|
Umbilical Region
The umbilical region, is one of the nine regions of the abdomen. It is the region that surrounds the area around the umbilicus and is placed approximately half way between the xiphoid process and the pubic symphysis. This region of the abdomen contains part of the stomach, the head of the pancreas, the duodenum, a section of the transverse colon and the lower aspects of the left and right kidney. The upper three regions, from left to right, are the left hypochondriac, epigastric, and right hypochondriac regions. The middle three regions, from left to right, are the left lumbar, umbilical, and right lumbar regions. The bottom three regions, from left to right, are the left inguinal In human anatomy, the inguinal region refers to either the groin or the lower lateral regions of the abdomen. It may also refer to: * Conjoint tendon, previously known as the inguinal aponeurotic falx, a structure formed from the transversus abd ..., hypogastric, and right inguinal regions. Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrants And Regions Of Abdomen
The human abdomen is divided into quadrants and regions by anatomists and physicians for the purposes of study, diagnosis, and treatment. The division into four quadrants allows the localisation of pain and tenderness, scars, lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which organs and tissues may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant. These terms are not used in comparative anatomy, since most other animals do not stand erect. The left lower quadrant includes the left iliac fossa and half of the flank. The equivalent in other animals is ''left posterior quadrant''. The left upper quadrant extends from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage. This is the ''left anterior quadrant'' in other animals. The right upper quadrant extends from umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent in other animals is ''right anterior quadrant''. The right lower quadrant extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus, commonly known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. All placental mammals have a navel, although it is generally more conspicuous in humans. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphoid Process
The xiphoid process , or xiphisternum or metasternum, is a small cartilaginous process (extension) of the inferior (lower) part of the sternum, which is usually ossified in the adult human. It may also be referred to as the ensiform process. Both the Greek-derived ''xiphoid'' and its Latin equivalent ''ensiform'' mean 'swordlike' or 'sword-shaped' Structure The xiphoid process is considered to be at the level of the 9th thoracic vertebra and the T7 dermatome. Development In newborns and young (especially small) infants, the tip of the xiphoid process may be both seen and felt as a lump just below the sternal notch. At 15 to 29 years old, the xiphoid usually fuses to the body of the sternum with a fibrous joint. Unlike the synovial articulation of major joints, this is non-movable. Ossification of the xiphoid process occurs around age 40. Variation The xiphoid process can be naturally bifurcated or sometimes perforated (xiphoidal foramen). These variances in morphology are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
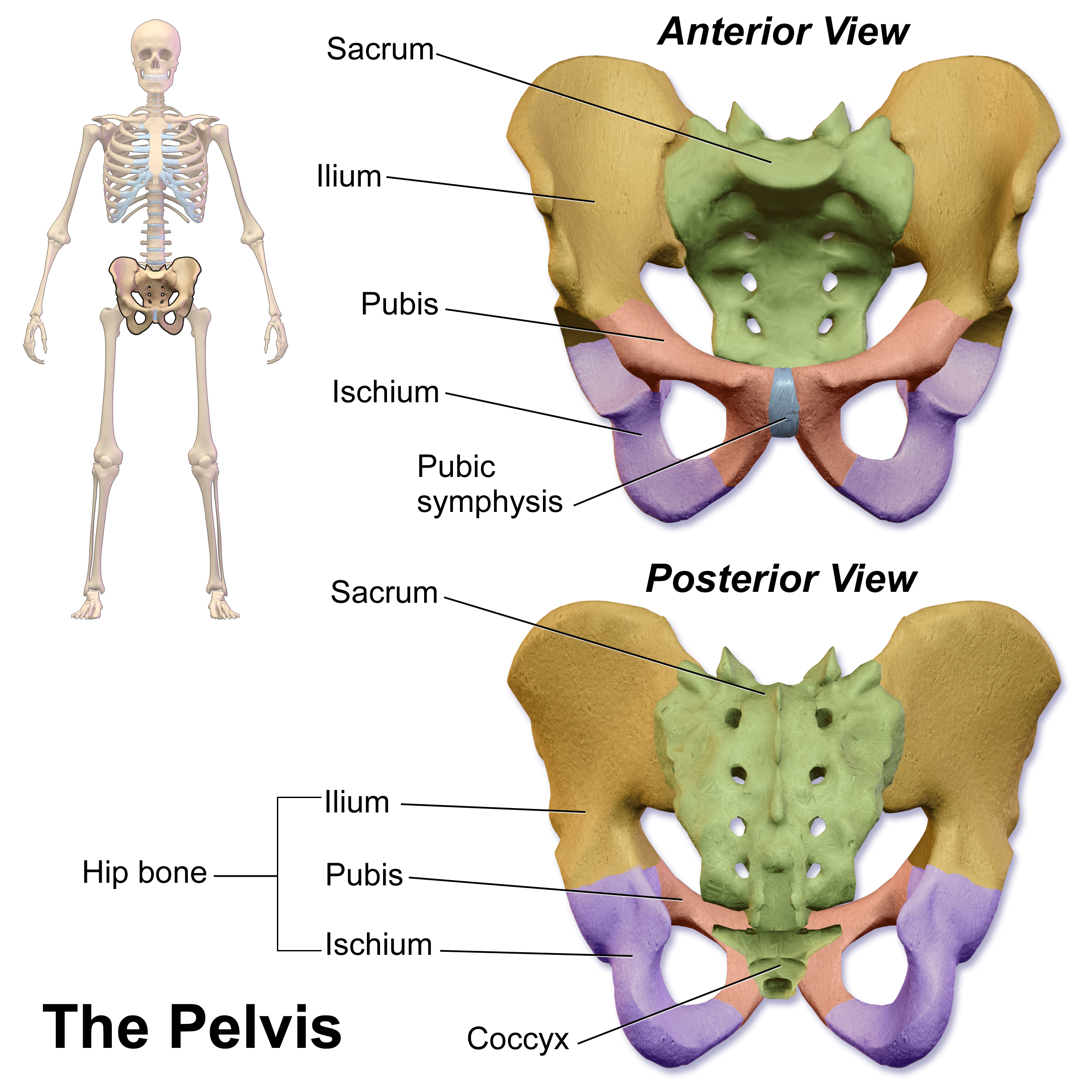
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is close to the clitoris. In most adults it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubic bones are covered by a thin layer of hyalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the jejunum, middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. Duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (horizontal) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Structure The duodenum is a C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duoden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Colon
