|
Urvara (crater)
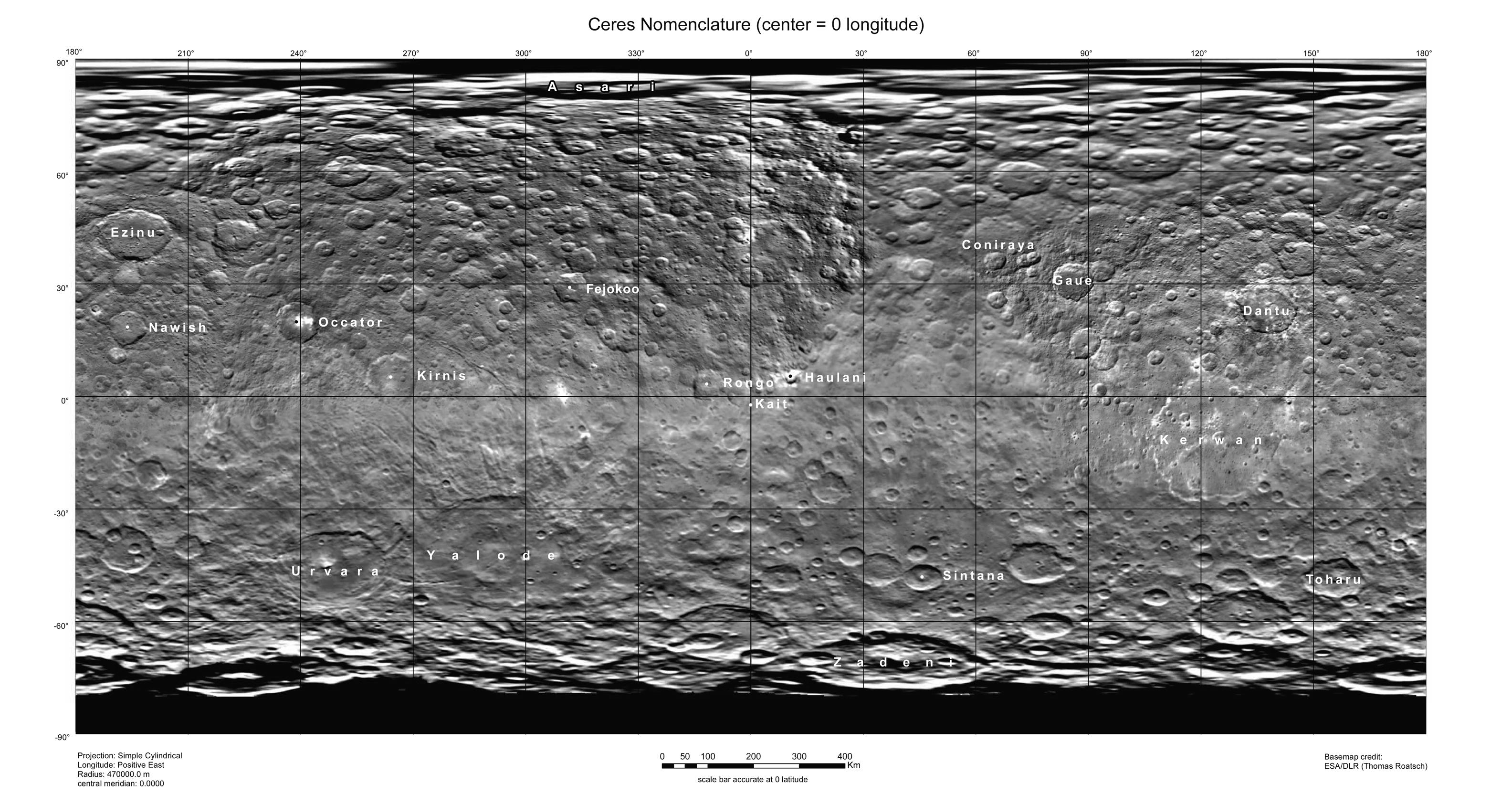
Urvara ( sa, উর্বর, urvárā) is the third-largest confirmed crater on Ceres after Kerwan and neighboring Yalode. Urvara means fertile. It is named after the ancient Indo-Iranian personification of fertility (plants in the '' Avesta'', fertile fields in the ''Rig Veda''). It has a central peak, and a number of unexplained ridges intersect it. See also *List of geological features on Ceres Ceres is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The IAU has adopted two themes for naming surface features on Ceres: agricultural deities for craters and agricultural festivals for everything else. ... References {{Ceres Impact craters on asteroids Surface features of Ceres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawn (spacecraft)
''Dawn'' is a retired space probe that was launched by NASA in September 2007 with the mission of studying two of the three known protoplanets of the asteroid belt: 4 Vesta, Vesta and Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres. In the fulfillment of that mission—the ninth in NASA's Discovery Program—''Dawn'' entered orbit around Vesta on July 16, 2011, and completed a 14-month survey mission before leaving for Ceres in late 2012. It entered orbit around Ceres on March 6, 2015. In 2017, NASA announced that the planned nine-year mission would be extended until the probe's hydrazine fuel supply was depleted. On November 1, 2018, NASA announced that ''Dawn'' had depleted its hydrazine, and the mission was ended. The spacecraft is currently in a derelict, but stable, orbit around Ceres. ''Dawn'' is the first spacecraft to orbit two extraterrestrial bodies, the first spacecraft to visit either Vesta or Ceres, and the first to orbit a dwarf planet. The ''Dawn'' mission was managed by NASA's Jet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (dwarf Planet)
Ceres (; minor-planet designation: 1 Ceres) is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It was the first asteroid discovered, on 1 January 1801, by Giuseppe Piazzi at Palermo Astronomical Observatory in Sicily and announced as a new planet. Ceres was later classified as an asteroid and then a dwarf planetthe only one always inside Neptune's orbit. Ceres's small size means that even at its brightest, it is too dim to be seen by the naked eye, except under extremely dark skies. Its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.7 to 9.3, peaking at opposition (when it is closest to Earth) once every 15- to 16-month synodic period. As a result, its surface features are barely visible even with the most powerful telescopes, and little was known about it until the robotic NASA spacecraft ''Dawn'' approached Ceres for its orbital mission in 2015. ''Dawn'' found Ceres's surface to be a mixture of water ice, and hydrated minerals such as carbonates and clay. Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerwan (crater)
Kerwan () is the largest confirmed crater and one of the largest geological features on Ceres. It was discovered on February 19, 2015 from ''Dawn'' images as it approached Ceres. The crater is distinctly shallow for its size, and lacks a central peak. A central peak might have been destroyed by a 15-kilometer-wide crater at the center of Kerwan. The crater is likely to be young relative to the rest of Ceres's surface, as Kerwan has largely obliterated the cratering in the southern part of Vendimia Planitia.Marchi, S et al. “The missing large impact craters on Ceres.” Nature communications vol. 7 12257. 26 Jul. 2016, doi:10.1038/ncomms12257 Kerwan is roughly antipodal to Ahuna Mons, the largest, or at least youngest, mountain on Ceres. Seismic energy from the Kerwan-forming impact may have focused on the opposite side of Ceres, fracturing the outer layers of the crust and facilitating the movement of high-viscosity cryomagma (consisting of muddy water ice softened by its conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalode (crater)
Yalode () is the second-largest confirmed crater on Ceres, after Kerwan. It is adjacent to another large crater, Urvara and serves as the namesake for the Yalode Quadrange. Yalode named after the Dahomeyan ( Fon) deity of the yam harvest, Yalodé; the name Yalode was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 3 July 2015. Geology Yalode is a heavily degraded impact basin, hosting numerous smaller craters such as Besua. Yalode is geologically homogeneous, with its interior compositionally similar to surrounding areas. Yalode is itself superimposed by the Urvara basin, the third-largest crater on Ceres; both are surrounded by extensive ejecta deposits. Yalode and the regions surrounding it appear to be heavily tectonized. The floor of Yalode basin features parallel fractures that are larger and more developed than those found in other large impact basins on Ceres. The fractures in Yalode appear to have formed in at least two distinct generations and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language. The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the liturgical group is the ''Yasna'', which takes its name from the Yasna ceremony, Zoroastrianism's primary act of worship, and at which the ''Yasna'' text is recited. The most important portion of the ''Yasna'' texts are the five Gathas, consisting of seventeen hymns attributed to Zoroaster himself. These hymns, together with five other short Old Avestan texts that are also part of the ''Yasna'', are in the Old (or 'Gathic') Avestan language. The remainder of the ''Yasna'''s texts are in Younger Avestan, which is not only from a later stage of the language, but also from a different geographic region. Extensions to the Yasna ceremony include the texts of the ''Vendidad'' and the ''Visperad''. The ''Visperad'' extensions consist mainly of addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. The sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted since the 2nd millennium BCE. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the bulk of the ''Rigveda'' Samhita was composed in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent (see) Rigvedic rivers), most likely between 1500 and 1000 BCE, although a wider approximation of 19001200 BCE has also been given. The text is layered, consisting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Geological Features On Ceres
Ceres is a dwarf planet in the asteroid belt that lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The IAU has adopted two themes for naming surface features on Ceres: agricultural deities for craters and agricultural festivals for everything else. As of 2020, the IAU has approved names for 151 geological features on Ceres: craters, montes, catenae, rupēs, plana, tholi, planitiae, fossae and sulci. In July 2018, NASA released a comparison of physical features found on Ceres with similar ones present on Earth. ''Piazzi'', named after Giuseppe Piazzi, the discoverer of Ceres, is a dark region southwest of Dantu crater in ground-based images that was named before ''Dawn'' arrived at Ceres. Overview of features Catenae Craters Ceres is saturated with impact crater An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Craters On Asteroids
Impact may refer to: * Impact (mechanics), a high force or shock (mechanics) over a short time period * Impact, Texas, a town in Taylor County, Texas, US Science and technology * Impact crater, a meteor crater caused by an impact event * Impact event, the collision of a meteoroid, asteroid or comet with Earth * Impact factor, a measure of the citations to a science or social science journal Books and magazines * ''Impact'' (novel), a 2010 novel by Douglas Preston *''Impact Press'', a former Orlando, Florida-based magazine * Impact Magazines, a former UK magazine publisher * ''Impact'' (conservative magazine), a British political magazine * ''Impact'' (British magazine), a British action film magazine * ''Impact'', a French action film magazine spun off from ''Mad Movies'' * ''Impact'' (UNESCO magazine), a former UNESCO quarterly titled ''IMPACT of science on society'' * ''Impact'' (student magazine), a student magazine for the University of Nottingham, England * '' Bath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)