|
Ullmann Reaction
The Ullmann reaction or Ullmann coupling is a coupling reaction between aryl halides. Traditionally this reaction is effected by copper, but palladium and nickel are also effective catalysts. The reaction is named after Fritz Ullmann. Mechanism The mechanism of the Ullmann reaction is extensively studied. Complications arise because the reactions are often heterogeneous. With copper as the halide acceptor, organocopper intermediates are invoked. Scope A typical example of classic Ullmann biaryl coupling is the conversion of ''ortho''-chloronitrobenzene into 2,2'-dinitrobiphenyl with a copper - bronze alloy. : : The traditional version of the Ullmann reaction requires harsh reaction conditions, and the reaction has a reputation for erratic yields. Because of these problems many improvements and alternative procedures have been introduced. The classical Ullmann reaction is limited to electron deficient aryl halides and requires harsh reaction conditions. Modern variants of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Ullmann
Fritz Ullmann (July 2, 1875 in Fürth – March 17, 1939 in Berlin) was a German chemist. Ullmann was born in Fürth and started studying chemistry in Nuremberg, but received his PhD of the University of Geneva for work with Carl Gräbe in 1895. After some time in Geneva he went to Berlin in 1905. Ullmann taught technical chemistry during 1905-1913 and 1922-1925 at the ''Technischen Hochschule Berlin'' now ''Technische Universität Berlin'', first as part of the ordinary teaching staff, later on as a professor. In 1900 he introduced dimethyl sulfate as an alkylating agent. Between 1914 and 1922, when he was back in Geneva, he published the first edition of the "Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie" in 12 volumes () in English the ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', a publication that exists to this day. He was married to Irma Goldberg who was his assistant from 1905 to 1910 at his laboratory. They named after themselves the following reactions: the Ullmann rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
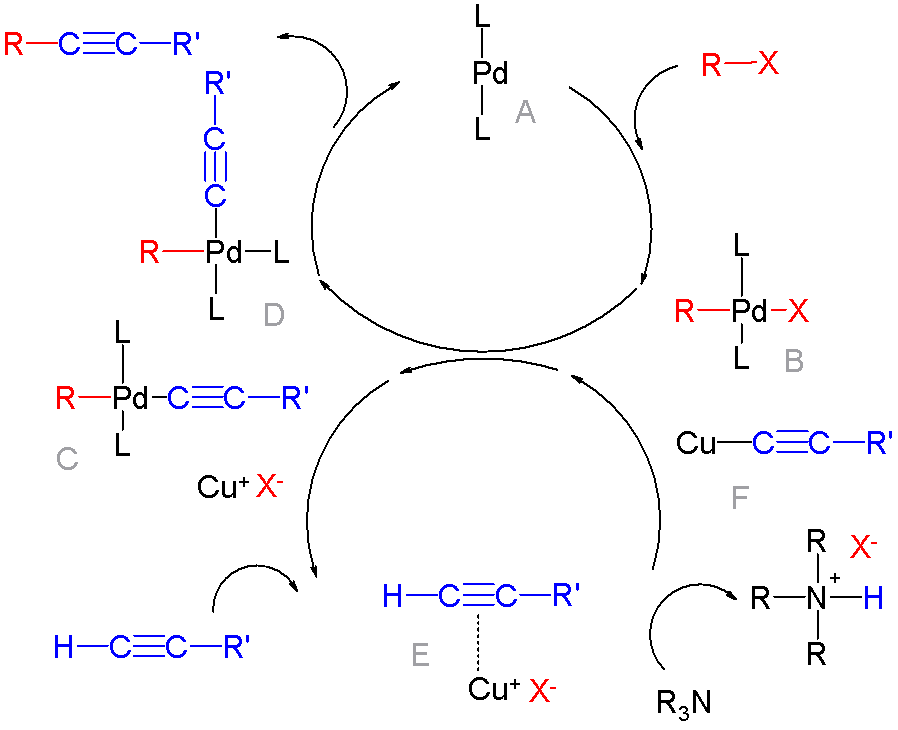
Palladium Coupling Reactions
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two fragments are joined together with the aid of a metal catalyst. In one important reaction type, a main group organometallic compound of the type R-M (R = organic fragment, M = main group center) reacts with an organic halide of the type R'-X with formation of a new carbon–carbon bond in the product R-R'. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. It is often used in arylations. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism The mechanism generally involves reductive elimination of the organic substituents R and R' on a metal complex of the type LnMR(R') (where L is some arbitrary spectator ligand). The crucial intermediate LnMR(R') is formed in a two step process from a low valence precursor Ln. The oxidative addition of an organic halide (RX) to LnM gives LnMR(X). Subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
A nucleophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide, on an aromatic ring. Aromatic rings are usually nucleophilic, but some aromatic compounds do undergo nucleophilic substitution. Just as normally nucleophilic alkenes can be made to undergo conjugate substitution if they carry electron-withdrawing substituents, so normally nucleophilic aromatic rings also become electrophilic if they have the right substituents.This reaction differs from a common SN2 reaction, because it happens at a trigonal carbon atom (sp2 hybridization). The mechanism of SN2 reaction does not occur due to steric hindrance of the benzene ring. In order to attack the C atom, the nucleophile must approach in line with the C-LG (leaving group) bond from the back, where the benzene ring lies. It follows the general rule for which SN2 reactions occur only at a tetrahedral carbon atom. The SN1 mechanism is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organocopper Compound
Organocopper compounds is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to copper chemical bond. Organocopper chemistry is the study of organocopper compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis and reactions. They are reagents in organic chemistry. The first organocopper compound, the explosive copper(I) acetylide Cu2C2 (Cu−C≡C−Cu), was synthesized by Rudolf Christian Böttger in 1859 by passing acetylene gas through a solution of copper(I) chloride: :C2H2 + 2 CuCl → Cu2C2 + 2 HCl Structure and bonding Organocopper compounds are diverse in structure and reactivity, but organocopper compounds are largely limited in oxidation states to copper(I), sometimes denoted Cu+. As a d10 metal center, it is related to Ni(0), but owing to its higher oxidation state, it engages in less pi-backbonding. Organic derivatives of Cu(II) and Cu(III) are invoked as intermediates but rarely isolated or even observed. In terms of geometry, copper(I) adopts symmetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Spin Resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials that have unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes and organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford. Theory Origin of an EPR signal Every electron has a magnetic moment and spin quantum number s = \tfrac , with magnetic components m_\mathrm = + \tfrac or m_\mathrm = - \tfrac . In the presence of an external magnetic field with strength B_\mathrm , the electron's magnetic moment aligns itself either antiparallel ( m_\mathrm = - \tfrac ) or parallel ( m_\mathrm = + \tfrac ) to the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazoline
Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula . It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines (emphasis on plural), which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond. Oxazoline itself has no applications however oxazolines have been widely investigated for potential applications. These applications include use as ligands in asymmetric catalysis, as protecting groups for carboxylic acids and increasingly as monomers for the production of polymers. Isomers Synthesis The synthesis of 2-oxazoline rings is well established and in general proceeds via the cyclisation of a 2-amino alcohol (typically obtained by the reduction of an amino acid) with a suitable functional group. The overall mechanism is usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ullman Assymetric Reaction
Ullman is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Al Ullman (1914–1986), American politician *Berthold Ullman (1882–1965), American classical scholar *Edward Ullman (1912–1976), American geographer *Ellen Ullman, American author *Elwood Ullman (1903–1985), American film comedy writer *Eugene Paul Ullman (1877-1953) American Impressionist painter *Harlan K. Ullman (born 1941), American political author and commentator *James Ramsey Ullman (1907–1971), American writer and mountaineer *Jeffrey Ullman (born 1942), American computer scientist * Johan Ullman (born 1953), Swedish inventor * Jordan Ullman, part of the duo Majid Jordan * Leslie Ullman (born 1947), an American poet *Liv Ullman (born 1938), American Actress *Micha Ullman (born 1939), an Israeli sculptor, professor of art *Michael T. Ullman (born 1962), American neuroscientist *Montague Ullman (1916–2008), American psychiatrist and parapsychologist *Norm Ullman (born 1935), Canadian ice hockey forward *R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Close Sonogashira
Ring may refer to: * Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry * To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell :(hence) to initiate a telephone connection Arts, entertainment and media Film and literature * ''The Ring'' (franchise), a Japanese horror media franchise based on the novel series by Koji Suzuki ** ''Ring'' (novel series) *** ''Ring'' (Suzuki novel), 1991 ** ''Ring'' (film), or ''The Ring'', a 1998 Japanese horror film by Hideo Nakata *** ''The Ring'' (2002 film), an American horror film, remake of the 1998 Japanese film ** ''Ring'' (1995 film), a TV film ** ''Rings'' (2005 film), a short film by Jonathan Liebesman ** ''Rings'' (2017 film), an American horror film * ''Ring'' (Baxter novel), a 1994 science fiction novel * ''Ring'' (Alexis novel), a 2021 Canadian novel by André Alexis Gaming * ''Ring'' (video game), 1998 * Rings (''Sonic the Hedgehog''), a collectible in ''Sonic the Hedgehog'' games Music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ullmann Biphenyl Synthesis
Ullmann is a German surname also associated with Jewish Europeans. It means "man from Ulm". Notable people with the surname include: * Alexander de Erény Ullmann (1850–1897), Hungarian deputy and political economist *Andrew Ullmann (born 1963), German physician and politician * Christoph Ullmann (born 1983), German ice hockey player *Emerich Ullmann (1861–1937), Austrian surgeon *Fritz Ullmann (1875–1939), German chemist *Gebhard Ullmann (born 1957), German jazz musician and composer * Harrison Ullmann (1936–2000), American journalist *Jeffrey Ullman (born 1942), American computer scientist * Karl Ullmann (1796–1865), German Protestant theologian *Kostja Ullmann (born 1984), German actor *Linn Ullmann (born 1966), Norwegian author and journalist *Liv Ullmann (born 1938), Norwegian actress *Lisa Ullmann (1907–1985), German-British dance teacher * Martin Ullmann (born 1986), German footballer * Mona Ullmann (born 1967), Norwegian Paralympic athlete ('' no, it'') *Myron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biphenylene
Biphenylene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2. It is a pale, yellowish solid with a hay-like odor. Despite its unusual structure, it behaves like a traditional polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Bonding Biphenylene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, composed of two benzene rings joined by two bridging bonds (as opposed to a normal ring fusion), thus forming a 6-4-6 arene system. The resulting planar structure was one of the first π-electronic hydrocarbon systems discovered to show evidence of antiaromaticity. The spectral and chemical properties show the influence of the central nring, leading to considerable interest in the system in terms of its degree of lessened aromaticity. Questions of bond alternation and ring currents have been investigated repeatedly. Both X-ray diffraction and electron diffraction studies show a considerable alternation of bond lengths, with the bridging bonds between the benzenoid rings having the unusually great length of 1.524 Å. The sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |