|
Utroba Cave
The Utroba Cave, also known as Womb Cave, is a prehistoric cave sanctuary in Kardzhali Province, Bulgaria. The cave resembles a human vulva and dates to the Thracian period. Historians believe that it was once used as a fertility shrine. It is known in Bulgarian as (, , ) or (, , 'Womb Cave'). History The cave is located 20 kilometers from the city of Kardzhali near the village of Ilinitsa and it dates to 480 BC. It is also referred to as "The Cave Womb" or "Womb Cave" because the entrance is the shape of a vulva. The inside of the cave resembles a uterus. Locally it is also called "The Blaring Rock". Researchers believe that the entrance to the cave was a slit, which was then widened by humans. The entrance to the cave is tall and wide and inside the cave there is a -tall altar which has been carved. Archaeologist Nikolay Ovcharov believes that the cave and altar were used by the Thracians. There are several Thracian sanctuaries found in Bulgaria. Ovcharov believes that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardzhali Province
Kardzhali Province ( bg, Област Кърджали, Oblast Kărdžali, tr, Kırcaali ili) is a province of southern Bulgaria, neighbouring Greece with the Greek regional units of Xanthi, Rhodope, and Evros to the south and east. It is 3209.1 km2 in area. Its main city is Kardzhali. History The territory of Kardzhali province was acquired by Bulgaria during the First Balkan War in 1912. In 1913 the region was organized as the district (окръг, ''okrăg'' in Bulgarian) of Mestanli. This district was part of Stara Zagora province from 1934 until 1949, then it was transferred to the newly formed Haskovo district. In 1959 Kardzhali became the center of a new district with similar borders to the current province. Between 1987 and 1999, the region was part of Haskovo Province, after which it was restored, now as a province and with slightly changed borders. Municipalities The Kardzhali province (област, ''oblast'') contains seven municipalities (singular: общ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
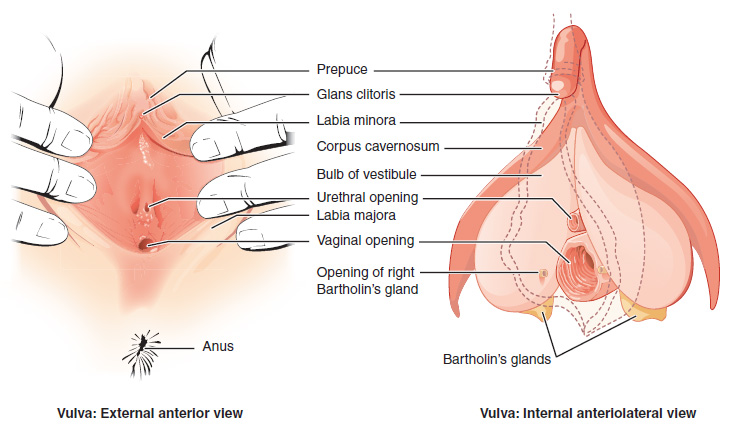
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibule, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area between northern Greece, southern Russia, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture... There may have been as many as a million Thracians, diveded among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans (mostly Present (time), modern day Bulgaria, Turkey and Greece) but were also located in Anatolia, Anatolia (Asia Minor) and other locations in Eastern Europe. The exact origin of Thracians is unknown, but it is believed that proto-Thracians descended from a purported mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers, arriving from the rest of Asia and Africa through the Asia Minor (Anatolia). The proto-Thracian culture developed int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardzhali
Kardzhali ( bg, Кърджали , ''Kărdžali''; tr, Kırcaali; gr, Κάρτζαλι, ''Kártzali''), sometimes spelt Kardžali or Kurdzhali, is a town in the Eastern Rhodopes in Bulgaria, centre of Kardzhali Municipality and Kardzhali Province. The noted Kardzhali Dam is located nearby. Name Named after the 14th-century Ottoman conqueror Kırca Ali, from the Turkish name Kırca and the Islamic name Ali, derived from an Arabic root which means "high" or "elevated". Geography Kardzhali is located in the low eastern part of Rhodope Mountains, on both banks of the river Arda between the Kardzhali Reservoir to the west and the Studen Kladenets Reservoir to the east. The town is southeast of Sofia. It has a crossroad position from Thrace to the Aegean Sea — part of European transportation route 9, via the Makaza mountain pass. Climate Kardzhali has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa), that is bordering closely on a humid subtropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilinitsa
Ilinitsa is a village in Kardzhali Municipality, Kardzhali Province, southern Bulgaria Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon .... Accessed Dec 21, 2014 References Villages in Kardzhali Province {{Kardzhali-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganism, Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, Judaism, modern paganism, and in certain Islamic communities around Caucasia and Asia Minor. Many historical-medieval faiths also made use of them, including the Roman, Greek, and Norse religions. Etymology The modern English word '' altar'' was derived from Middle English '' altar'', from Old English '' alter'', taken from Latin '' altare'' ("altar"), probably related to '' adolere'' ("burn"); thus "burning place", influenced by '' altus'' ("high"). It displaced the native Old English word '' wēofod''. Altars in antiquity File:Tel Be'er Sheva Altar 2007041.JPG, Horned altar at Tel Be'er Sheva, Israel. File:3217 - Athens - Sto… of Attalus Museum - Kylix - Photo by Giovanni Dall'Orto, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolay Ovcharov
Nikolay Ovcharov (Bulgarian: Николай Овчаров) (born 1957 in Veliko Tarnovo) is a Bulgarian archaeologist and thracologist. He graduated history in Sofia University in 1976 and specialized Thracology in Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. Now Professor Ovcharov teaches history in the New Bulgarian University and the Slavic University in Moscow. He has published 18 books and more than 250 articles. Nikolay Ovcharov discovered a unique ancient Thracian city of Perperikon in the Eastern Rhodopes. It is thought that the famous sanctuary and oracular shrine dedicated to Dionysus of the Bessi was situated there. Later he discovered an ancient Thracian surface tomb in Tatul which was soon recognized as an exclusive religious centre. According to Ovcharov, the site is the sanctuary and tomb of an influential Thracian leader who was deified after his death. He links it with the cult of Orpheus. In 2005, German scholars from the University of Heidelberg confirmed that the two rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phallus
A phallus is a penis (especially when erect), an object that resembles a penis, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. In art history a figure with an erect penis is described as ithyphallic. Any object that symbolically—or, more precisely, iconically—resembles a penis may also be referred to as a phallus; however, such objects are more often referred to as being phallic (as in "phallic symbol"). Such symbols often represent fertility and cultural implications that are associated with the male sexual organ, as well as the male orgasm. Etymology The term is a loanword from Latin ''phallus'', itself borrowed from Greek (''phallos''), which is ultimately a derivation from the Proto-Indo-European root *''bʰel''- "to inflate, swell". Compare with Old Norse (and modern Icelandic) ''boli'' "bull", Old English ''bulluc'' "bullock", Greek "whale". Archaeology The Hohle phallus, a 28,000-year-old siltstone phallus discovered in the Hohle Fels cave and reassembled in 2005, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Religion
The Thracian religion refers to the mythology, ritual practices and beliefs of the Thracians, a collection of closely related ancient Indo-European peoples who inhabited eastern and southeastern Europe and northwestern Anatolia throughout antiquity and who included the Thracians proper, the Getae, the Dacians, and the Bithynians. The Thracians themselves did not leave an extensive written corpus of their mythology and rituals, but information about their beliefs is nevertheless available through epigraphic and iconographic sources, as well as through ancient Greek writings. Origin The Thracian religion, and especially its creation myth and its pantheon, were derived from the Proto-Indo-European religion. The Thracian conceptualisation of the world, which held that it was composed of the four elements (Air, Earth, Fire, Water), is attested from the early Bronze Age, around the fourth millennium BCE, and was recorded in poems and hymns originally composed in the late Bronze Age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Kardzhali Province
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID-19 pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




