|
Utatsusauridae
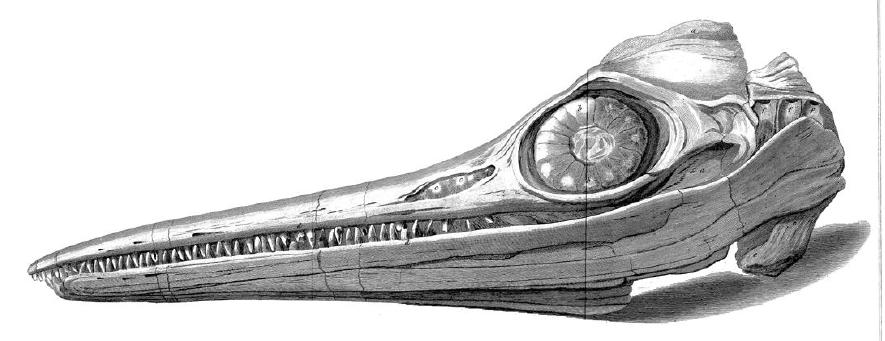
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyopterygia
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors. Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongated bodies and long, spool-shaped vertebrae, indicating that they swam in a sinuous, eel-like manner. This allowed for quick movements and maneuverability that were advantages in shallow-water hunting. Even at this early stage, they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land. These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of Pangea, as they are known the Late Olenekian and Early Anisian (early part of the Triassic period) of Japan, China, Canada, and Spitsbergen (No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaurs
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utatsusaurus BW
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utatsusaurus
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapsida
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are sometimes placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 snakes, lizards, tuatara, turtles, and crocodiles. Characteristics The name Diapsida means "two arches", and diapsids are tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauria
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs (such as crocodilians, dinosaurs, etc.) and lepidosaurs ( lizards and kin), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely related to archosaurs than to lepidosaurs as part of Archelosauria, Sauria can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Depending on the systematics, Sauria includes all modern reptiles or most of them (including birds, a type of archosaur) as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians. Systematics Recent genomic studiesCrawford, Nicholas G., et al. "More than 1000 ultraconserved elements provide evidence that turtles are the sister g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |