the third was a interleaved memory module for 486 motherboards. OPTi measured the latter two chipsets to reduce the component count on 486 motherboards clocked at 40 MHz (or 11 MIPS) to as few as 20. In 1991, Chips and Technologies filed a patent infringement suit against OPTi, alleging unauthorized u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VESA
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve the information, search for Entity Number C1645094. and has its office in San Jose. It claims a membership of over 300 companies. In November 1988, NEC Home Electronics announced its creation of the association to develop and promote a Super VGA computer display standard as a successor to IBM's proprietary Video Graphics Array (VGA) display standard. Super VGA enabled graphics display resolutions up to 800×600 pixels, compared to VGA's maximum resolution of 640×480 pixels—a 56% increase. The organization has since issued several additional standards related to computer video displays. Widely used VESA standards include DisplayHDR, DisplayPort, and Flat Display Mounting Interface. Standards * Feature connector (VFC), obsolete connector that was ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
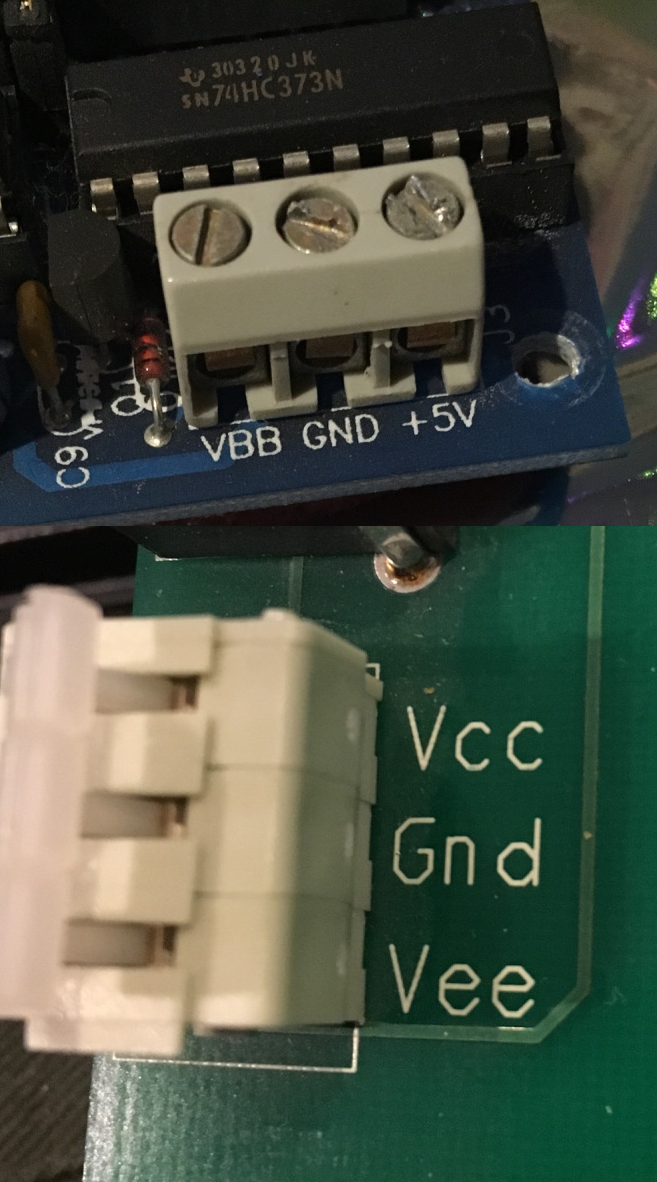
IC Power-supply Pin
IC power-supply pins denote a voltage and current supply terminals in electric, electronics engineering, and in Integrated circuit design. Integrated circuits (ICs) have at least two pins that connect to the power rails of the circuit in which they are installed. These are known as the power-supply pins. However, the labeling of the pins varies by IC family and manufacturer. The double subscript notation usually corresponds to a first letter in a given IC family (transistors) notation of the terminals (e.g. VDD supply for a drain terminal in FETs etc.). The simplest labels are V+ and V−, but internal design and historical traditions have led to a variety of other labels being used. V+ and V− may also refer to the non-inverting (+) and inverting (−) voltage inputs of ICs like op amps. For power supplies, sometimes one of the supply rails is referred to as ground (abbreviated "GND") positive and negative voltages are relative to the ground. In digital electronics, negativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VLB Pins , the forerunners of today Auxiliary Coastguard in the United Kingdom
{{disambiguation ...
VLB may refer to: Science and technology * VESA Local Bus, a local bus based on the Intel 80486 CPU * Very large board, a large printed circuit board * Vincaleukoblastine, or vinblastine, an antitumor alkaloid Other uses * VLB Berlin (Versuch- u. Lehranstalt für Brauerei in Berlin), a brewing school and trade organization in Berlin * Volunteer Life Brigade A Volunteer Life Brigade is a search and rescue organisation which assists HM Coastguard in the United Kingdom in coastal emergencies. Around 40 VLBs were established in the mid-to-late 19th century; today just three remain, continuing to provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Chipsets
This article provides a list of motherboard chipsets made by Intel, divided into three main categories: those that use the PCI bus for interconnection (the 4xx series), those that connect using specialized "hub links" (the 8xx series), and those that connect using PCI Express (the 9xx series). The chipsets are listed in chronological order. Pre-chipset situation An earlier chipset support for Intel 8085 microprocessor can be found at MCS-85 family section. Early IBM XT-compatible mainboards did not have a chipset yet, but relied instead on a collection of discrete TTL chips by Intel: * the 8284 clock generator * the 8288 bus controller * the 8254 Programmable Interval Timer * the 8255 parallel I/O interface * the 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller * the 8237 DMA controller Early chipsets To integrate the functions needed on a mainboard into a smaller amount of ICs, Intel licensed the ZyMOS POACH chipset for its Intel 80286 and Intel 80386SX processors (the 822 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabyte Ga486im Motherboard Observe Croped
The gigabyte () is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The prefix ''giga'' means 109 in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is one billion bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte is GB. This definition is used in all contexts of science (especially data science), engineering, business, and many areas of computing, including storage capacities of hard drives, solid state drives, and tapes, as well as data transmission speeds. However, the term is also used in some fields of computer science and information technology to denote (10243 or 230) bytes, particularly for sizes of RAM. Thus, prior to 1998, some usage of ''gigabyte'' has been ambiguous. To resolve this difficulty, IEC 80000-13 clarifies that a ''gigabyte'' (GB) is 109 bytes and specifies the term ''gibibyte'' (GiB) to denote 230 bytes. These differences are still readily seen for example, when a 400 GB drive's capacity is displayed by Microsoft Windows as 372 GB inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Multiplier
In computing, the clock multiplier (or CPU multiplier or bus/core ratio) sets the ratio of an internal CPU clock rate to the externally supplied clock. A CPU with a 10x multiplier will thus see 10 internal cycles (produced by PLL-based frequency multiplier circuitry) for every external clock cycle. For example, a system with an external clock of 100 MHz and a 36x clock multiplier will have an internal CPU clock of 3.6 GHz. The external address and data buses of the CPU (often collectively termed front side bus (FSB) in PC contexts) also use the external clock as a fundamental timing base; however, they could also employ a (small) multiple of this base frequency (typically two or four) to transfer data faster. The internal frequency of microprocessors is usually based on FSB frequency. To calculate internal frequency the CPU multiplies bus frequency by a number called the clock multiplier. For calculation, the CPU uses actual bus frequency, and not effective bus frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-side Bus
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture has been replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect or Direct Media Interface in modern volume CPUs. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announced, in the 1990s. "Front side" refers to the extern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Corruption
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of it. Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |