|
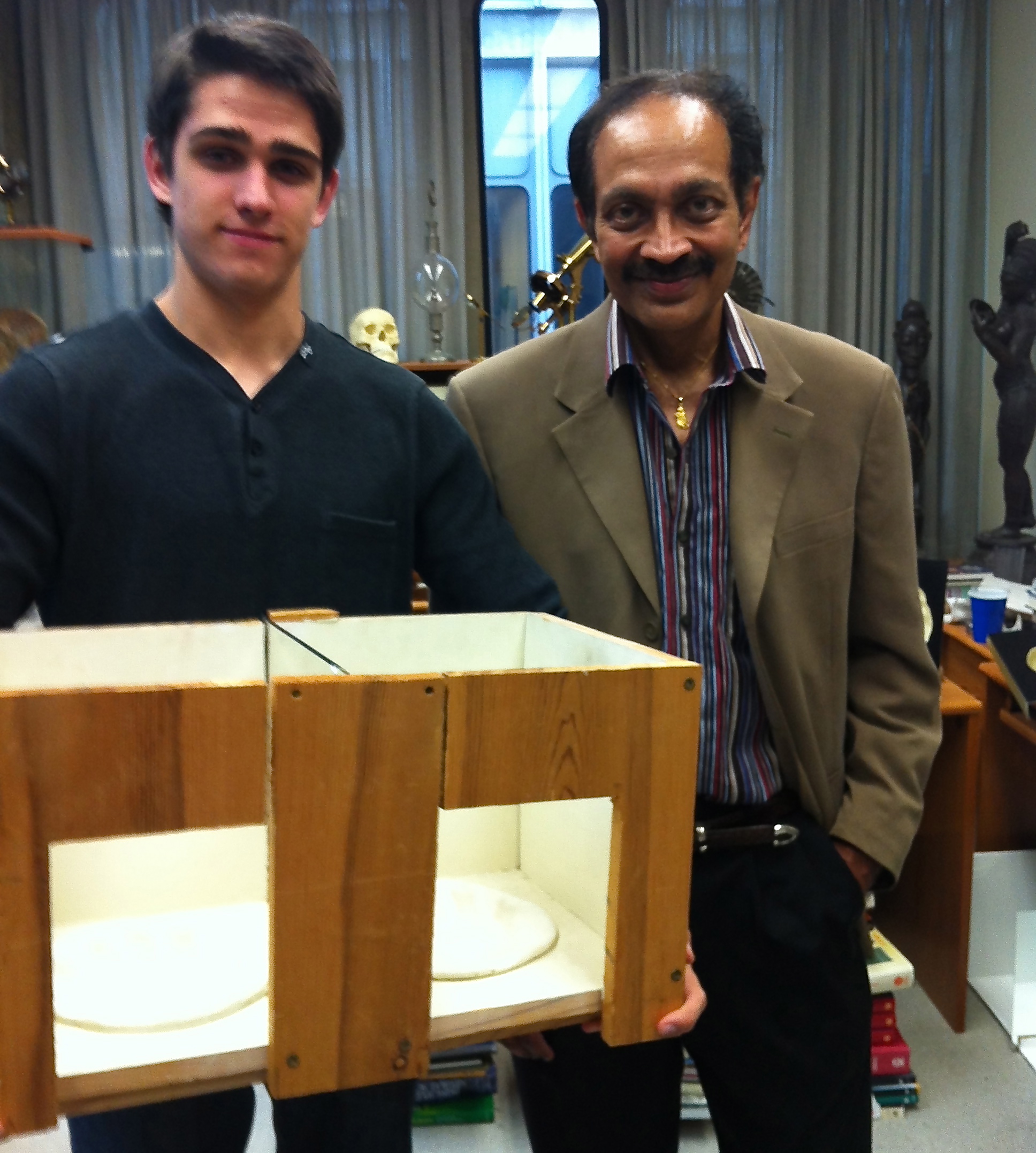
V. S. Ramachandran
Vilayanur Subramanian Ramachandran (born 10 August 1951) is an Indian-American neuroscientist. He is known for his wide-ranging experiments and theories in behavioral neurology, including the invention of the mirror box. Ramachandran is a distinguished professor in UCSD's Department of Psychology, where he is the director of the Center for Brain and Cognition. After earning a medical degree in India, Ramachandran studied experimental neuroscience at Cambridge, obtaining his PhD there in 1978. Most of his research has been in the fields of behavioral neurology and visual psychophysics. After early work on human vision, Ramachandran turned to work on wider aspects of neurology including phantom limbs and phantom pain. Ramachandran invented mirror therapy which is now used to treat amputees with phantom limb pain and also to help restore motor control in stroke victims with weakened limbs. Ramachandran's popular books ''Phantoms in the Brain'' (1998), ''The Tell-Tale Brain'' (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time 100
''Time'' 100 (often stylized as ''TIME'' 100) is an annual listicle of the 100 most influential people in the world, assembled by the American news magazine ''Time''. First published in 1999 as the result of a debate among American academics, politicians, and journalists, the list is now a highly publicized annual event. Appearing on the list is often seen as an honor, and ''Time'' makes it clear that entrants are recognized for changing the world, regardless of the consequences of their actions. The final list of influential individuals is exclusively chosen by ''Time'' editors, with nominations coming from the ''Time'' 100 alumni and the magazine's international writing staff. Only the winner of the Reader's Poll, conducted days before the official list is revealed, is chosen by the general public. The corresponding commemorative gala is held annually in Manhattan. In 2019, Time began publishing the ''Time'' 100 Next list, which "spotlights 100 rising stars who are shaping the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Therapy
Mirror therapy (MT) or mirror visual feedback (MVF) is a therapy for pain or disability that affects one side of the patient more than the other side. It was invented by Vilayanur S. Ramachandran to treat post-amputation patients who had phantom limb pain (PLP). Ramachandran created a visual (and psychological) illusion of two intact limbs by putting the patient's affected limb into a "mirror box," with a mirror down the center (facing toward a patient's intact limb). The patient then looks into the mirror on the side with the good limb and makes "mirror symmetric" movements, as a symphony conductor might, or as a person does when they clap their hands. The goal is for the patient to imagine regaining control over a missing limb. Because the subject is seeing the reflected image of the good limb moving, it appears as if the phantom limb is also moving. Through the use of this artificial visual feedback, it becomes possible for the patient to "move" the phantom limb and to unclench ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alladi Krishnaswamy Iyer
Dewan Bahadur Sir Alladi Krishnaswamy Iyer (14 May 1883 – 3 October 1953) was an Indian lawyer and member of the Constituent Assembly of India, which was responsible for framing the Constitution of India. He also served as the advocate general of Madras State from 1929 to 1944. Neuroscientist Vilayanur S. Ramachandran is his grandson. Alladi Ramakrishnan, an Indian physicist and the founder of the Institute of Mathematical Sciences was his son. Early life Krishnaswamy Iyer was born in 1883 to a Tamil family in the small village of Pudur in Madras State (present day Nellore district of Andhra Pradesh). His father, Ekamra Sastry, was a priest. Krishnaswamy passed his matriculation examination in 1899 and joined the Madras Christian College to study history. He used his spare time to attend classes in law and passed the B.L. exam and became one of the leading members of the bar. He was made a Dewan Bahadur in 1930 and was knighted in the 1932 New Year Honours list. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capgras Syndrome
Capgras delusion or Capgras syndrome is a psychiatric disorder in which a person holds a delusion that a friend, spouse, parent, or other close family member (or pet) has been replaced by an identical impostor. It is named after Joseph Capgras (1873–1950), the French psychiatrist who first described the disorder. The Capgras delusion is classified as a delusional misidentification syndrome, a class of delusional beliefs that involves the misidentification of people, places, or objects. It can occur in acute, transient, or chronic forms. Cases in which patients hold the belief that time has been "warped" or "substituted" have also been reported. The delusion most commonly occurs in individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia but has also been seen in brain injury, dementia with Lewy bodies, and other dementia. It presents often in individuals with a neurodegenerative disease, particularly at an older age. It has also been reported as occurring in association with diabetes, hypothy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Tell-Tale Brain
''The Tell-Tale Brain: A Neuroscientist's Quest for What Makes Us Human'' is a 2010 nonfiction book by V. S. Ramachandran that explores, from a neurological viewpoint, the uniqueness of human nature. Synopsis Ramachandran discusses seven main concepts which define the human aspect of self and how each may be disrupted by a specific neurological disorder. The concepts are: unity, continuity, embodiment, privacy, social embedding, free will, and self-awareness. In the first chapter, Ramachandran discusses the human ability to change and adapt, illustrating the concept from his work on phantom limbs. The second chapter describes some of his work with visual perception and cognition, addressing the concept of human awareness. In chapter three, he connects ideas about synesthesia to creativity. Chapters four and five talk about mirror neurons, while chapter six discusses human language. Ramachandran proposes "nine laws of aesthetics," which he discusses in chapters seven and eight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantoms In The Brain
''Phantoms in the Brain: Probing the Mysteries of the Human Mind'' (also published as ''Phantoms in the Brain: Human Nature and the Architecture of the Mind'') is a 1998 popular science book by neuroscientist V.S. Ramachandran and ''New York Times'' science writer Sandra Blakeslee, discussing neurophysiology and neuropsychology as revealed by case studies of neurological disorders. The book, which began as a lecture presented to the Society for Neuroscience, features a foreword by neuroscientist and author Oliver Sacks. Synopsis Ramachandran discusses his work with patients exhibiting phantom limbs, the Capgras delusion, pseudobulbar affect and hemispatial neglect following stroke, and religious experiences associated with epileptic seizure, among other disorders. Ramachandran uses these cases to illustrate the construction of body image, and the functioning of mood, decision-making, self-deception, and artistic skill. In the final chapter of the book, Ramachandran addresses th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantom Pain
Phantom pain is a perception that an individual experiences relating to a limb or an organ that is not physically part of the body, either because it was removed or was never there in the first place. However, phantom limb sensations can also occur following nerve avulsion or spinal cord injury. Sensations are recorded most frequently following the amputation of an arm or a leg, but may also occur following the removal of a breast, tooth, or an internal organ. Phantom limb pain is the feeling of pain in an absent limb or a portion of a limb. The pain sensation varies from individual to individual. Phantom limb sensation is any sensory phenomenon (except pain) which is felt at an absent limb or a portion of the limb. It has been known that at least 80% of amputees experience phantom sensations at some time of their lives. Some experience some level of this phantom pain and feeling in the missing limb for the rest of their lives. The term "phantom limb" was first coined by Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phantom Limbs
