|
Userkare
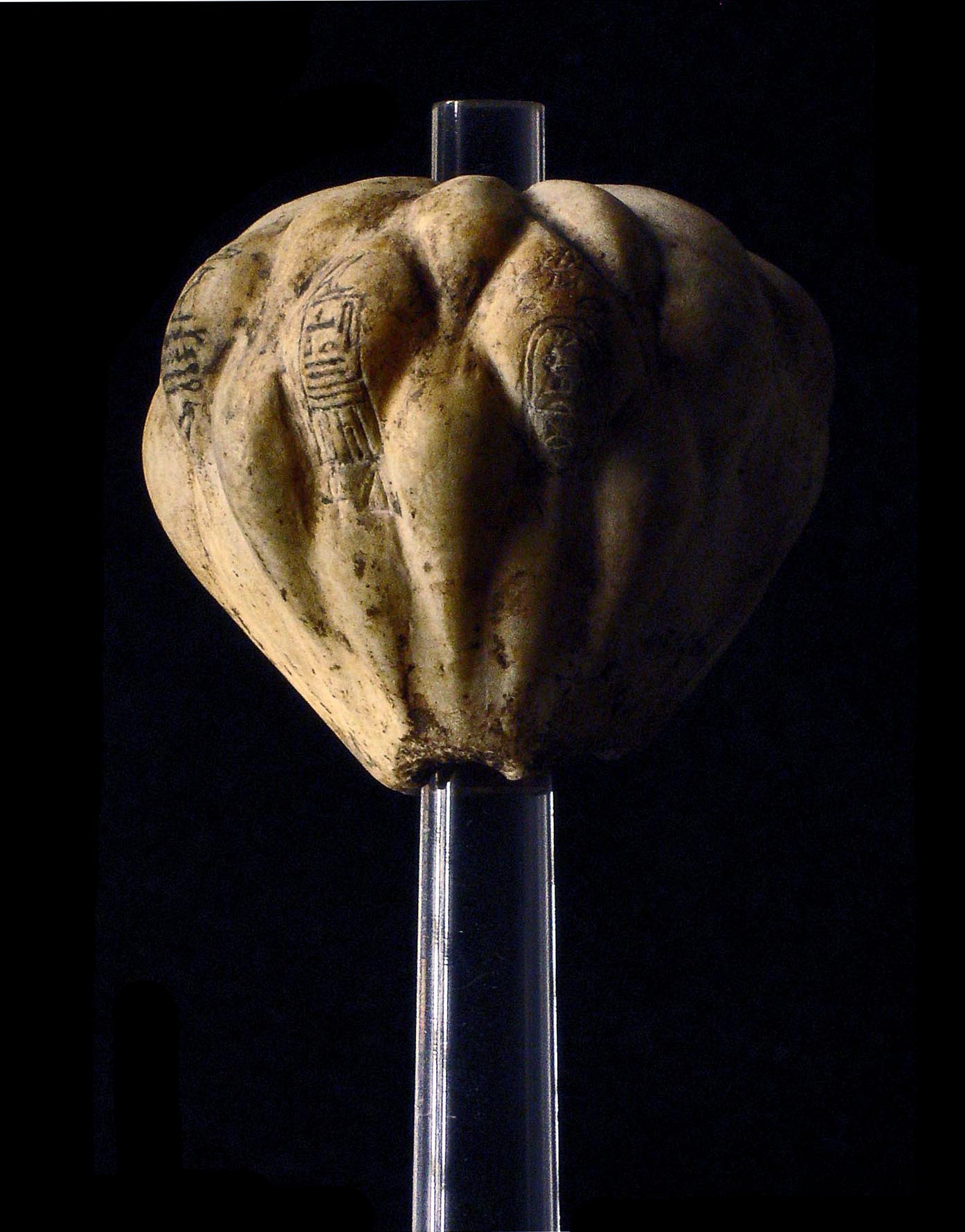
Userkare (also Woserkare, meaning "Powerful is the soul of Ra") was the second pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty, reigning briefly, 1 to 5 years, in the late 24th to early 23rd century BC. Userkare's relation to his predecessor Teti and successor Pepi I is unknown and his reign remains enigmatic. Although he is attested in historical sources, Userkare is completely absent from the tomb of the Egyptian officials who lived during his reign. In addition, the Egyptian priest Manetho reports that Userkare's predecessor Teti was murdered. Userkare is often considered to have been a short-lived usurper. Alternatively, he may have been a regent who ruled during Teti's son's childhood who later ascended the throne as Pepi I. Attestations Historical sources Userkare is present on the Abydos King List, a list of kings written during the reign of Seti I (1290–1279 BC) over 1000 years after the early Sixth Dynasty. Userkare's cartouche occupies the 35th entry of the list, between thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepi I
Pepi I Meryre (also Pepy I) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, third king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled for over 40 years at the turn of the 24th and 23rd centuries BC, toward the end of the Old Kingdom period. He was the son of Teti, the founder of the dynasty, and ascended the throne only after the brief intervening reign of the shadowy Userkare. His mother was Iput, who may have been a daughter of Unas, the final ruler of the preceding Fifth Dynasty. Pepi I, who had at least six consorts, was succeeded by his son Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, with whom he may have shared power in a coregency at the very end of his reign. Pepi II Neferkare, who might also have been Pepi I's son, succeeded Merenre. Several difficulties accumulated during Pepi's reign, beginning with the possible murder of his father and the ensuing reign of Userkare. Later, probably after his twentieth year of reign, Pepi faced a harem conspiracy hatched by one of his consorts who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepi I Meryre
Pepi I Meryre (also Pepy I) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, third king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled for over 40 years at the turn of the 24th and 23rd centuries BC, toward the end of the Old Kingdom period. He was the son of Teti, the founder of the dynasty, and ascended the throne only after the brief intervening reign of the shadowy Userkare. His mother was Iput, who may have been a daughter of Unas, the final ruler of the preceding Fifth Dynasty. Pepi I, who had at least six consorts, was succeeded by his son Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, with whom he may have shared power in a coregency at the very end of his reign. Pepi II Neferkare, who might also have been Pepi I's son, succeeded Merenre. Several difficulties accumulated during Pepi's reign, beginning with the possible murder of his father and the ensuing reign of Userkare. Later, probably after his twentieth year of reign, Pepi faced a harem conspiracy hatched by one of his consorts who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Userkare Khendjer
Userkare Khendjer was the twenty-first pharaoh of the Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period.Darrell D. Baker: The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I - Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC, Stacey International, , 2008, p. 181 Khendjer possibly reigned for four to five years, archaeological attestations show that he was on the throne for at least three or four years three months and five days. Khendjer had a small pyramid built for himself in Saqqara and it is therefore likely that his capital was in Memphis. Chronological position The exact chronological position of Khendjer in the Thirteenth Dynasty is not known for certain owing to uncertainties affecting earlier kings of the dynasty. Turin King List The Turin King List mentions Khendjer in between Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep and ...kare Imyremeshaw. 7:19 The Dual King Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep reigned x years ... 7:20 The Dual King Userkare Khendjer, x years ... 7:21 The Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
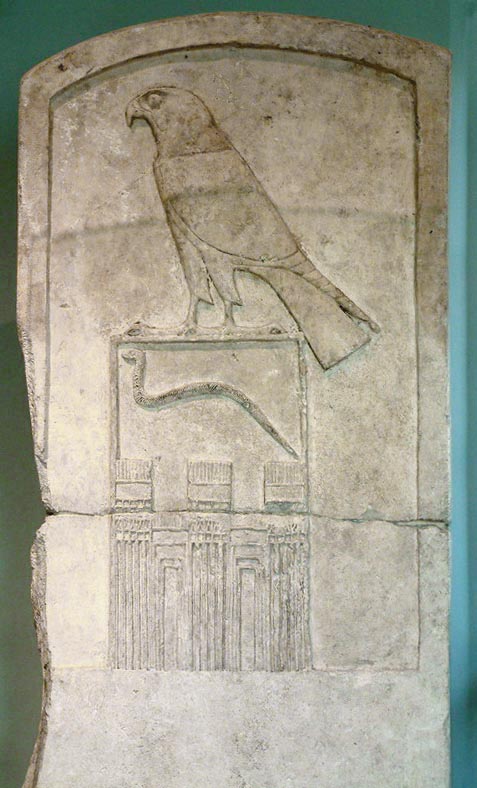
South Saqqara Stone
{{No footnotes, date=August 2020 The South Saqqara Stone is the lid of the sarcophagus of the ancient Egyptian queen Ankhenespepi, which was inscribed with a list for the reigns of the pharaohs of the 6th Dynasty from Teti, Userkare, Pepi I, Merenre to the early years of Pepi II under whom the document was likely created. It is essentially an annal document which records events in each year of a king's reign; unfortunately, it was reused in antiquity for Ankhesenpepi I's burial and many of its invaluable inscriptions have been erased. Discovery The South Saqqara Stone was discovered in 1932–33 by Gustave Jéquier in the westernmost of five storerooms south of the pyramid of Queen Iput II, within the pyramid complex of Pepi II (during whose reign it was created) at Saqqara. Description Made of basalt, it measures 2.43 metres by 0.92 metres and is 20 centimetres thick. It is inscribed on both sides, but much of the inscription is erased and unreadable. The recto appears to list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teti
Teti, less commonly known as Othoes, sometimes also Tata, Atat, or Athath in outdated sources, was the first king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. He was buried at Saqqara. The exact length of his reign has been destroyed on the Turin King List but is believed to have been about 12 years. Biography Teti had several wives: * Iput, the daughter of Unas, the last king of the Fifth dynasty. Iput was the mother of Pepi I. *Khuit, who may have been the mother of Userkare (according to Jonosi and Callender)Miroslav Verner, The Pyramids,1994 *Khentkaus IV *Neith Teti is known to have had several children. He was the father of at least three sons and probably ten daughters. Of the sons, two are well attested, a third one is likely: * Pepi I * Tetiankhkem * Nebkauhor, with the name of Idu, "king’s eldest son of his body", buried in the mastaba of Vizier Akhethetep/Hemi, buried in a fallen Vizier’s tomb, within the funerary complex of his maternal grandfather According to N. Kanawati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Sixth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty VI), along with the Third, Fourth and Fifth Dynasty, constitutes the Old Kingdom of Dynastic Egypt. Pharaohs Known pharaohs of the Sixth Dynasty are listed in the table below. Manetho accords the dynasty 203 regnal years from Teti to Nitocris, while the Turin Canon assigns 181 regnal years, but with three additional kings concluding with Aba – discounting the reigns of the added Eighth Dynasty kings, this is reduced to 155 regnal years. This estimate varies between both scholar and source. History The Sixth Dynasty is considered by many authorities as the last dynasty of the Old Kingdom, although ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'' includes Dynasties VII and VIII as part of the Old Kingdom. Manetho writes that these kings ruled from Memphis, since their pyramids were built at Saqqara, very close one to another. By the Fifth Dynasty, the religious institution had established itself as the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khuit
Khuit II was a wife of King Teti, the first pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Biography Khuit may have been the first prominent royal wife from the reign of Teti. If so, her position would later be taken over by Iput. Khuit may have been the mother of King Userkare (according to Jánosi and Callender), but this is not at all certain and some would have a queen named Khentkaus IV as the mother of Userkare. Khuit was a mother of Tetiankhkem, whilst Khuit's daughter could be Seshseshet Sheshit. According to her monuments Khuit held the titles: * King’s Wife (''ḥmt-niswt'') and King’s Wife, his beloved (''ḥmt-niswt mryt.f'') * Companion of Horus (''smrt-ḥrw'') Burial The pyramids of Iput I and Khuit were discovered between July 1897 and February 1899 by Victor Loret Victor Clement Georges Philippe Loret (1 September 1859 – 3 February 1946) was a French Egyptologist. Biography His father, Clément Loret, was a professional organist and composer, of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahure
Sahure (also Sahura, meaning "He who is close to Re") was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the second ruler of the Fifth Dynasty (c. 2465 – c. 2325 BC). He reigned for about 13 years in the early 25th century BC during the Old Kingdom Period. Sahure's reign marks the political and cultural high point of the Fifth Dynasty. He was probably the son of his predecessor Userkaf with Queen NeferhetepesII, and was in turn succeeded by his son Neferirkare Kakai. During Sahure's rule, Egypt had important trade relations with the Levantine coast. Sahure launched several naval expeditions to modern-day Lebanon to procure cedar trees, slaves and exotic items. His reign may have witnessed the flourishing of the Egyptian navy, which included a high-seas fleet as well as specialized racing boats. Relying on this, Sahure ordered the earliest attested expedition to the land of Punt, which brought back large quantities of myrrh, malachite and electrum. Sahure is shown celebrating the success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary state, unitary republic that consists of Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to demographics of Syria, diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrians, Syrian Arabs, Kurds in Syria, Kurds, Syrian Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrians in Syria, Assyrians, Armenians in Syria, Armenians, Circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary
The royal titulary or royal protocol is the standard naming convention taken by the pharaohs of ancient Egypt. It symbolised worldly power and holy might, also acting as a sort of mission statement for the duration of a monarch's reign (although sometimes it even changed during the reign). The full titulary, consisting of five names, did not come into standard usage until the Middle Kingdom but remained in use as late as the Roman Empire. Origins In order that the pharaoh, who held divine office, could be linked to the people and the gods, special epithets were created for them at their accession to the throne. These titles also served to demonstrate one's qualities and link them to the terrestrial realm. The five names were developed over the centuries beginning with the Horus name. This name identified the figure as a representative of the god Horus. The Nebty name was the second part of the royal titular of Upper and Lower Egypt. This name placed the king under the protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khufu
Khufu or Cheops was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period ( 26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having commissioned the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, but many other aspects of his reign are poorly documented. The only completely preserved portrait of the king is a three-inch high ivory figurine found in a temple ruin of a later period at Abydos in 1903. All other reliefs and statues were found in fragments, and many buildings of Khufu are lost. Everything known about Khufu comes from inscriptions in his necropolis at Giza and later documents. For example, Khufu is the main character noted in the Westcar Papyrus from the 13th dynasty. Most documents that mention king Khufu were written by ancient Egyptian and Greek historians around 300 BC. Khufu's obituary is presented there in a conflicting wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
In music or music theory, a thirteenth is the note thirteen scale degrees from the root of a chord and also the interval between the root and the thirteenth. The interval can be also described as a compound sixth, spanning an octave plus a sixth. The thirteenth is most commonly major or minor . A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (major or minor) thirds, the last being above the 11th of an eleventh chord. Thus a thirteenth chord is a tertian (built from thirds) chord containing the interval of a thirteenth, and is an extended chord if it includes the ninth and/or the eleventh. "The jazzy thirteenth is a very versatile chord and is used in many genres." Since 13th chords tend to become unclear or confused with other chords when inverted, they are generally found in root position.Benward & Saker (2009). ''Music in Theory and Practice: Volume II'', p.179. Eighth Edition. . For example, depending on voicing, a major triad with an added major sixth is usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |