|
Underwater Gliders
An underwater glider is a type of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) that employs variable-buoyancy propulsion instead of traditional propellers or thrusters. It employs variable buoyancy in a similar way to a profiling float, but unlike a float, which can move only up and down, an underwater glider is fitted with hydrofoils (underwater wings) that allow it to glide forward while descending through the water. At a certain depth, the glider switches to positive buoyancy to climb back up and forward, and the cycle is then repeated. While not as fast as conventional AUVs, gliders offer significantly greater range and endurance compared to traditional AUVs, extending ocean sampling missions from hours to weeks or months, and to thousands of kilometers of range. The typical up-and-down, sawtooth-like profile followed by a glider can provide data on temporal and spatial scales unattainable by powered AUVs and much more costly to sample using traditional shipboard techniques. A wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RU02 Flying In Sargasso Sea
''Ru, ru, or RU may refer to: Russia * Russia (ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code) * Russian language (ISO 639 alpha-2 code) * .ru, the Internet country code top-level domain for Russia China * Rù (入), the entering tone in Chinese language phonetics * Rú (儒), a Chinese language term for Confucianism * Ru (surname) (茹), a Chinese surname * Ru River (汝), in Henan, China * Ru ware, a type of Chinese pottery Educational institutions * Radboud University Nijmegen, in Nijmegen, Netherlands * Radford University, in Virginia, USA * Rai University in Gujarat, India * Rajshahi University in Bangladesh * Rama University in India * Ramkhamhaeng University in Thailand * Regis University in Colorado, USA * Reykjavík University Iceland * Rhodes University in Grahamstown, South Africa * Rockefeller University in New York, USA * Rockhurst University in Missouri, USA * Roosevelt University in Chicago, Illinois, USA * Rowan University in New Jersey, USA * Ruse University in Bulgari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example of convection, specifically atmospheric convection. Thermals on Earth The Sun warms the ground, which in turn warms the air directly above. The warm air near the surface expands, becoming less dense than the surrounding air. The lighter air rises and cools due to its expansion in the lower pressure at higher altitudes. It stops rising when it has cooled to the same temperature, thus density, as the surrounding air. Associated with a thermal is a downward flow surrounding the thermal column. The downward-moving exterior is caused by colder air being displaced at the top of the thermal. The size and strength of thermals are influenced by the properties of the lower atmosphere (the ''troposphere''). When the air is cold, bubbles of warm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backscatter
In physics, backscatter (or backscattering) is the reflection of waves, particles, or signals back to the direction from which they came. It is usually a diffuse reflection due to scattering, as opposed to specular reflection as from a mirror, although specular backscattering can occur at normal incidence with a surface. Backscattering has important applications in astronomy, photography, and medical ultrasonography. The opposite effect is forward scatter, e.g. when a translucent material like a cloud diffuses sunlight, giving soft light. Backscatter of waves in physical space Backscattering can occur in quite different physical situations, where the incoming waves or particles are deflected from their original direction by different mechanisms: *Diffuse reflection from large particles and Mie scattering, causing alpenglow and gegenschein, and showing up in weather radar; * Inelastic collisions between electromagnetic waves and the transmitting medium (Brillouin scattering and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductivity (electrolytic)
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems. In many cases, conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids (TDS). High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0.05 μS/cm at 25 °C, typical drinking water is in the range of 200–800 μS/cm, while sea water is about 50 mS/cm ncorrect according to source(or 50,000 μS/cm). Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge. Dilute solutions follow Kohlrausch's Laws of concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
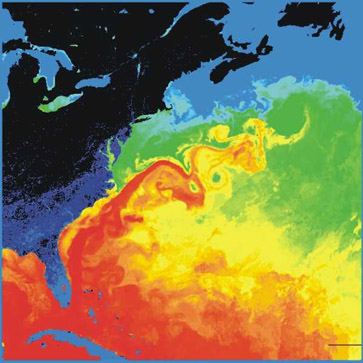
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the United States then veers east near 36 latitude (North Carolina) and moves toward Northwest Europe as the North Atlantic Current. The process of Boundary current, western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northwards accelerating current off the east coast of North America. At about , it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the coastal areas of the east coast of the United States from Florida to southeast Virginia (near 36 north latitude), and to a greater degree the climate of Northwest Europe. There is consensus that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transatlantic Crossing
Transatlantic crossings are passages of passengers and cargo across the Atlantic Ocean between Europe or Africa and the Americas. The majority of passenger traffic is across the North Atlantic between Western Europe and North America. Centuries after the dwindling of sporadic Viking trade with Markland, a regular and lasting transatlantic trade route was established in 1566 with the Spanish West Indies fleets, following the voyages of Christopher Columbus. By sea Prior to the 19th century, transatlantic crossings were undertaken in sailing ships, and the journeys were time-consuming and often perilous. The first trade route across the Atlantic was inaugurated by Spain a few decades after the European Discovery of the Americas, with the establishment of the West Indies fleets in 1566, a convoy system that regularly linked its territories in the Americas with Spain for over two centuries. Portugal created a similar maritime route between its ports in Brazil and the Portuguese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaglider
The Seaglider is a deep-diving Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) designed for missions lasting many months and covering thousands of miles. In military applications the Seaglider is more commonly referred to as an Unmanned Underwater Vehicle (UUV). Seaglider was initially developed by the University of Washington. iRobot received an exclusive five-year license to produce the Seaglider for customers outside the University of Washington in June 2008. May 2013 Kongsberg Underwater Technology, Inc. (part of Kongsberg Maritime) announced that they have completed negotiations with the University of Washington's Center for Commercialization to obtain the sole rights to produce, market and continue the development of Seaglider ™ technology. Systems Seaglider measures temperature, salinity and other quantities in the ocean, sending back data using global satellite telemetry. Seaglider UUVs are in use worldwide, collecting oceanic physical properties and performing various other missi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)