|
Utah Oil Sands
In the United States a large supply of Oil Sands, oil sands are found in Eastern Utah. These deposits of bitumen or heavy crude oil have the ability to generate about 12 to 19 billion barrels from a number of prominent sites. History Since the early 1900s the oil sand deposits have been extracted mainly for the use of road pavement. Later, in the 1970s, oil companies began to experiment with the deposits in the hope of using it for their benefit. These experiments ended in the late 1980s when the technologies being used were concluded inefficient and too expensive.The Utah Tar Sands. Oil Sands Recovery Technology. Nevtah Capital Management Corp., 7 July 2008. Web. 12 Oct. 2009 Recently, oil companies have again become interested in Utah's oil sands. Now that conventional oil is becoming harder to find, oil sands have bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, soaked with bitumen, a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum. Significant bitumen deposits are reported in Canada, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Venezuela. The estimated worldwide deposits of oil are more than ; the estimates include deposits that have not been discovered. Proven reserves of bitumen contain approximately 100 billion barrels, and total natural bitumen reserves are estimated at worldwide, of which , or 70.8%, are in Alberta, Canada. Crude bitumen is a thick, sticky form of crude oil, so viscous that it will not flow unless heated or diluted with lighter hydrocarbons such as light crude oil or natural-gas condensate. At room temperature, it is much like cold molasses. The Orinoco Belt in Venezuela is sometimes des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its west by Nevada. Utah also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the southwest, with more than 180,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin. Utah has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups such as the ancient Puebloans, Navajo and Ute. The Spanish were the first Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term asphaltum was also used. Full text at Internet Archive (archive.org) The word is derived from the Ancient Greek ἄσφαλτος ''ásphaltos''. The largest natural deposit of asphalt in the world, estimated to contain 10 million tons, is the Pitch Lake located in La Brea in southwest Trinidad (Antilles island located on the northeastern coast of Venezuela), within the Siparia Regional Corporation. The primary use (70%) of asphalt is in road construction, where it is used as the glue or binder mixed with aggregate particles to create asphalt concrete. Its other main uses are for bituminous waterproofing products, including production of roofing felt and for sealing flat roofs. In material sciences and engineering, the terms "asphalt" an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Fuel
Alternative fuel, known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuels, other than conventional fuels like; '' fossil fuels'' (petroleum (oil), coal, and natural gas), as well as nuclear materials such as uranium and thorium, as well as artificial radioisotope fuels that are made in nuclear reactors. Some well-known alternative fuels include bio-diesel, bio-alcohol ( methanol, ethanol, butane), refuse-derived fuel, chemically stored electricity (batteries and fuel cells), hydrogen, non-fossil methane, non-fossil natural gas, vegetable oil, propane and other biomass sources. Background A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as heat energy or to be used for work. The main purpose of fuel is to store energy, which should be in a stable form and can be easily transported to the place of use. Almost all fuels are chemical fuels. The user employs this fuel to gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
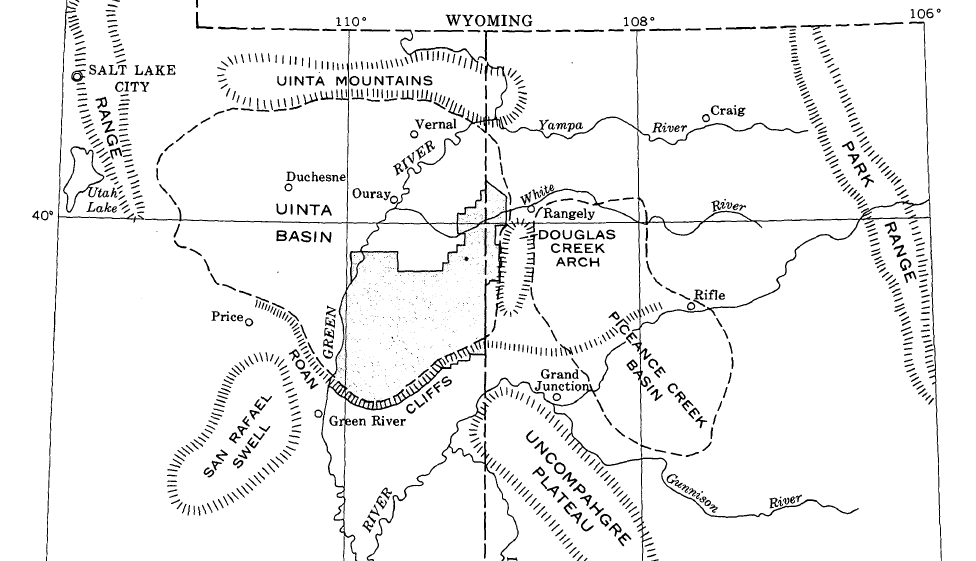
Uintah Basin
The Uinta Basin (also known as the Uintah Basin) is a physiographic section of the larger Colorado Plateaus province, which in turn is part of the larger Intermontane Plateaus physiographic division. It is also a geologic structural basin in eastern Utah, east of the Wasatch Mountains and south of the Uinta Mountains. The Uinta Basin is fed by creeks and rivers flowing south from the Uinta Mountains. Many of the principal rivers (Strawberry River, Currant Creek, Rock Creek, Lake Fork River, and Uintah River) flow into the Duchesne River which feeds the Green River—a tributary of the Colorado River. The Uinta Mountains forms the northern border of the Uinta Basin. They contain the highest point in Utah, Kings Peak, with a summit 13,528 feet (4123 metres) above sea level. The climate of the Uinta Basin is semi-arid, with occasionally severe winter cold. History Father Escalante's expedition visited the Uinta Basin in September 1776. 1822–1840 French Canadian tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Petroleum Industry In The United States
The history of the petroleum industry in the United States goes back to the early 19th century, although the indigenous peoples, like many ancient societies, have used petroleum seeps since prehistoric times; where found, these seeps signaled the growth of the industry from the earliest discoveries to the more recent. Petroleum became a major industry following the oil discovery at Oil Creek, Pennsylvania, in 1859. For much of the 19th and 20th centuries, the US was the largest oil producing country in the world. US regained the position of the largest oil producing country in the world in 2018 and has it kept every year since as of 2022. 19th century Before the Drake well Native Americans had known of the oil in western Pennsylvania, and had made some use of it for many years before the mid-19th century. Early European explorers noted seeps of oil and natural gas in western Pennsylvania and New York. Interest grew substantially in the mid-1850s as scientists reported on the pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah Oil Sands Joint Venture
The Utah Oil Sands Joint Venture is a joint venture between Nevtah Capital Management, Inc., and Black Sands Energy Corp. to develop oil sands resources at the Uintah Basin in Utah Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it .... History Oil-sands extraction in Utah started in the 1960s when two extraction plants were constructed. Western Industries opened a strip-mine and built a pilot plant along the east side of the Whiterocks River and Major Oil Company opened a strip-mine and built a pilot plant on the west side off the Whiterocks River. In 2005, Nevtah Capital Management and Cassandra Energy (now: Black Sands Energy) formed a joint venture to develop Utah's oil sands and opened a pilot plant at the Asphalt Ridge lease location. The pilot plant became in operation in Nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bituminous Sands
Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, soaked with bitumen, a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum. Significant bitumen deposits are reported in Canada, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Venezuela. The estimated worldwide deposits of oil are more than ; the estimates include deposits that have not been discovered. Proven reserves of bitumen contain approximately 100 billion barrels, and total natural bitumen reserves are estimated at worldwide, of which , or 70.8%, are in Alberta, Canada. Crude bitumen is a thick, sticky form of crude oil, so viscous that it will not flow unless heated or diluted with lighter hydrocarbons such as light crude oil or natural-gas condensate. At room temperature, it is much like cold molasses. The Orinoco Belt in Venezuela is sometimes descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |