|
Uskoks
The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a guerrilla war against the Ottomans, and they formed small units and rowed swift boats. Since the uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual subsidy, they resorted to acts of piracy. The exploits of the Uskoks contributed to a renewal of war between Venice and the Ottoman Empire (1571–1573). An extremely curious picture of contemporary manners is presented by the Venetian agents, whose reports on this war resemble a knightly chronicle of the Middle Ages. These chronicles contain information pertaining to single combats, tournaments and other chivalrous adventures. Many of these troops served abroad. After a series of incidents that escalated into the Uskok War (1615–1618), the Uskok activity in their stronghold of Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nehaj Fortress
The Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj ) is a fortress on the hill Nehaj in the town of Senj, Croatia. The name ''Nehaj'' comes from the Croatian term ''Ne hajati'' , which means 'don't care'. In Croatian this fortress has also other names, which are: ''Kula Nehaj'' , what means ''Nehaj Tower'', and ''Nehajgrad'' , what means ''Nehajtown''. This name was given to the hill and the Fortress by the Uskoks, who built on the top of this hill the Fortress for defensive purposes. They gave the hill and the Fortress such a name because they wanted to emphasize to the citizens of the town of Senj, and all of those that lived in the vicinity of the town of Senj that they should not care that someone will conquer this hill or the Fortress until they are there. It was built by Croatian army general Ivan Lenković, a captain of the ''Uskoks'', on the hill Nehaj.Bousfield (2003), p. 227. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortress Nehaj
The Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj ) is a Fortification, fortress on the hill Nehaj in the town of Senj, Croatia. The name ''Nehaj'' comes from the Croatian language, Croatian term ''Ne hajati'' , which means 'don't care'. In Croatian this fortress has also other names, which are: ''Kula Nehaj'' , what means ''Nehaj Tower'', and ''Nehajgrad'' , what means ''Nehajtown''. This name was given to the hill and the Fortress by the Uskoks, who built on the top of this hill the Fortress for defensive purposes. They gave the hill and the Fortress such a name because they wanted to emphasize to the citizens of the town of Senj, and all of those that lived in the vicinity of the town of Senj that they should not care that someone will conquer this hill or the Fortress until they are there. It was built by Croatian army general Ivan Lenković, a captain of the ''Uskoks'', on the hill Nehaj.Bousfield (2003), p. 227. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uskok War
The Uskok War, also known as the War of Gradisca, was fought by the Austrians, Croats, and Spanish on one side and the Venetians, Dutch, and English on the other. It is named for the Uskoks, soldiers from Croatia used by the Austrians for irregular warfare. Since the Uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual salary, they resorted to piracy. In addition to attacking Turkish ships, they attacked Venetian merchantmen. Although the Venetians tried to protect their shipping with escorts, watchtowers, and other protective measures, the cost became prohibitive: 120,000 thalers annually during the 1590s, 200,000 in the 1600s, and 360,000 by 1615.Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Thirty Years' War'', 2nd edition. 1997. In December 1615 Venetian troops besieged Gradisca, on the Isonzo River. The Venetians launched a diplomatic campaign for allies, since the Uskoks were vassals of Archduke Ferdinand of Inner Austria (who was likely to seek help from the Holy Roman Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
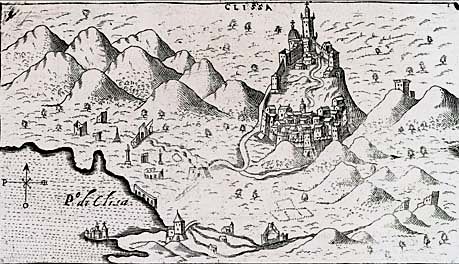
Klis Fortress
) from Vrana, Zadar County, Vrana, in the name of Bosnia (region), Bosnian King Tvrtko I of Bosnia, Tvrtko I * 1394–1401 Ban Nicholas II Garay, Nikola II Gorjanski in the name of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Sigismund * 1401–1434 Croatian noble Prince Ivan III Nelipac (Ivaniš Nelipić), Ivaniš Nelipić * 1434–1436 Croatian noble and Ban of Croatia Ivan Frankopan, at that time in war with king Sigismund * 1436–1437 Ivan Frankopan's widow peaceful handover the fortress * 1437–1458 Croatian noble Matko Talovac and later Petar Talovac, Petar and Vladislav in the name of Holy Roman Empire 4.) Major strategic value Klis Fortress in the 16th century. * 1513–1537 Croatian noble, Prince of Klis Petar Kružić * 1537–1596 Ottoman Empire * 1596–1596 Uskoks seized the fortress by treachery, but the Turks recovered it fairly quickly, in the same year * 1596–1648 Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire after Cretan War (1645–1669), Candian War. 5.) Lost its main strategi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senj
Senj (; it, Segna, la, Senia, Hungarian language, Hungarian and german: Zengg) is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains. The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj) which was completed in 1558. For a time this was the seat of the Uskoks ( it, Uscocchi), who were Christian refugees from Ottoman Bosnia resettled here to protect the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg borderlands. The Republic of Venice accused the Uskoks of piracy and declared Uskok War, war on them which led to their expulsion following a truce in 1617. Senj is to be found in the Lika-Senj County of Croatia, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Gospić-Senj and the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rijeka. History Senj has apparently been inhabited since prehistoric times. A settlement called ''Athyinites'' in today's Senj was mentioned in Ancient Greece, Greek documents dated to 4th century BC. The Illyrians, Illyrian tribe Iapydes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and later the Austrian and Austro-Hungarian Empire. It acted as the ''cordon sanitaire'' against incursions from the Ottoman Empire. The establishment of the new defense system in Hungary and Croatia took place in the 16th century, following the election of Ferdinand I as king. Six districts under special military administration were established in Hungary and Croatia. The Croatian Military Frontier and the Slavonian Military Frontier came under the jurisdiction of the Croatian Sabor and ban. In 1627, they were placed under the direct control of the Habsburg military. For more than two centuries, they would retain complete civilian and military authority over the area, up to the abolition of the Military Frontier in 1881. During the 17th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Lenković
Ivan Lenković (died 22 June 1569) was a Habsburg Croatian army general and the leader of the Uskoks. He carried the title of baron. He is noted for the construction of Nehaj Fortress and as a captain of the Senj area.Bousfield (2003), p. 227. He also contributed in organizing the Military Frontier. During the Ottoman wars in Europe, Klis Fortress was on 7 April 1569, liberated by Split noblemen Ivan Alberti and Nikola Cindro.Listeš (1998), pp. 1–169. Bey Mustafa responded by bringing under Klis Fortress more than 10,000 soldiers. General Ivan Lenković with 1,000 uskoks came in relief, to some 1500 Klis defenders. During the battle, Ivan Lenković withdrew, after he himself was wounded, and the fortress was delivered to the Turks, on 31 May. But this temporary relief resound in Europe, and among the local population. He died in Metlika on 22 June 1569 and is buried in Novo Mesto Franciscan Church. See also *Uskoks *Fortress Nehaj *Petar Kružić Petar Kružić ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klis
Klis ( hr, Klis, it, Clissa, tr, Kilis) is a Croatian municipality located around a mountain fortress bearing the same name. It is located in the region of Dalmatia, located just northeast of Solin, Croatia, Solin and Split, Croatia, Split near the eponymous mountain pass. It has a population of 3,001, totalling 4,801 together with the eight other villages in its municipality (2011 census). The Klis mountain pass separates the mountains Mosor and Mali Kozjak, Kozjak at an altitude of 360m. It has had a major strategic value throughout history because any inland force passing through Klis would have been able to easily reach the entire region of Split (city), Split and Kaštela. During the Ottoman wars in Europe an already existing Roman fortress on a nearby hill was expanded into Klis Fortress. It was the centre of Sanjak of Klis, a sanjak within the Eyalet of Bosnia, Province of Bosnia during Ottoman rule. Klis was also ruled by the Kingdom of Bosnia, the Venetian Republic, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clissa
Klis ( hr, Klis, it, Clissa, tr, Kilis) is a Croatian municipality located around a mountain fortress bearing the same name. It is located in the region of Dalmatia, located just northeast of Solin and Split near the eponymous mountain pass. It has a population of 3,001, totalling 4,801 together with the eight other villages in its municipality (2011 census). The Klis mountain pass separates the mountains Mosor and Kozjak at an altitude of 360m. It has had a major strategic value throughout history because any inland force passing through Klis would have been able to easily reach the entire region of Split and Kaštela. During the Ottoman wars in Europe an already existing Roman fortress on a nearby hill was expanded into Klis Fortress. It was the centre of a sanjak within the Province of Bosnia during Ottoman rule. Klis was also ruled by the Kingdom of Bosnia, the Venetian Republic, and Austria-Hungary. Due to its geographical position Klis is also susceptible to a rather st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovene Language
Slovene ( or ), or alternatively Slovenian (; or ), is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language, a sub-branch that is part of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is spoken by about 2.5 million speakers worldwide (excluding speakers of Kajkavian), mainly ethnic Slovenes, the majority of whom live in Slovenia, where it is the sole official language. As Slovenia is part of the European Union, Slovene is also one of its 24 Languages of the European Union, official and working languages. Standard Slovene Standard Slovene is the national standard language that was formed in the 18th and 19th century, based on Upper Carniolan dialect group, Upper and Lower Carniolan dialect groups, more specifically on language of Ljubljana and its adjacent areas. The Lower Carniolan dialect group was the dialect used in the 16th century by Primož Trubar for his writings, while he also used Slovene as spoken in Lju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavic Languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West and East) by a belt of German, Hungarian and Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect within this continuum. *Eastern ** Bulgarian – (ISO 639-1 code: bg; ISO 639-2 code: bul; SIL code: bul; Linguasphere: 53-AAA-hb) ** Macedonian – (ISO 639-1 code: mk; ISO 639-2(B) code: mac; IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his alphabet on the previous Slavonic-Serbian script, following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written", removing obsolete letters and letters representing iotified vowels, introducing from the Latin alphabet instead, and adding several consonant letters for sounds specific to Serbian phonology. During the same period, linguists led by Ljudevit Gaj adapted the Latin alphabet, in use in western South Slavic areas, using the same principles. As a result of this joint effort, Serbian Cyrillic and Gaj's Latin alphabets for Serbian-Croatian have a complete one-to-one congruence, with the Latin digraphs Lj, Nj, and Dž counting as single letters. Karadžić's Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)