|
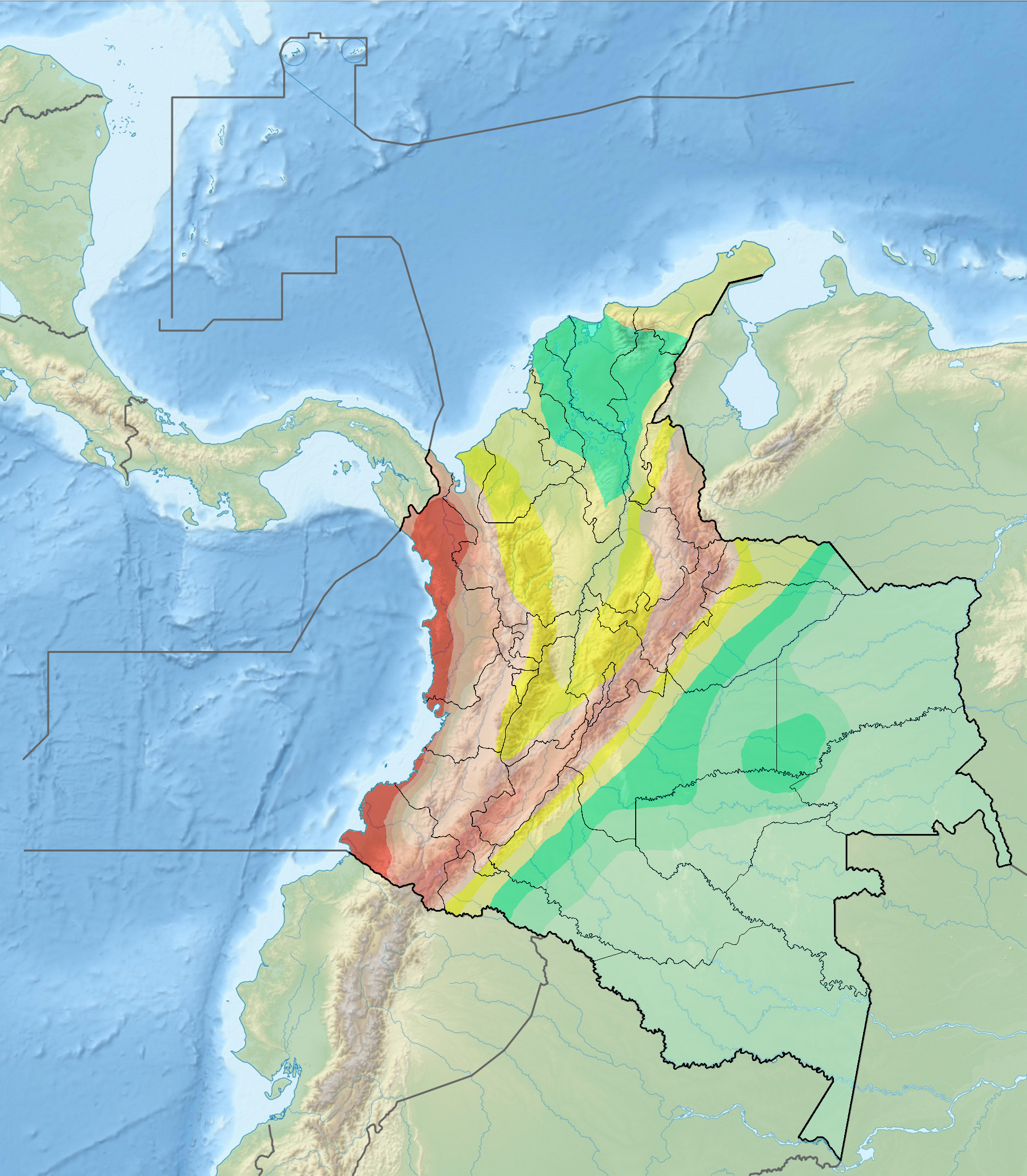
Usme Fault
The Usme Fault ( es, Falla de Usme) is a dextral oblique normal fault in the department of Cundinamarca in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 022.7 ± 6 in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Etymology The fault is named after Usme, southern locality of the Colombian capital Bogotá.Paris et al., 2000a, p.48 Description The Usme Fault is located in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, south of Bogotá and extends along the western margin of the Tunjuelo River valley. The fault underlies the Sumapaz Páramo.Paris et al., 2000b The fault displaces Cretaceous and Tertiary rocks as well as Quaternary alluvial and glacial (moraine) deposits. The fault valley shows features suggesting a half-graben with a steep slope wall on the west and low-angle slope on the east. The fault forms a steep, prominent circa high east-facing scarp on Cretaceous rocks that show initial dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usme
Usme is the 5th locality of the Capital District of Bogotá, capital city of Colombia. Usme is located in the south of Bogotá, bordering to the north the localities of San Cristóbal, Rafael Uribe Uribe and Tunjuelito, to the west the locality of Ciudad Bolívar, to the south the locality of Sumapaz, and to the east, behind the Eastern Hills, the municipalities of Ubaque, Chipaque and Une in the Department of Cundinamarca. History Usme was inhabited first by indigenous groups during the Herrera Period and later by the Muisca. The modern locality of Usme was founded in 1650 as "''San Pedro de Usme''" which became a center for the rural areas nearby dedicated to agricultural activities. These supplied food to Bogotá. It was named after San Pedro (Saint Peter) and Usme from Muysccubun, meaning ''Nest of love''.Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunjuelo River
The Tunjuelo or Tunjuelito River is a river on the Bogotá savanna and a left tributary of the Bogotá River. The river, with a length of originates in the Sumapaz Páramo and flows northward through the Usme Synclinal to enter the Colombian capital Bogotá. There, the river is mostly canalised flowing westward into the Bogotá River. It is one of the three main rivers of the city, together with the Fucha River, Fucha and Juan Amarillo Rivers. Etymology The names Tunjuelo and Tunjuelito ("little Tunjuelo") are derived from the Cerro de los Tunjos, also Los Tunjos Lake, named after the ''tunjos'', the Muisca religion, religious votive figurines of the indigenous language of the Muisca people, Muisca, who inhabited the Bogotá savanna before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, Spanish conquest.Osorio Osorio, 2007, p.29 Description The Tunjuelo River has a total length of and originates in the Sumapaz Páramo, in the southern part of Bogotá.Osorio Osorio, 2007, p.12 It flows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Frontal Fault System
The Eastern Frontal Fault System ( es, Sistema de Fallas de la Falla Frontal de la Cordillera Oriental) is a megaregional system of oblique and thrust faults cross-cutting Colombia from Ecuador in the south to Venezuela in the north. The system from south to north covers ten out of 32 departments of Colombia; Nariño, Putumayo, Cauca, Huila, Caquetá, Cundinamarca, Meta, Boyacá, Casanare and Arauca. The Eastern Frontal Fault System underlies and affects the capitals of Putumayo, Mocoa, Caquetá, Florencia, Meta, Villavicencio and Casanare, Yopal. The fault system has a total length of with a cumulative length of the faults of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 042.1 ± 19 bordering and crossing the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault system forms the boundary between the North Andes microplate and the South American Plate. Several segments of the fault system are active, with major earthquakes occurring in historical time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vianí Fault
The Vianí Fault ( es, Falla de Vianí) is a dextral oblique thrust fault in the department of Cundinamarca in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northwest to southeast strike of 055.5 ± 15 in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Etymology The fault is named after Vianí, Cundinamarca.Paris et al., 2000a, p.48 Description The Vianí Fault is located on the western slope of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault places Lower Cretaceous rocks of the Villeta Group ( Trincheras, Simijaca, Hiló and Capotes Formations), to the northwest against Upper Cretaceous rocks of the Güagüaquí Group to the southeast. In the southern area of the fault, the north–south oriented Vianí Fault thrusts the Seca Formation on top of the Hoyón Formation. Farther to the north at Vianí, the fault strike changes to northeast–southwest and the fault displaces the Bituima Fault.Plancha 227, 1998 The fault trace is char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogotá Fault
The Bogotá Fault ( es, Falla de Bogotá) is a major inactive slightly dextral oblique thrust fault in the department of Cundinamarca in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of , while other authors designate a length of , and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 013.5 ± 7 across the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, central part of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault stretches from the Gallo River at the Sumapaz Páramo in the south to the Teusacá River in the north and borders the Bogotá savanna and the Colombian capital to the east. The Bogotá Fault formed the pronounced Eastern Hills, with the well-known Monserrate and Guadalupe Hills, east of the Colombian capital. The brecciated fault zone is exposed along the road from Bogotá to La Calera and a vertical displacement of at least has been determined. The hanging wall of the reverse fault contains the Late Cretaceous Chipaque Formation and Guadalupe Group and the footwall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Scarp
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement along faults. They are exhibited either by differential movement and subsequent erosion along an old ''inactive'' geologic fault (a sort of old rupture), or by a movement on a recent active fault. Characteristics Fault scarps often contain highly fractured rock of both hard and weak consistency. In many cases, bluffs form from the upthrown block and can be very steep. The height of the scarp formation is equal to the vertical displacement along the fault. Active scarps are usually formed by tectonic displacement, e.g. when an earthquake changes the elevation of the ground and can be caused by any type of fault, including strike-slip faults, whose motion is primarily horizontal. This movement is usually episodic, with the height of the bluf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-graben
A half-graben is a geological structure bounded by a fault along one side of its boundaries, unlike a full graben where a depressed block of land is bordered by parallel faults. Rift and fault structure A rift is a region where the lithosphere extends as two parts of the Earth's crust pull apart. Often a rift will form in an area of the crust that is already weakened by earlier geological activity. Extensional faults form parallel to the axis of the rift. An extensional fault may be seen as a crack in the crust that extends down at an angle to the vertical. As the two sides pull apart, the hanging wall ("hanging over" the sloping fault) will move downward relative to the footwall. The crust thins and sinks, forming a rift basin. Warm mantle material wells up, melting the crust and often causing volcanoes to emerge in the rift basin. Extensional basins may appear to be caused by a graben, or depressed block of land, sinking between parallel normal faults that dip towards th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders (in which case it is often referred to as boulder clay) down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines were formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines (till-covered areas forming sheets on flat or irregular topography) and medial moraines (moraines formed where two glaciers meet). Etymology The word ''moraine'' is borrowed from French , which in turn is derived from the Savoyard Italian ("mound of earth"). ''Morena'' in this case was derived from Proven� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |