|
Utility Functions On Divisible Goods
This page compares the properties of several typical utility functions of divisible goods. These functions are commonly used as examples in consumer theory. The functions are ordinal utility functions, which means that their properties are invariant under positive monotone transformation. For example, the Cobb–Douglas function could also be written as: w_x \log + w_y\log. Such functions only become interesting when there are two or more goods (with a single good, all monotonically increasing functions are ordinally equivalent). The utility functions are exemplified for two goods, x and y. p_x and p_y are their prices. w_x and w_y are constant positive parameters and r is another constant parameter. u_y is a utility function of a single commodity (y). I is the total income (wealth) of the consumer. References * {{Cite book, author=Hal Varian, author-link=Hal Varian, title=Intermediate micro-economics, isbn=0393927024, year=2006 chapter 5. Acknowledgements This page has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Function
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. The term has been adapted and reapplied within neoclassical economics, which dominates modern economic theory, as a utility function that represents a single consumer's preference ordering over a choice set but is not comparable across consumers. This concept of utility is personal and based on choice rather than on pleasure received, and so is specified more rigorously than the original concept but makes it less useful (and controversial) for ethical decisions. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person can make a preference ordering. The utility obtained from these alternatives is an unknown function of the utilities obtained from each alternative, not the sum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Good
In economics, a complementary good is a good whose appeal increases with the popularity of its complement. Technically, it displays a negative cross elasticity of demand and that demand for it increases when the price of another good decreases. If A is a complement to B, an increase in the price of A will result in a negative movement along the demand curve of A and cause the demand curve for B to shift inward; less of each good will be demanded. Conversely, a decrease in the price of A will result in a positive movement along the demand curve of A and cause the demand curve of B to shift outward; more of each good will be demanded. This is in contrast to a substitute good, whose demand decreases when its substitute's price decreases. When two goods are complements, they experience ''joint demand'' - the demand of one good is linked to the demand for another good. Therefore, if a higher quantity is demanded of one good, a higher quantity will also be demanded of the other, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelastic Utility
In economics, the isoelastic function for utility, also known as the isoelastic utility function, or power utility function, is used to express utility in terms of consumption or some other economic variable that a decision-maker is concerned with. The isoelastic utility function is a special case of hyperbolic absolute risk aversion and at the same time is the only class of utility functions with constant relative risk aversion, which is why it is also called the CRRA utility function. It is : u(c) = \begin \frac & \eta \ge 0, \eta \neq 1 \\ \ln(c) & \eta = 1 \end where c is consumption, u(c) the associated utility, and \eta is a constant that is positive for risk averse agents. Since additive constant terms in objective functions do not affect optimal decisions, the term –1 in the numerator can be, and usually is, omitted (except when establishing the limiting case of \ln(c) as below). When the context involves risk, the utility function is viewed as a von Neumann–Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Elasticity Of Substitution
Constant elasticity of substitution (CES), in economics, is a property of some production functions and utility functions. Several economists have featured in the topic and have contributed in the final finding of the constant. They include Tom McKenzie, John Hicks and Joan Robinson. The vital economic element of the measure is that it provided the producer a clear picture of how to move between different modes or types of production. Specifically, it arises in a particular type of aggregator function which combines two or more types of consumption goods, or two or more types of production inputs into an aggregate quantity. This aggregator function exhibits constant elasticity of substitution. CES production function Despite having several factors of production in substitutability, the most common are the forms of elasticity of substitution. On the contrary of restricting direct empirical evaluation, the constant Elasticity of Substitution are simple to use and hence are wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiconvex Function
In mathematics, a quasiconvex function is a real number, real-valued function (mathematics), function defined on an interval (mathematics), interval or on a convex set, convex subset of a real vector space such that the inverse image of any set of the form (-\infty,a) is a convex set. For a function of a single variable, along any stretch of the curve the highest point is one of the endpoints. The negative of a quasiconvex function is said to be quasiconcave. All convex functions are also quasiconvex, but not all quasiconvex functions are convex, so quasiconvexity is a generalization of convexity. ''Univariate'' Unimodality, unimodal functions are quasiconvex or quasiconcave, however this is not necessarily the case for functions with multiple argument of a function, arguments. For example, the 2-dimensional Rosenbrock function is unimodal but not quasiconvex and functions with Star_domain, star-convex sublevel sets can be unimodal without being quasiconvex. Definition and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasilinear Utility
In economics and consumer theory, quasilinear utility functions are linear in one argument, generally the numeraire. Quasilinear preferences can be represented by the utility function u(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) = x_1 + \theta (x_2, \ldots, x_n) where \theta is strictly concave. A useful property of the quasilinear utility function is that the Marshallian/Walrasian demand for x_2, \ldots, x_n does not depend on wealth and is thus not subject to a wealth effect; The absence of a wealth effect simplifies analysis and makes quasilinear utility functions a common choice for modelling. Furthermore, when utility is quasilinear, compensating variation (CV), equivalent variation (EV), and consumer surplus are algebraically equivalent. In mechanism design, quasilinear utility ensures that agents can compensate each other with side payments. Definition in terms of preferences A preference relation \succsim is quasilinear with respect to commodity 1 (called, in this case, the ''numerair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitute Good
In microeconomics, two goods are substitutes if the products could be used for the same purpose by the consumers. That is, a consumer perceives both goods as similar or comparable, so that having more of one good causes the consumer to desire less of the other good. Contrary to complementary goods and independent goods, substitute goods may replace each other in use due to changing economic conditions. An example of substitute goods is Coca-Cola and Pepsi; the interchangeable aspect of these goods is due to the similarity of the purpose they serve, i.e fulfilling customers' desire for a soft drink. These types of substitutes can be referred to as close substitutes. Definition Economic theory describes two goods as being close substitutes if three conditions hold: # products have the same or similar performance characteristics # products have the same or similar occasion for use and # products are sold in the same geographic area Performance characteristics describe what the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Utilities
In economics and consumer theory, a linear utility function is a function of the form: ::u(x_1,x_2,\dots,x_m) = w_1 x_1 + w_2 x_2 + \dots w_m x_m or, in vector form: ::u(\overrightarrow) = \overrightarrow \cdot \overrightarrow where: * m is the number of different goods in the economy. * \overrightarrow is a vector of size m that represents a bundle. The element x_i represents the amount of good i in the bundle. * \overrightarrow is a vector of size m that represents the subjective preferences of the consumer. The element w_i represents the relative value that the consumer assigns to good i. If w_i=0, this means that the consumer thinks that product i is totally worthless. The higher w_i is, the more valuable a unit of this product is for the consumer. A consumer with a linear utility function has the following properties: * The preferences are strictly monotone: having a larger quantity of even a single good strictly increases the utility. * The preferences are weakly convex, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Good
Independent goods are goods that have a zero cross elasticity of demand. Changes in the price of one good will have no effect on the demand for an independent good. Thus independent goods are neither complements nor substitutes. For example, a person's demand for nails is usually independent of his or her demand for bread, since they are two unrelated types of goods. Note that this concept is subjective and depends on the consumer's personal utility function. A Cobb-Douglas utility function implies that goods are independent. For goods in quantities ''X''1 and ''X''2, prices ''p''1 and ''p''2, income ''m'', and utility function parameter ''a'', the utility function : u(X_1, X_2) = X_1^a X_2^, when optimized subject to the budget constraint that expenditure on the two goods cannot exceed income, gives rise to this demand function for good 1: X_1= am/p_1, which does not depend on ''p''2. See also * Consumer theory * Good (economics and accounting) In economics, goods are i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
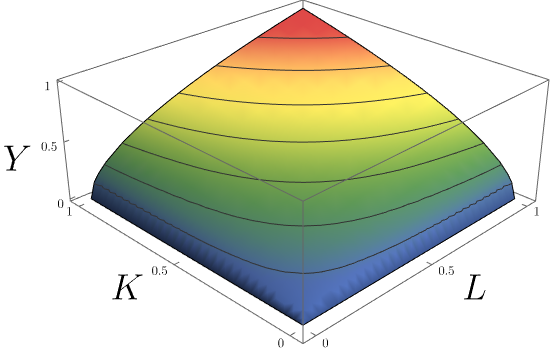
Cobb–Douglas Production Function
In economics and econometrics, the Cobb–Douglas production function is a particular functional form of the production function, widely used to represent the technological relationship between the amounts of two or more inputs (particularly physical capital and labor) and the amount of output that can be produced by those inputs. The Cobb–Douglas form was developed and tested against statistical evidence by Charles Cobb and Paul Douglas between 1927 and 1947; according to Douglas, the functional form itself was developed earlier by Philip Wicksteed. Formulation In its most standard form for production of a single good with two factors, the function is : Y=AL^\beta K^\alpha where: * ''Y'' = total production (the real value of all goods produced in a year or 365.25 days) * ''L'' = labour input (person-hours worked in a year or 365.25 days) * ''K'' = capital input (a measure of all machinery, equipment, and buildings; the value of capital input divided by the price of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leontief Utilities
In economics, especially in consumer theory, a Leontief utility function is a function of the form: u(x_1,\ldots,x_m)=\min\left\ . where: * m is the number of different goods in the economy. * x_i (for i\in 1,\dots,m) is the amount of good i in the bundle. * w_i (for i\in 1,\dots,m) is the weight of good i for the consumer. This form of utility function was first conceptualized by Wassily Leontief. Examples Leontief utility functions represent complementary goods. For example: * Suppose x_1 is the number of left shoes and x_2 the number of right shoes. A consumer can only use pairs of shoes. Hence, his utility is \min(x_1,x_2). * In a cloud computing environment, there is a large server that runs many different tasks. Suppose a certain type of a task requires 2 CPUs, 3 gigabytes of memory and 4 gigabytes of disk-space to complete. The utility of the user is equal to the number of completed tasks. Hence, it can be represented by: \min(, , ). Properties A consumer with a Leontie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |