|
USS YP-16
USS ''YP-16'' was a wooden-hulled patrol vessel in commission in the fleet of the United States Coast Guard as ''CG-267'' from 1925 to 1934, and in the fleet of the United States Navy as ''YP-16'' from 1934 until 1941. She was sunk by Japanese aircraft during the Japanese attack on Guam. History She was laid down at the Seattle shipyard of the Lake Union Dry Dock and Machine Works, Seattle, one of 203 "Six-Bitters" ordered by the United States Coast Guard. She was designed for long-range picket and patrol duty during Prohibition for postings 20 to 30 miles from shore. The date of her launching and completion is uncertain although the class design was finalized in April 1924 and all of the Six-Bitters were commissioned by 1925. She was commissioned in 1925 as ''CG-267''. In January 1934, she was transferred to the United States Navy and designated as a Yard Patrol Craft (YP). She was assigned to the 13th Naval District where she trained reservists. On 22 October 1940, she along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS YP-18
USS ''YP-18'' was a wooden-hulled patrol vessel in commission in the fleet of the United States Coast Guard as ''CG-263'' from 1925 to 1934, and in the fleet of the United States Navy as ''YP-18'' from 1934 until 1938. History She was laid down at the Seattle shipyard of the Lake Union Dry Dock and Machine Works, one of 203 "Six-Bitters" ordered by the United States Coast Guard. She was designed for long-range picket and patrol duty during Prohibition for postings 20 to 30 miles from shore. The date of her launching and completion is uncertain although the class design was finalized in April 1924 and all of the Six-Bitters were commissioned by 1925. She was commissioned in 1925 as ''CG-263''. On 21 February 1934, she was transferred to the United States Navy and designated as a Yard Patrol Craft (YP). She was assigned to the 13th Naval District where she trained reservists. She was struck from the Naval List A Navy Directory, formerly the Navy List or Naval Register is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Japanese-run Internment Camps During World War II
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
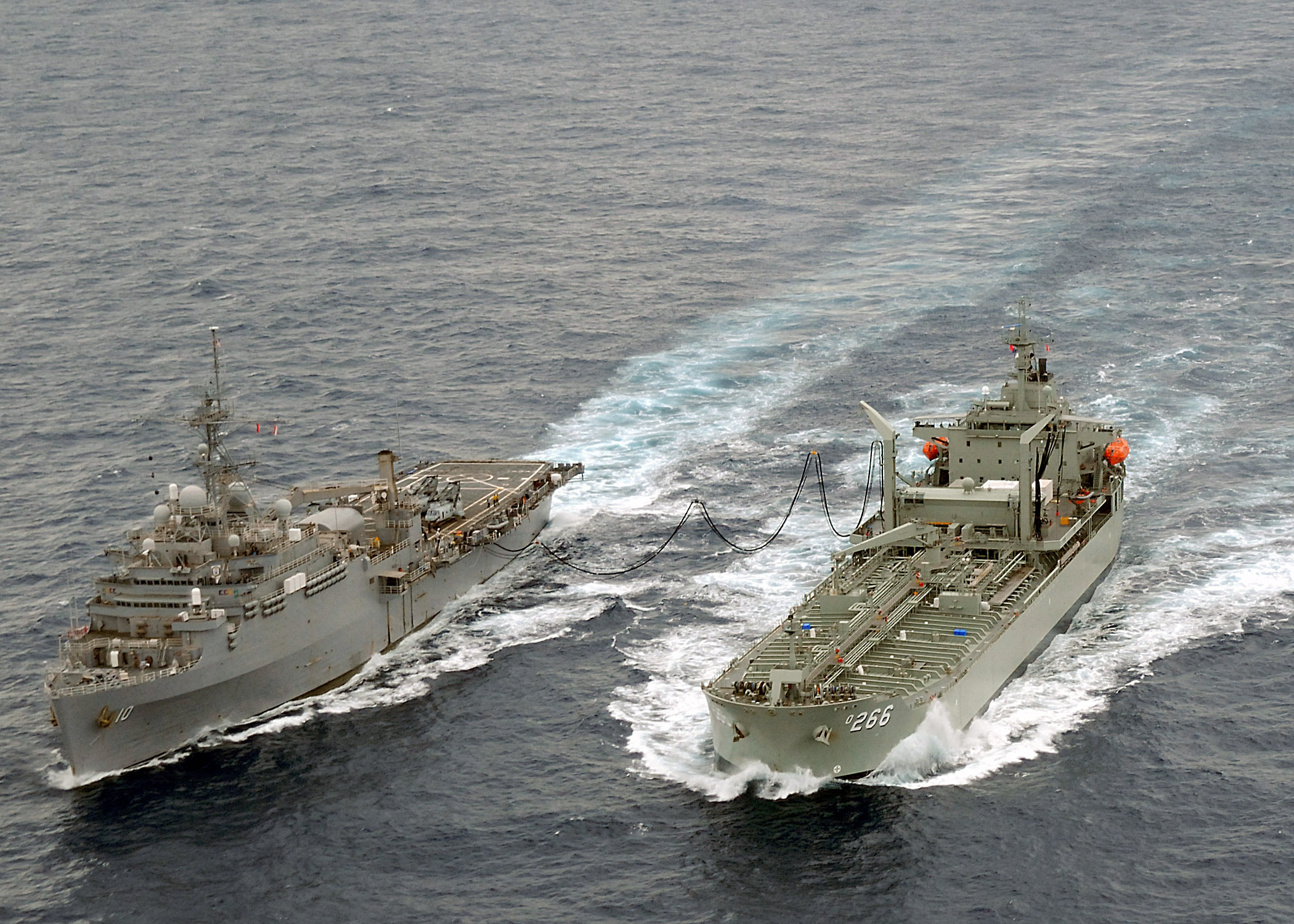
Replenishment Oiler
A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers. The United States Navy's hull classification symbol for this type of ship was AOR. Replenishment oilers are slower and carry fewer dry stores than the U.S. Navy's modern fast combat support ships, which carry the classification AOE. History The development of the "oiler" paralleled the change from coal- to oil-fired boilers in warships. Prior to the adoption of oil fired machinery, navies could extend the range of their ships either by maintaining coaling stations or for warships to raft together with colliers and for coal to be manhandled aboard. Though arguments related to fuel security were made against such a change, the ease with which liquid fuel could be transferred led in part to its adoption by navies worldwide. One of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th Naval District
The naval district was a U.S. Navy military and administrative command ashore. Apart from Naval District Washington, the Districts were disestablished and renamed Navy Regions about 1999, and are now under Commander, Naval Installations Command (CNIC). They were established for the purpose of decentralizing the Navy Department's functions with respect to the control of the coastwise sea communications and the shore activities outside the department proper, and for the further purpose of centralizing under one command: : (a) For military coordination, all naval activities, and : (b) For administrative coordination, all naval activities with specific exceptions, within the district and the waters thereof. The limits of the naval districts are laid down in article 1480, Navy Regulations. Those limits extend to seaward so far as to include the coastwise sea lanes (art. 1486 (1), Navy Regulations). "Each naval district shall be commanded by a designated commandant, who is the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
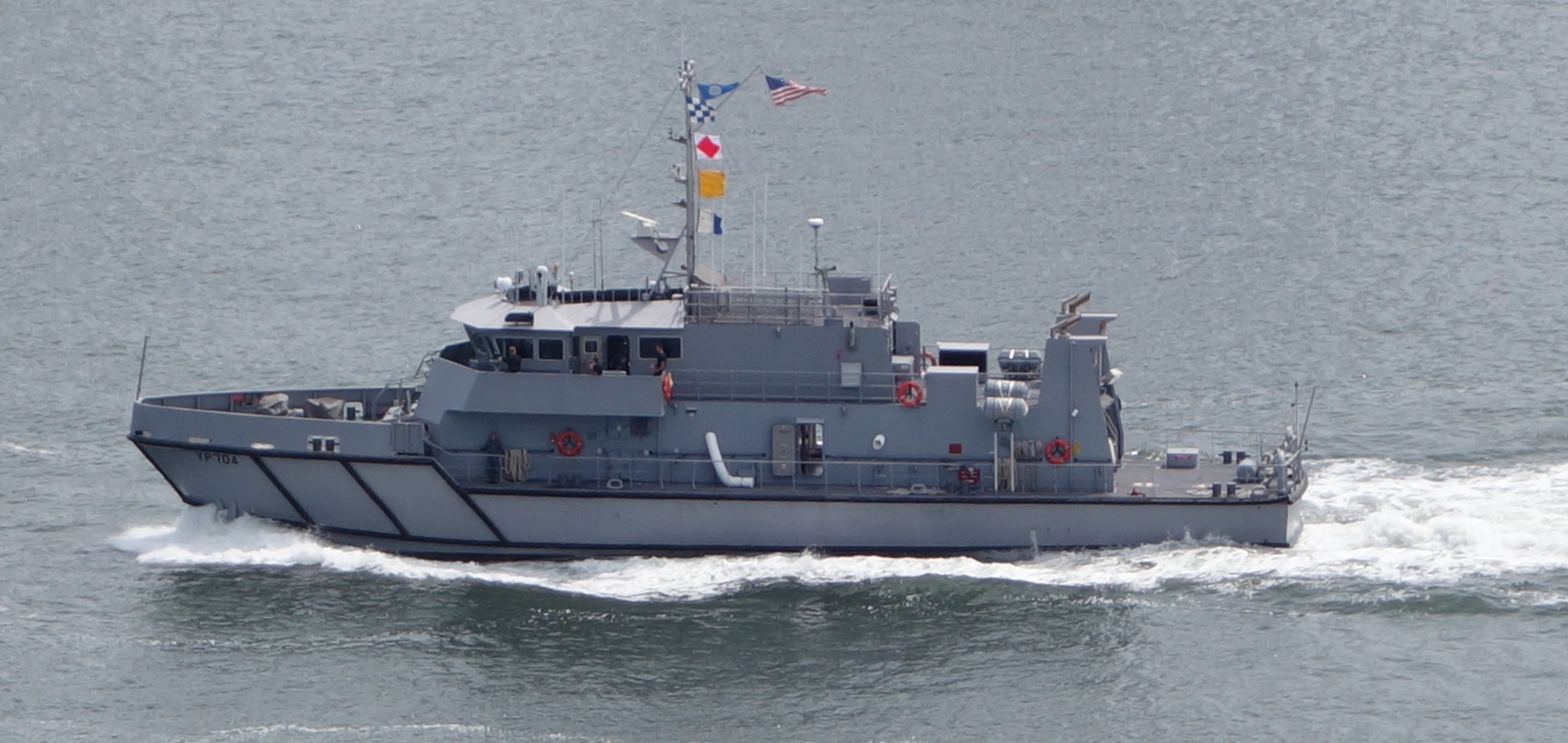
Yard Patrol Craft
Yard Patrol craft are used by the United States Navy for training and for research purposes. They are designated as YP in the hull classification symbol system. They were nicknamed "Yippy boats" after the "YP" classification symbol. World War II Following the attack on Pearl Harbor the United States Navy leased California based tuna boats for the duration of the war or "until victory". On 16 February 1942, San Diego Port Director Commander W.J. Morcott called a meeting of tuna skippers and crews at the Naval Reserve Armory telling the men "The Navy needs men to man the lippers– experienced men, like yourselves. Needless to say, duty in the war zones will be hazardous". Six hundred tuna boat men volunteered to join their boats in the navy. The boats were painted navy grey and had their names replaced with numerical designations. The ships patrolled the coasts of the United States, the Panama Canal and served in several battles of the South Pacific, particularly the Battle of Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic beverages. The word is also used to refer to a period of time during which such bans are enforced. History Some kind of limitation on the trade in alcohol can be seen in the Code of Hammurabi (c. 1772 BCE) specifically banning the selling of beer for money. It could only be bartered for barley: "If a beer seller do not receive barley as the price for beer, but if she receive money or make the beer a measure smaller than the barley measure received, they shall throw her into the water." In the early twentieth century, much of the impetus for the prohibition movement in the Nordic countries and North America came from moralistic convictions of pietistic Protestants. Prohibition movements in the West coincided with the advent of women's su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Six-Bitter
The United States Coast Guard wooden-hulled 75-foot patrol boats (also called "Six-Bitters") were built during Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition to help interdict alcohol smugglers ("rum-running, rum runners"). Their nickname was derived from the slang terms for money#United States, slang term "six bits" meaning 75 U.S. cents. Design and construction During Prohibition, the U.S. Coast Guard had a need for picket boats to help intercept smugglers ferrying alcohol from offshore freighters to the mainland. The Coast Guard response was to develop a two-tiered plan. Larger cutters were to be stationed offshore to find "mother ships" and interdict them if they strayed inside U.S. territorial waters (mother ships were in almost all cases of foreign registry and could not be boarded while in international waters) while smaller, faster patrol boats were used as picket ships to intercept high speed boats or "rum-runners" that made the transfer of contraband to the shore. The Coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
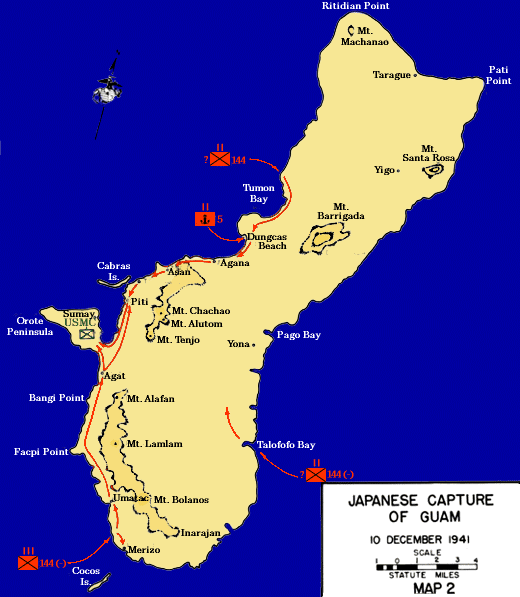
Battle Of Guam (1941)
The Battle of Guam was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II, and took place from 8 December to 10 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between Japan and the United States. The American garrison was defeated by Japanese forces on 10 December, which resulted in an occupation until the Second Battle of Guam in 1944. Background Guam is the southernmost part of the Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean. It is the largest of the islands, with an area of 225 square miles. Guam's interior is rugged, with heavy tropical forests in the north of the island and wooded hills in the south. Much of the island's coastline is edged with coral reefs and cliffs, though beaches suitable for landing troops exist in the center of the west coast. Guam has a tropical climate, though December forms part of the dry season. The United States captured Guam from the Kingdom of Spain on 21 June 1898 during the Spanish–American War. The next year Spain sold the other islands in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest and most powerful coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies. The U.S. Coast Guard is a humanitarian and security service. It protects the United States' borders and economic and security interests abroad; and defends its sovereignty by safeguarding sea lines of communication and commerce across vast territorial waters spanning 95,000 miles of coastline and its Exclusive Economic Zone. With national and economic security depending upon open global trade a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 1-pounder Pom-pom
The QF 1 pounder, universally known as the pom-pom due to the sound of its discharge, was a 37 mm British autocannon, the first of its type in the world. It was used by several countries initially as an infantry gun and later as a light anti-aircraft gun. History Hiram Maxim originally designed the Pom-Pom in the late 1880s as an enlarged version of the Maxim machine gun. Its longer range necessitated exploding projectiles to judge range, which in turn dictated a shell weight of at least , as that was the lightest exploding shell allowed under the Saint Petersburg Declaration of 1868 and reaffirmed in the Hague Convention of 1899. Early versions were sold under the Maxim-Nordenfelt label, whereas versions in British service (i.e. from 1900) were labelled Vickers, Sons and Maxim (VSM) as Vickers had bought out Maxim-Nordenfelt in 1897 but they are the same gun. Service by nation Belgium The Belgian Army used the gun on a high-angle field carriage mounting. Finlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft Horsepower
Horsepower (hp) is a unit of measurement of power, or the rate at which work is done, usually in reference to the output of engines or motors. There are many different standards and types of horsepower. Two common definitions used today are the mechanical horsepower (or imperial horsepower), which is about 745.7 watts, and the metric horsepower, which is approximately 735.5 watts. The term was adopted in the late 18th century by Scottish engineer James Watt to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses. It was later expanded to include the output power of other types of piston engines, as well as turbines, electric motors and other machinery. The definition of the unit varied among geographical regions. Most countries now use the SI unit watt for measurement of power. With the implementation of the EU Directive 80/181/EEC on 1 January 2010, the use of horsepower in the EU is permitted only as a supplementary unit. History The development of the stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)