A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Approximately 80 to 100% of individuals with an amputation experience sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painful phantom limb sensation. These sensations are relatively common in amputees and usually resolve within two to three years without treatment. Research continues to explore the underlying mechanisms of phantom limb pain (PLP) and effective treatment options. Signs and symptoms Most (80% to 100%) amputees experience a phantom limb, with some of them having non-painful sensations. The amputee may feel very strongly that the phantom limb is still part of the body. People will sometimes feel as if they are gesturing, feel itches, twitch, or even try to pick things up. The missing limb often feels shorter and may feel as if it is in a distorted and painful position. Occasionally, the pain can be made worse by stress, anxiety and weather chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychophysics
Psychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions". ''Psychophysics'' also refers to a general class of methods that can be applied to study a perceptual system. Modern applications rely heavily on threshold measurement, ideal observer analysis, and signal detection theory. Psychophysics has widespread and important practical applications. For example, in the study of digital signal processing, psychophysics has informed the development of models and methods of lossy compression. These models explain why humans perceive very little loss of signal quality when audio and video sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Neurology
Behavioral neurology is a subspecialty of neurology that studies the impact of neurological damage and disease upon behavior, memory, and cognition, and the treatment thereof. Two fields associated with behavioral neurology are neuropsychiatry and neuropsychology. In the United States, 'Behavioral Neurology & Neuropsychiatry' has been recognized as a single subspecialty by the United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties (UCNS) since 2004. Syndromes and diseases commonly studied by behavioral neurology include: * Agraphia * Agnosias * Agraphesthesia * Alexia (acquired dyslexia) * Amnesias * Anosognosia * Aphasias * Apraxias * Aprosodias * Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder * Autism * Dementia * Dyslexia * Epilepsy * Hemispatial Neglect * Psychosis * Stroke * Traumatic brain injury History While descriptions of behavioral syndromes go back to the ancient Greeks and Egyptians, it was during the 19th century that behavioral neurology began to arise, first with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror Box
Mirror therapy (MT) or mirror visual feedback (MVF) is a therapy for pain or disability that affects one side of the patient more than the other side. It was invented by Vilayanur S. Ramachandran to treat post-amputation patients who had phantom limb pain (PLP). Ramachandran created a visual (and psychological) illusion of two intact limbs by putting the patient's affected limb into a "mirror box," with a mirror down the center (facing toward a patient's intact limb). The patient then looks into the mirror on the side with the good limb and makes "mirror symmetric" movements, as a symphony conductor might, or as a person does when they clap their hands. The goal is for the patient to imagine regaining control over a missing limb. Because the subject is seeing the reflected image of the good limb moving, it appears as if the phantom limb is also moving. Through the use of this artificial visual feedback, it becomes possible for the patient to "move" the phantom limb and to unclench ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |