|
USS Valley Forge (CV-45)
USS ''Valley Forge'' (CV/CVA/CVS-45, LPH-8) was one of 24 s built during and shortly after World War II for the United States Navy. The ship was the first US Navy ship to bear the name, and was named after Valley Forge, the 1777–1778 winter encampment of General George Washington's Continental Army. ''Valley Forge'' was commissioned in November 1946, too late to serve in World War II, but saw extensive service in the Korean War and the Vietnam War. She was reclassified in the early 1950s as an attack carrier (CVA), then to an antisubmarine carrier (CVS), and finally to an amphibious assault ship (LPH), carrying helicopters and Marines. As a CVS she served in the Atlantic and Caribbean. She was the prime recovery vessel for an early unmanned Mercury space mission. After conversion to an LPH she served extensively in the Vietnam War. ''Valley Forge'' was awarded eight battle stars for Korean War service and nine for Vietnam War service, as well as three Navy Unit Commendations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas A-4 Skyhawk
The Douglas A-4 Skyhawk is a single-seat subsonic carrier-capable light attack aircraft developed for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps in the early 1950s. The delta-winged, single turbojet engined Skyhawk was designed and produced by Douglas Aircraft Company, and later by McDonnell Douglas. It was originally designated A4D under the U.S. Navy's pre-1962 designation system. The Skyhawk is a relatively light aircraft, with a maximum takeoff weight of , and has a top speed of . The aircraft's five hardpoints support a variety of missiles, bombs, and other munitions. It is capable of carrying a bomb load equivalent to that of a World War II–era Boeing B-17 bomber, and can deliver nuclear weapons using a low-altitude bombing system and a "loft" delivery technique. The A-4 was originally powered by the Wright J65 turbojet engine; from the A-4E onwards, the Pratt & Whitney J52 engine was used. Skyhawks played key roles in the Vietnam War, the Yom Kippur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Star
A service star is a miniature bronze or silver five-pointed star inch (4.8 mm) in diameter that is authorized to be worn by members of the eight uniformed services of the United States on medals and ribbons to denote an additional award or service period. The service star may also be referred to as a campaign star or battle star depending on which award the star is authorized for and the manner in which the device is used for the award. Service stars, campaign stars, and battle stars are worn with one point of the star pointing up on the suspension ribbon of a medal or service ribbon. A silver star is worn instead of five bronze stars. A service star is sometimes mistaken for a Bronze Star (Bronze Star Medal) or Silver Star (Silver Star Medal). The service star is also similar to the gold and silver -inch stars that may be authorized to be worn on specific individual decorations of certain services to denote additional decorations. Service stars Expeditionary medals Servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft (ship), propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbines
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful Work (physics), work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a electric generator, generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachinery, turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with Turbine blade, blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels. Gas turbine, Gas, steam turbine, steam, and water turbine, water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Credit for invention of the steam turbine is given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boilers
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babcock & Wilcox
Babcock & Wilcox is an American renewable, environmental and thermal energy technologies and service provider that is active and has operations in many international markets across the globe with its headquarters in Akron, Ohio, USA. Historically, the company is best known for their steam boilers. Background The company was founded in 1867 in Providence, Rhode Island, by partners Stephen Wilcox and George Babcock to manufacture and market Wilcox's patented water-tube boiler. B&W's list of innovations and firsts include the world's first installed utility boiler (1881); manufacture of boilers to power New York City's first subway (1902); first pulverized coal power plant (1918); design and manufacture of components for , the world's first nuclear-powered submarine (1953–55); the first supercritical pressure coal-fired boiler (1957); design and supply of reactors for the first U.S. built nuclear-powered surface ship, (1961).''Steam/its generation and use'', 41st Edition The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterline Length
A vessel's length at the waterline (abbreviated to L.W.L)Note: originally Load Waterline Length is the length of a ship or boat at the level where it sits in the water (the ''waterline''). The LWL will be shorter than the length of the boat overall (''length overall'' or LOA) as most boats have bows and stern protrusions that make the LOA greater than the LWL. As a ship becomes more loaded, it will sit lower in the water and its ambient waterline length may change; but the registered L.W.L it is measured from a default load condition. This measure is significant in determining several of a vessel's properties, such as how much water it displaces, where the bow and stern waves occur, hull speed, amount of bottom-paint needed, etc. Traditionally, a stripe called the "boot top" is painted around the hull just above the waterline. In sailing boats, longer waterline length will usually enable a greater maximum speed, because it allows greater sail area, without increasing beam or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Overall
__NOTOC__ Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, and is also used for calculating the cost of a marina berth (for example, £2.50 per metre LOA). LOA is usually measured on the hull alone. For sailing ships, this may ''exclude'' the bowsprit and other fittings added to the hull. This is how some racing boats and tall ships use the term LOA. However, other sources may include bowsprits in LOA. Confusingly, LOA has different meanings. "Sparred length", "Total length including bowsprit", "Mooring length" and "LOA including bowsprit" are other expressions that might indicate the full length of a sailing ship. LOD Often used to distinguish between the length of a vessel including projections (e.g. bow sprits, etc.) from the length of the hull itself, the Length on Deck or LOD is often repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
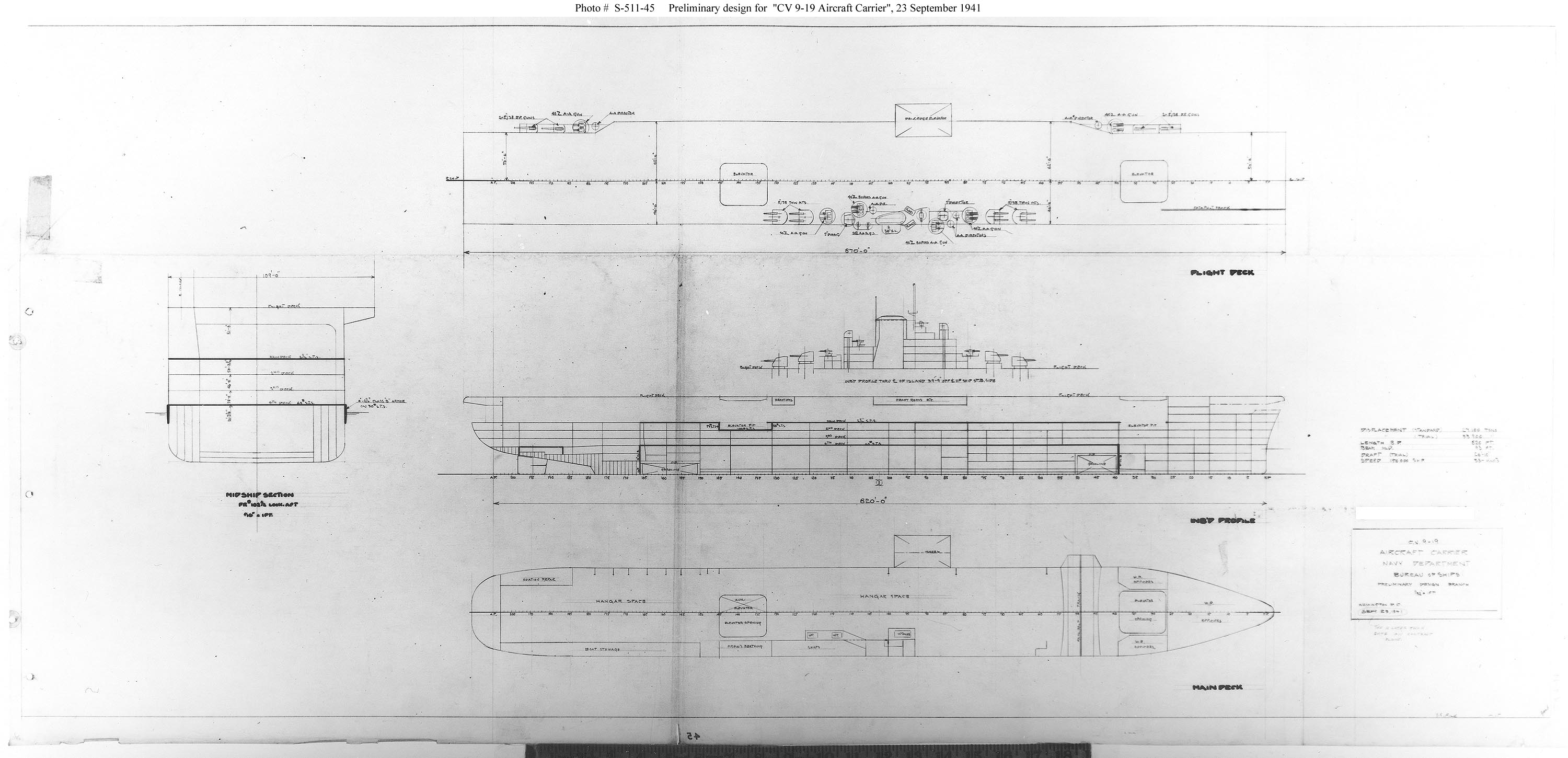
Essex-class Aircraft Carrier
The ''Essex'' class was a class of aircraft carriers of the United States Navy. The 20th century's most numerous class of capital ship, the class consisted of 24 vessels, which came in "short-hull" and "long-hull" versions. Thirty-two ships were ordered, but as World War II wound down, six were canceled before construction, and two were canceled after construction had begun. Fourteen saw combat during World War II. None were lost to enemy action, though several sustained crippling damage. ''Essex''-class carriers were the backbone of the U.S. Navy from mid-1943 and, with the three carriers added just after the war, continued to be the heart of U.S. naval strength until supercarriers joined the fleet in the 1960s and 1970s. Several of the carriers were rebuilt to handle heavier and faster aircraft of the early jet age, and some served until well after the Vietnam War. Overview The preceding s and the designers' list of trade-offs and limitations forced by arms control treaty obl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_patch_1961.png)





.jpg)