In human anatomy, the transverse colon is the longest and most movable part of the colon. Anatomical position It crosses the abdomen from the ascending colon at the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure) with a downward convexity to the descending colon where it curves sharply on itself beneath the lower end of the spleen forming the left colic flexure (splenic flexure). In its course, it describes an arch, the concavity of which is directed backward and a little upward. Toward its splenic end there is often an abrupt U-shaped curve which may descend lower than the main curve. It is almost completely invested by the peritoneum, and is connected to the inferior border of the pancreas by a large and wide duplicature of that membrane, the transverse mesocolon. It is in relation, by its upper surface, with the liver and gall-bladder, the greater curvature of the stomach, and the lower end of the spleen; by its under surface, with the small intestine; by its anterior surface, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypochondrium
In anatomy, the division of the abdomen into regions can employ a nine-region scheme. The hypochondrium refers to the two hypochondriac regions in the upper third of the abdomen; the left hypochondrium and right hypochondrium. They are located on the lateral sides of the abdominal wall respectively, inferior to (below) the thoracic cage, being separated by the epigastrium. The liver is in the right hypochondrium, extending through the epigastrium and reaching the left hypochondrium. The spleen and some of the stomach are in the left hypochondrium. Definitions, etymology, and modern controversies The word derives from the Greek word υποχόνδριο ("hypochondrio"). This Greek word means literally "below the cartilage" which refers to the costal cartilages. In other words, the word refers to the area of the ventral trunk that is located below the costal cartilages. The word once referred only to the soft portion of the abdomen between the rib cage and the navel (the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigastric Region
In anatomy, the epigastrium (or epigastric region) is the upper central region of the abdomen. It is located between the costal margins and the subcostal plane. Pain may be referred to the epigastrium from damage to structures derived from the foregut. Structure The epigastrium is one of the nine regions of the abdomen, along with the right and left hypochondria, right and left lateral regions (lumbar areas or flanks), right and left inguinal regions (or fossae), and the umbilical and pubic regions. It is located between the costal margins and the subcostal plane. During breathing, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, displacing the viscera and producing an outward movement of the upper abdominal wall (epigastric region). It is a convergence of the diaphragm and the abdominals, so that "when both sets of muscles (diaphragm and abdominals) tense, the epigastrium pushes forward". Therefore, the epigastric region is not a muscle nor is it an organ, but it is a zone of activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar
In tetrapod Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ... anatomy, lumbar is an adjective that means ''of or pertaining to the abdominal segment of the torso, between the diaphragm (anatomy), diaphragm and the sacrum.'' The lumbar region is sometimes referred to as the lower vertebral column, spine, or as an area of the back in its proximity. In human anatomy the five lumbar vertebrae (vertebrae in the lumbar region of the back) are the largest and strongest in the movable part of the spinal column, and can be distinguished by the absence of a foramen transversarium, foramen in the transverse process, and by the absence of facets on the sides of the body. In most mammals, the lumbar region of the spine curves outward. The actual spinal cord terminates between vertebrae one a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |