|
USH1G
Usher syndrome type-1G protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USH1G'' gene. This gene encodes a protein that contains three ankyrin domains, a class I PDZ-binding motif and a sterile alpha motif. The encoded protein interacts with harmonin, which is associated with Usher syndrome type 1C. This protein plays a role in the development and maintenance of the auditory and visual systems and functions in the cohesion of hair bundles formed by inner ear The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ... sensory cells. Mutations in this gene are associated with Usher syndrome type 1G (USH1G). References Further reading * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Usher Syndrome Type I {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usher Syndrome, Type 1C
Usher syndrome, also known as Hallgren syndrome, Usher–Hallgren syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa–dysacusis syndrome or dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in any one of at least 11 genes resulting in a combination of hearing loss and visual impairment. It is a major cause of deafblindness and is at present incurable. Usher syndrome is classed into three subtypes (I, II and III) according to the genes responsible and the onset of deafness. All three subtypes are caused by mutations in genes involved in the function of the inner ear and retina. These mutations are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The occurrence of Usher syndrome varies across the world and across the different syndrome types, with rates as high as 1 in 12,500 in Germany to as low as 1 in 28,000 in Norway. Type I is most common in Ashkenazi Jewish and Acadian populations, and type III is rarely found outside Ashkenazi Jewish and Finnish populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonin
Harmonin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USH1C gene. It is expressed in sensory cells of the inner ear and retina, where it plays a role in hearing, balance, and vision. Mutations at the USH1C locus cause Usher syndrome type 1c and nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Gene and protein structure The USH1C gene is located on chromosome 11 and contains 28 exons. Alternative splicing generates multiple mRNA transcript variants, some of which are associated with the rare disorder phenotypes of Usher syndrome and nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. The encoded protein harmonin has multiple protein isoforms due to the alternative splicing, including a standard isoform with 552 amino acids. Harmonin contains a PDZ domain, which assists in attaching the protein to the cell membrane and to cytoskeletal components. Inner ear function Harmonin is found at the apex of inner hair cells (IHCs), which convert mechanical signals from sound waves into electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
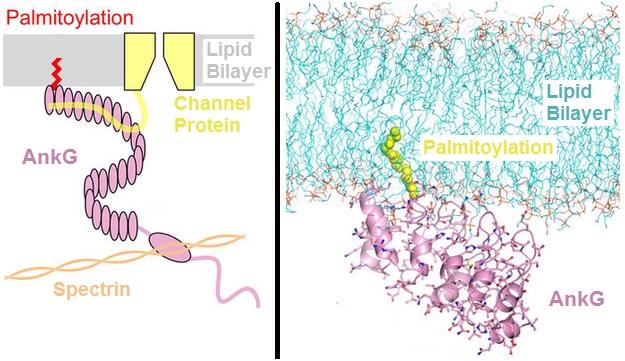
Ankyrin
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that mediate the attachment of integral membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin based membrane cytoskeleton. Ankyrins have binding sites for the beta subunit of spectrin and at least 12 families of integral membrane proteins. This linkage is required to maintain the integrity of the plasma membranes and to anchor specific ion channels, ion exchangers and ion transporters in the plasma membrane. The name is derived from the Greek word ἄγκυρα (''ankyra'') for "anchor". Structure Ankyrins contain four functional domains: an N-terminal domain that contains 24 tandem ankyrin repeats, a central domain that binds to spectrin, a death domain that binds to proteins involved in apoptosis, and a C-terminal regulatory domain that is highly variable between different ankyrin proteins. Membrane protein recognition The 24 tandem ankyrin repeats are responsible for the recognition of a wide range of membrane proteins. These 24 repeats contain 3 struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Motif
In a polymer, chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common Biomolecular structure#Tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrelated molecules. A structural motif does not have to be associated with a sequence motif; it can be represented by different and completely unrelated sequences in different proteins or RNA. In nucleic acids Depending upon the sequence and other conditions, nucleic acids can form a variety of structural motifs which is thought to have biological significance. ;Stem-loop: Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded DNA or, more commonly, in RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |